
Concept explainers
Draw structural formulas for the following amino acids, identify the chiral carbon atom in each one, and circle the four different groups attached to the chiral carbon.
a. valine
b. glutamate
c. asparagine
d. cysteine
(a)
Interpretation:
The structural formula for the amino acid, valine is to be drawn. The chiral carbon atom in it is to be identified. The four different groups attached to the chiral carbon atom are to be circled.
Concept introduction:
Amino acids are organic compounds which combine sequentially to generate a protein. They are known as the building blocks of the human body. The main elements present in amino acids are carbon, nitrogen and oxygen while the side chains attached to the chiral carbon atom contain other elements.
Answer to Problem 19.5E
The structural formula for the amino acid, valine is shown below.
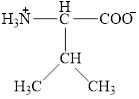
The chiral carbon atom in it is shown below.
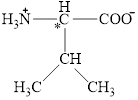
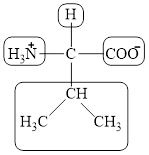
The four different groups attached to the chiral carbon atom are circled as shown below.
Explanation of Solution
Amino acids are formed by an amine and a carboxylic acid attached to a carbon atom with a characteristic side chain. The carboxylic acid in amino acids is usually in an ionic form and therefore, it is known as carboxylate group.
The structure of valine is given below.

Figure 1
The chiral carbon atom in it is shown below.

Figure 2
The four different groups attached to the chiral carbon atom are circled as shown below.

Figure 3
The structural formula for the amino acid, valine is shown in Figure 1. The chiral carbon atom in it is shown in Figure 2. The four different groups attached to the chiral carbon atom are shown in Figure 3.
(b)
Interpretation:
The structural formula for the amino acid, glutamate is to be drawn. The chiral carbon atom in it is to be identified. The four different groups attached to the chiral carbon atom are to be circled.
Concept introduction:
Amino acids are organic compounds which combine sequentially to generate a protein. They are known as the building blocks of the human body. The main elements present in amino acids are carbon, nitrogen and oxygen while the side chains attached to the chiral carbon atom contain other elements.
Answer to Problem 19.5E
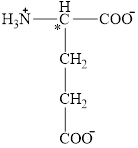
The structural formula for the amino acid, glutamate is shown below.
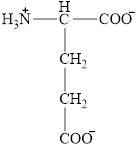
The chiral carbon atom in it is shown below.
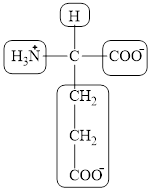
The four different groups attached to the chiral carbon atom are circled as shown below.
Explanation of Solution
Amino acids are formed by an amine and a carboxylic acid attached to a carbon atom with a characteristic side chain. The carboxylic acid in amino acids is usually in an ionic form and therefore, it is known as carboxylate group.
The structure of glutamate is given below.

Figure 4
The chiral carbon atom in it is shown below.

Figure 5
The four different groups attached to the chiral carbon atom are circled as shown below.

Figure 6
The structural formula for the amino acid, glutamate is shown in Figure 4. The chiral carbon atom in it is shown in Figure 5. The four different groups attached to the chiral carbon atom are shown in Figure 6.
(c)
Interpretation:
The structural formula for the amino acid, aspargine is to be drawn. The chiral carbon atom in it is to be identified. The four different groups attached to the chiral carbon atom are to be circled.
Concept introduction:
Amino acids are organic compounds which combine sequentially to generate a protein. They are known as the building blocks of the human body. The main elements present in amino acids are carbon, nitrogen and oxygen while the side chains attached to the chiral carbon atom contain other elements.
Answer to Problem 19.5E
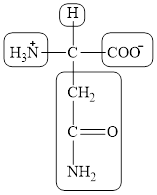
The structural formula for the amino acid, aspargine is shown below.
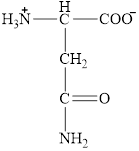
The chiral carbon atom in it is shown below.
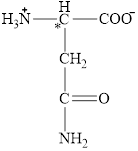
The four different groups attached to the chiral carbon atom are circled as shown below.
Explanation of Solution
Amino acids are formed by an amine and a carboxylic acid attached to a carbon atom with a characteristic side chain. The carboxylic acid in amino acids is usually in an ionic form and therefore, it is known as carboxylate group.
The structure of aspargine is given below.

Figure 7
The chiral carbon atom in it is shown below.

Figure 8
The four different groups attached to the chiral carbon atom are circled as shown below.

Figure 9
The structural formula for the amino acid, aspargine is shown in Figure 7. The chiral carbon atom in it is shown in Figure 8. The four different groups attached to the chiral carbon atom are shown in Figure 9.
(d)
Interpretation:
The structural formula for the amino acid, cysteine is to be drawn. The chiral carbon atom in it is to be identified. The four different groups attached to the chiral carbon atom are to be circled.
Concept introduction:
Amino acids are organic compounds which combine sequentially to generate a protein. They are known as the building blocks of the human body. The main elements present in amino acids are carbon, nitrogen and oxygen while the side chains attached to the chiral carbon atom contain other elements.
Answer to Problem 19.5E
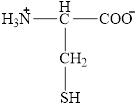
The structural formula for the amino acid, cysteine is shown below.
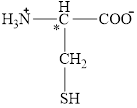
The chiral carbon atom in it is shown below.
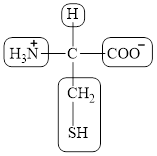
The four different groups attached to the chiral carbon atom are circled as shown below.
Explanation of Solution
Amino acids are formed by an amine and a carboxylic acid attached to a carbon atom with a characteristic side chain. The carboxylic acid in amino acids is usually in an ionic form and therefore, it is known as carboxylate group.
The structure of cysteine is given below.

Figure 10
The chiral carbon atom in it is shown below.

Figure 11
The four different groups attached to the chiral carbon atom are circled as shown below.

Figure 12
The structural formula for the amino acid, cysteine is shown in Figure 10. The chiral carbon atom in it is shown in Figure 11. The four different groups attached to the chiral carbon atom are shown in Figure 12.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
Bundle: Chemistry For Today: General, Organic, And Biochemistry, 9th + Owlv2 With Mindtap Reader, 1 Term (6 Months) Printed Access Card
- The Ksp for lead iodide ( Pbl₂) is 1.4 × 10-8. Calculate the solubility of lead iodide in each of the following. a. water Solubility = mol/L b. 0.17 M Pb(NO3)2 Solubility = c. 0.017 M NaI mol/L Solubility = mol/Larrow_forwardPleasssssseeee solve this question in cheeemsirty, thankss sirarrow_forwardPleasssssseeee solve this question in cheeemsirty, thankss sirarrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, World of ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780618562763Author:Steven S. ZumdahlPublisher:Houghton Mifflin College Div
World of ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780618562763Author:Steven S. ZumdahlPublisher:Houghton Mifflin College Div World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co





