
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The full name along with the anomeric designation of the following compound should be determined:
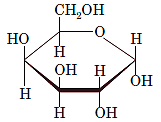
Concept Introduction: A common way of writing structural formula which represent the cyclic structure of monosaccharides is said to be the Haworth projection, which is best represented by chair conformations.
A convention used to represent a 3-D stereo formula in 2-D representation is said to be Fischer projections. In this projection, the vertical lines represent bonds below the plane of the paper and horizontal lines represents bonds above the plane of the paper.
(a)
Answer to Problem 21P
Explanation of Solution
Drawing the Fischer projection of given compound as:
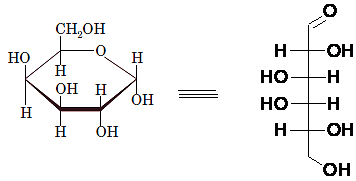
For a D-sugar, the group attached to the bottom chiral carbon is present at the right-hand side whereas for L-sugar it is present at left-hand side.
A new carbon stereocenter created by the conversion of an open structure to a cyclic structure is said to be the anomeric carbon. In carbohydrates, when the hydroxy group on an anomeric carbon is present on the same side as that of the
The anomeric carbon of the given compound is shown by “*”:
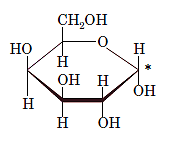
Since, in the given sugar the
Hence, the name of compound is
(b)
Interpretation: The full name along with the anomeric designation of the following compound should be determined:
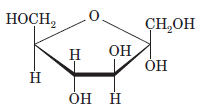
Concept Introduction: A common way of writing structural formula which represent the cyclic structure of monosaccharides is said to be the Haworth projection, which is best represented by chair conformations.
A convention used to represent a 3-D stereo formula in 2-D representation is said to be Fischer projections. In this projection, the vertical lines represent bonds below the plane of the paper and horizontal lines represents bonds above the plane of the paper.
(b)
Answer to Problem 21P
Explanation of Solution
Drawing the Fischer projection of given compound as:
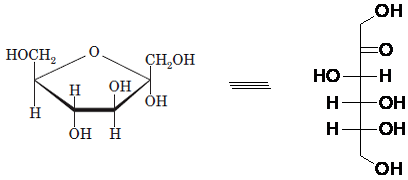
For a D-sugar, the
A new carbon stereocenter created by the conversion of an open structure to a cyclic structure is said to be the anomeric carbon. In carbohydrates, when the hydroxy group on an anomeric carbon is present on the same side as that of the
The anomeric carbon of the given compound is shown by “*”:
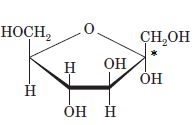
Since, in the given sugar the
Hence, the name of compound is
(c)
Interpretation: The full name along with the anomeric designation of the following compound should be determined:
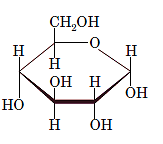
Concept Introduction: A common way of writing structural formula which represent the cyclic structure of monosaccharides is said to be the Haworth projection, which is best represented by chair conformations.
A convention used to represent a 3-D stereo formula in 2-D representation is said to be Fischer projections. In this projection, the vertical lines represent bonds below the plane of the paper and horizontal lines represents bonds above the plane of the paper.
(c)
Answer to Problem 21P
Explanation of Solution
Drawing the Fischer projection of given compound as:
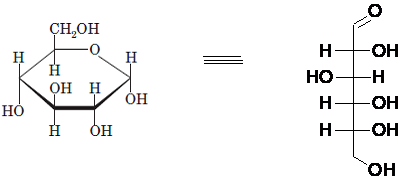
For a D-sugar, the
A new carbon stereocenter created by the conversion of an open structure to a cyclic structure is said to be the anomeric carbon. In carbohydrates, when the hydroxy group on an anomeric carbon is present on the same side as that of the
The anomeric carbon of the given compound is shown by “*”:
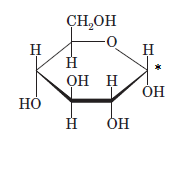
Since, in the given sugar the
Hence, the name of compound is
(d)
Interpretation: The full name along with the anomeric designation of the following compound should be determined:
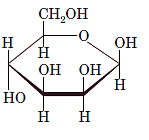
Concept Introduction: A common way of writing structural formula which represent the cyclic structure of monosaccharides is said to be the Haworth projection, which is best represented by chair conformations.
A convention used to represent a 3-D stereo formula in 2-D representation is said to be Fischer projections. In this projection, the vertical lines represent bonds below the plane of the paper and horizontal lines represents bonds above the plane of the paper.
(d)
Answer to Problem 21P
Explanation of Solution
Drawing the Fischer projection of given compound as:
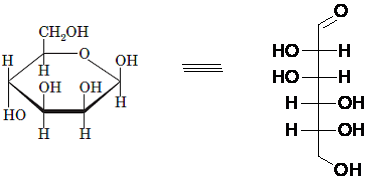
For a D-sugar, the
A new carbon stereocenter created by the conversion of an open structure to a cyclic structure is said to be the anomeric carbon. In carbohydrates, when the hydroxy group on an anomeric carbon is present on the same side as that of the
The anomeric carbon of the given compound is shown by “*”:
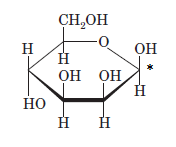
Since, in the given sugar the
Hence, the name of compound is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
INTRO.TO GENERAL,ORGAN...-OWLV2 ACCESS
- Curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s). Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. H CH3NH3+ :0: :0: HO CH3NH2 HH iSelect to Add Arrows i Select to Add Arrows i HH CH3NH3+ CH3NH2 Select to Add Arrows i CH3NH3 CH3NH2 ايكدا HH Select to Add Arrowsarrow_forwardThe reaction is carried out with gases: A → B + C at 300 K. The total pressure is measured as a function of time (table). If the reaction order is 2, calculate the rate or kinetic constant k (in mol-1 L s¹) Ptotal (atm) 492 676 760 808 861 t(s) 0 600 1200 1800 3000arrow_forwardcan someone give a description of this NMR including whether its a triplt singlet doublet where the peak is around at ppm and what functional group it representsarrow_forward
- 1. Determine the relationship between the following molecules as identical, diastereomers, or enantiomers (6 points, 2 points each). OH OH OH A-A OH HOT HO- ACHN and HO- ACHN OH HO HO ° OH and OH OH SH and ...SHarrow_forward20,0 Complete the electron pushing mechanism to y drawing the necomery unicaciones and carved on for Step 1: Add curved arms for the tint step, traiment with NalilĻ. The Nation 458 Step 2: Added for the second step, inalment with), how the "counterion bar Step 3: Daw the products of the last simplom organic and one incoganic spacient, including all nonbondingarrow_forwardplease provide the structure for this problem, thank you!arrow_forward
- Draw the Fischer projection from the skeletal structure shown below. HO OH OH OH OH H Q Drawing Atoms, Bonds and Rings Charges I ☐ T HO H H OH HO I CH2OH H OH Drag H OH -CH2OH CHO -COOH Undo Reset Remove Donearrow_forwardplease provide the structure for this problem, thank youarrow_forwardpresented by Morallen Lig Intermine the hand product for the given mution by adding atoms, bonds, nonhonding diarion panda скуль Step 3: Comp the draw the product Step 2: Agama workup Compithe 429 ملولةarrow_forward
- Reaction A 0,0arrow_forwardpresented by Morillon Leaning Predict the organic product for the min кусур HSC Adithane carved arnown to come than that to the condon slchroruis in acid in in aquishri with ноюarrow_forward6.15PM Sun Mar 30 K Draw the major product of this reaction. Include any relevant stereochemistry. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Problem 1 of O H [PhзPCH2CH3]*C|¯ NaH Drawing > Q Atoms, Bonds and Draw or tap a nearrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning





