
(a)
Interpretation:
It is to be shown how to carry out the given synthesis.
Concept introduction:
The protection of the alcoholic OH group is done by the treatment with silyl chloride (either
Answer to Problem 19.79P
The given synthesis is carried out as:
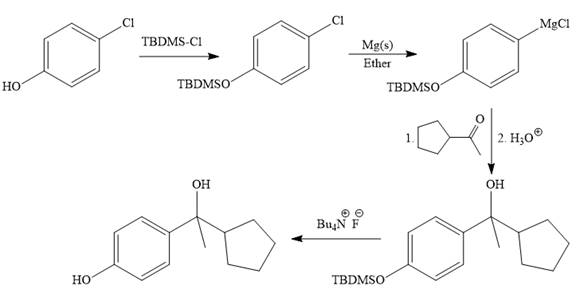
Explanation of Solution
The given synthesis is
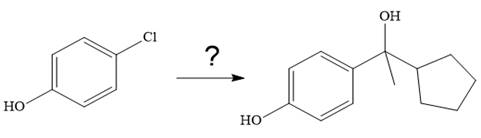
It is noticed that from the given starting material, a tertiary alcohol is synthesized. So the required step-up reaction carried out by using a Grignard reagent and corresponding ketone. This synthesis is given below:
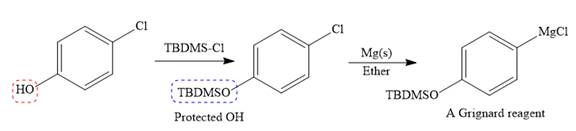
The given starting material is converted to corresponding Grignard reagent by the treatment with solid Mg metal in the ether as a solvent. But to avoid unwanted reactions of OH group with Mg metal this OH group protected first.
Then the Grignard reaction is carried out with the corresponding ketone to form the required tertiary alcohol.
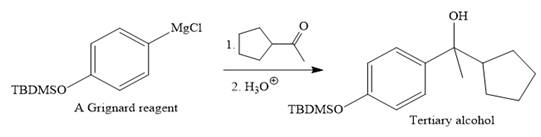
Finally, the deprotection of the OH group is done to produce the final required compound.
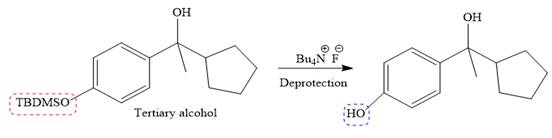
It is shown how to carry out the given synthesis.
(b)
Interpretation:
It is to be shown how to carry out the given synthesis.
Concept introduction:
The protection of the alcoholic OH group is done by the treatment with silyl chloride (either
Answer to Problem 19.79P
The given synthesis is carried out as:
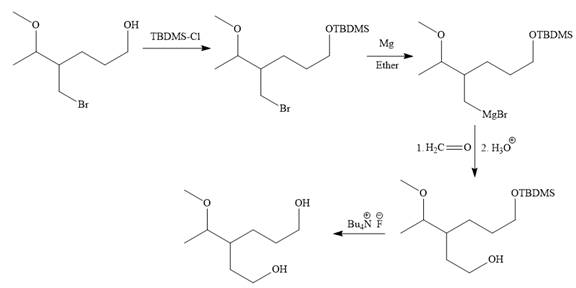
Explanation of Solution
The given synthesis is
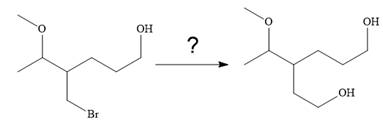
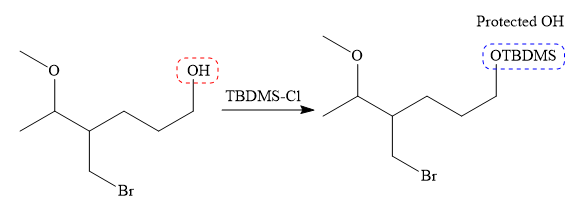
It is noticed that only the bromine atom of the starting material is replaced by the
Then the Br atom of the starting material subjected to Mg metal to form corresponding Grignard reagent.
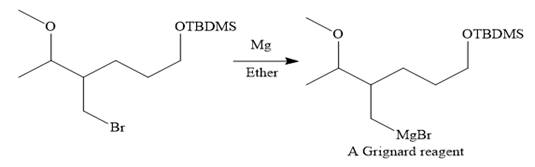
Above Grignard reagent is then treated with formaldehyde to carry out required step-up reaction via Grignard reaction. The acid workup step is needed for the Grignard reaction.
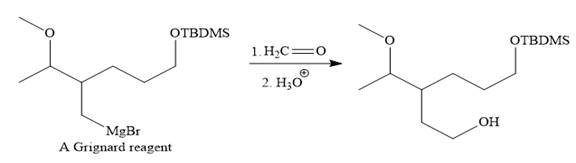
Finally, the deprotection of the protected OH group in the first step is carried out to form the final product.
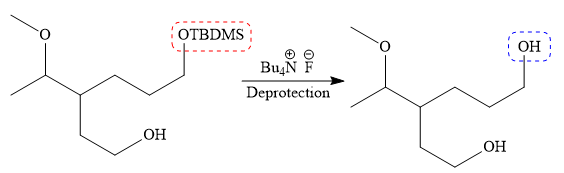
It is shown how to carry out the given synthesis.
(c)
Interpretation:
It is to be shown how to carry out the given synthesis.
Concept introduction:
Alkyl halide on treatment with solid magnesium metal corresponding Grignard reagent is formed. Grignard reagent on treatment with an aldehyde corresponding secondary alcohol is formed as the product during the workup step while ketone produces tertiary alcohol. The specialty of the Grignard reagent is when it treated with carbon dioxide (
Answer to Problem 19.79P
The given synthesis is carried out as:
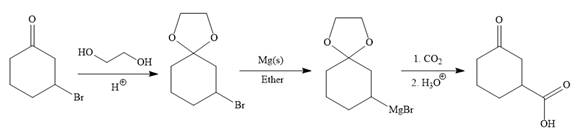
Explanation of Solution
The given synthesis is
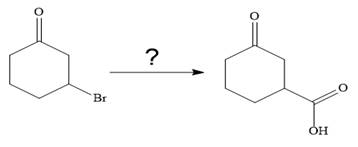
It is noticed that only a bromine atom of the starting material is replaced by a carboxylic acid group in the product. It is remembered that Grignard reagent when treated with carbon dioxide (
To carry out the required Grignard reaction the carbonyl group of the starting material is protected first to avoid an unwanted reaction.
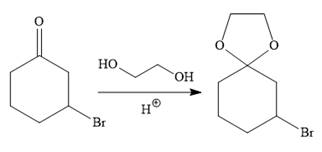
For the protection of ketone, it is treated with ethylene glycol in the presence of an acid catalyst. The protected form of the ketone is called ketal (a cyclic acetal).
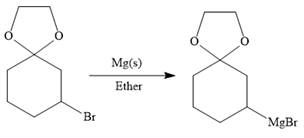
Above protected ketal then treated with Mg metal in the ether as a solvent to form the corresponding Grignard reagent.
The above Grignard reagent then treated with carbon dioxide to form the required product. Since acid workup step required in the Grignard reaction, the protected carbonyl group of the ketone is deprotected, too.
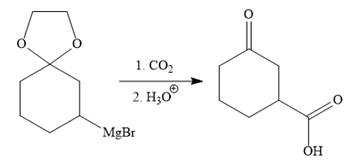
It is shown how to carry out the given synthesis.
(d)
Interpretation:
It is to be shown how to carry out the given synthesis.
Concept introduction:
The catalytic hydrogenation of the
Answer to Problem 19.79P
The given synthesis is carried out as:
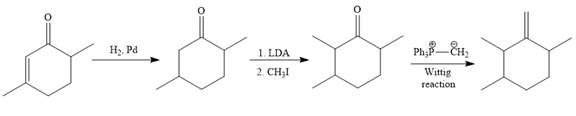
Explanation of Solution
The given synthesis is

To carry out the given synthesis following steps are carried out:
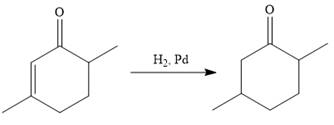
In the first step, the catalytic hydrogenation of the alkene group of the starting material is done as below:
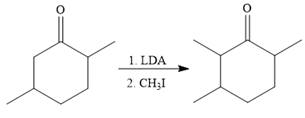
To reduce the only
Finally, a Wittig reaction is carried out to produce the required product.
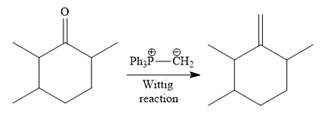
In the above Wittig reaction, the oxygen atom of the ketone is replaced by
It is shown how to carry out the given synthesis.
(e)
Interpretation:
It is to be shown how to carry out the given synthesis.
Concept introduction:
The protection of the carbonyl group of the ketone and aldehyde is carried out by the treatment with ethylene glycol in the presence of acid as the catalyst. The protected form of the carbonyl group is called acetal. For deprotection, simply acidic conditions are required. Catalytic hydrogenation of an
Answer to Problem 19.79P
The given synthesis is carried out as:
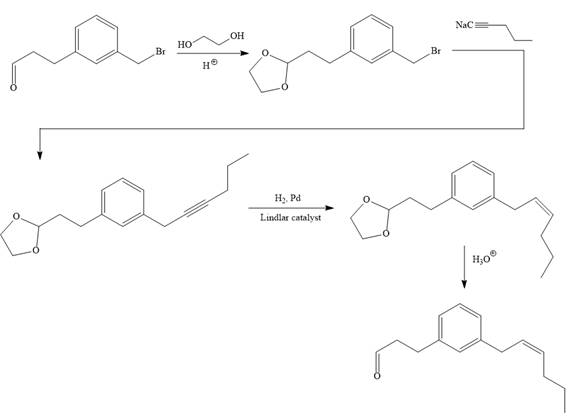
Explanation of Solution
The given synthesis is
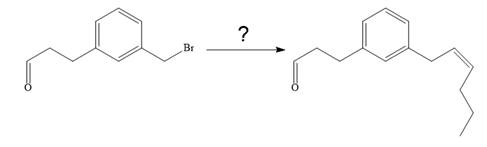
To carry out the given synthesis following steps are carried out:
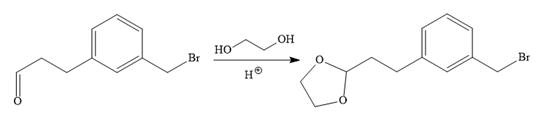
In the first step, the protection of the carbonyl group of the given starting material is done by the treatment with ethylene glycol in the presence of an acid (e.g.
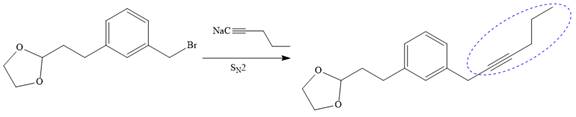
Now the required nucleophilic addition is done to insert required moiety in the product.
The triple bond of an above alkyne then subjected to catalytic hydrogenation with Lindlar catalyst to form the required cis alkene. Finally, a deprotection step carried out to produce the required product.
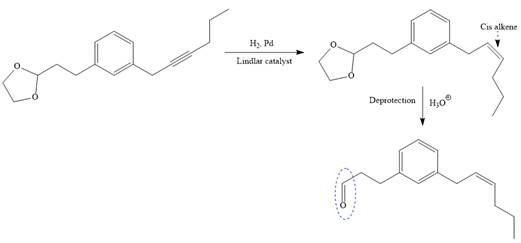
It is shown how to carry out the given synthesis.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
EBK GET READY FOR ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- What are the major products of the following reaction? Please provide a detailed explanation and a drawing to show how the reaction proceeds.arrow_forwardWhat are the major products of the following organic reaction? Please include a detailed explanation as well as a drawing as to how the reaction proceeds.arrow_forwardPredict the organic product that forms in the reaction below: H + гон OH H+ H+ ☑ O Note: You may assume you have an excess of either reactant if the reaction requires more than one of those molecules to form the product. In the drawing area below, draw the skeletal ("line") structure of the missing organic product X. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. S 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Centearrow_forward
- In the analysis of Mg content in a 25 mL sample, a titration volume of 5 mL was obtained using 0.01 M EDTA. Calculate the Mg content in the sample if the Ca content is 20 ppmarrow_forwardPredict the organic products that form in the reaction below: H. H+ + OH H+ Y Note: You may assume you have an excess of either reactant if the reaction requires more than one of those molecules to form the products. In the drawing area below, draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic products X and Y. You may draw the structures in any arrangement that you like, so long as they aren't touching. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. G X C © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Access +arrow_forward111 Carbonyl Chem Choosing reagants for a Wittig reaction What would be the best choices for the missing reagents 1 and 3 in this synthesis? 1. PPh3 3 1 2 2. n-BuLi • Draw the missing reagents in the drawing area below. You can draw them in any arrangement you like. Do not draw the missing reagent 2. If you draw 1 correctly, we'll know what it is. • Note: if one of your reagents needs to contain a halogen, use bromine. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. × ©2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Usearrow_forward
- A student proposes the transformation below in one step of an organic synthesis. There may be one or more reactants missing from the left-hand side, but there are no products missing from the right-hand side. There may also be catalysts, small inorganic reagents, and other important reaction conditions missing from the arrow. • Is the student's transformation possible? If not, check the box under the drawing area. . If the student's transformation is possible, then complete the reaction by adding any missing reactants to the left-hand side, and adding required catalysts, inorganic reagents, or other important reaction conditions above and below the arrow. • You do not need to balance the reaction, but be sure every important organic reactant or product is shown. + T X O O лет-ле HO OH HO OH This transformation can't be done in one step.arrow_forwardDetermine the structures of the missing organic molecules in the following reaction: X+H₂O H* H+ Y OH OH Note: Molecules that share the same letter have the exact same structure. In the drawing area below, draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic molecules X and Y. You may draw the structures in any arrangement that you like, so long as they aren't touching. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. X Sarrow_forwardPredict the major products of this organic reaction. If there aren't any products, because nothing will happen, check the box under the drawing area instead. No reaction. HO. O :☐ + G Na O.H Click and drag to start drawing a structure. XS xs H₂Oarrow_forward
- What are the angles a and b in the actual molecule of which this is a Lewis structure? H H C H- a -H b H Note for advanced students: give the ideal angles, and don't worry about small differences from the ideal groups may have slightly different sizes. a = b = 0 °arrow_forwardWhat are the angles a and b in the actual molecule of which this is a Lewis structure? :0: HCOH a Note for advanced students: give the ideal angles, and don't worry about small differences from the ideal that might be caused by the fact that different electron groups may have slightly different sizes. a = 0 b=0° Sarrow_forwardDetermine the structures of the missing organic molecules in the following reaction: + H₂O +H OH O OH +H OH X Note: Molecules that share the same letter have the exact same structure. In the drawing area below, draw the skeletal ("line") structure of the missing organic molecule X. Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





