
Concept explainers
Identify each compound from its spectral data.
(a)
Interpretation: The given compound is to be identified from its spectral data.
Concept introduction: IR spectroscopy is used to identify the functional group present in a compound. Each and every bond vibrates at a characteristic frequency. Proton
Answer to Problem 19.57P
The given compound from its spectrum data of IR, and
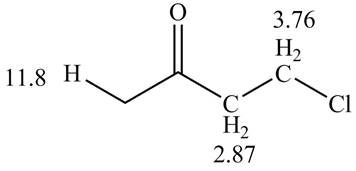
Figure 1
Explanation of Solution
The spectral data for the given compound is as follows:
IR absorptions at
Information from
The observed chemical shift value at
The observed chemical shift value at
The observed chemical shift values at
Thus, the structure of a given compound from its spectrum data of IR, and
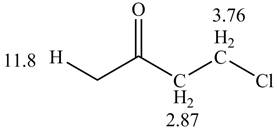
Figure 1
The given compound from its spectrum data of IR, and
(b)
Interpretation: The given compound is to be identified from its spectral data.
Concept introduction: IR spectroscopy is used to identify the functional group present in a compound. Each and every bond vibrates at a characteristic frequency. Proton
Answer to Problem 19.57P
The structure of a given compound from its spectrum data of IR, and
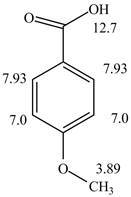
Figure 2
Explanation of Solution
The spectral data for the given compound is as follows:
IR absorptions at
Information from
The observed chemical shift values at
The observed chemical shift value at
The observed chemical shift value at
Thus, the structure of a given compound from its spectrum data of IR, and
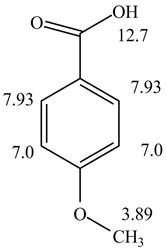
Figure 2
The given compound from its spectrum data of IR, and
(c)
Interpretation: The given compound is to be identified from its spectral data.
Concept introduction: IR spectroscopy is used to identify the functional group present in a compound. Each and every bond vibrates at a characteristic frequency. Proton
Answer to Problem 19.57P
The given compound from its spectrum data of IR, and
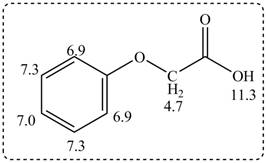
Figure 3
Explanation of Solution
The spectral data for the given compound is as follows:
IR absorptions at
Information from
The observed chemical shift values at
The observed chemical shift value at
The observed chemical shift value at
Thus, the structure of a given compound from its spectrum data of IR, and
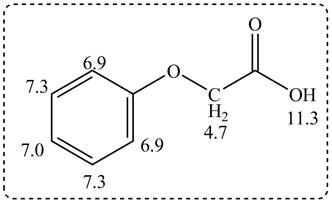
Figure 3
The given compound from its spectrum data of IR, and
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
Fundamentals Of Thermodynamics
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
- 3) Draw a detailed mechanism and predict the product of the reaction shown? 1) EtMgBr 2) H3O+arrow_forwardHow to draw the mechanism for this reaction?arrow_forward> H₂C=C-CH2-CH3 B. H₂O Pt C. + H2 + H₂O H D. 16. Give the IUPAC name for each of the following: B. Cl Cl c. Cl Cl 17. Draw the line-angle formula for each of the following compounds: 1. phenol 2. 1,3-dichlorobenzene 3. 4-ethyltoluene < Previous Submit Assignment Next ▸arrow_forward
- Consider the following nucleophilic substitution reaction. The compound listed above the arrow is the solvent for the reaction. If nothing is listed over the arrow, then the nucleophile is also the solvent for the reaction. Part 1 of 2 Br CH,CN + I¯ What is the correct mechanism for the reaction? Select the single best answer. @SN2 ○ SN 1 Part: 1/2 Part 2 of 2 Draw the products for the reaction. Include both the major organic product and the inorganic product. If more than one stereoisomer is possible, draw only one stereoisomer. Include stereochemistry where relevant. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. X હૈarrow_forward20.33 Think-Pair-Share (a) Rank the following dienes and dienophiles in order of increasing reactivity in the Diels-Alder reaction. (i) CO₂Et (ii) COEt || CO₂Et MeO MeO (b) Draw the product that results from the most reactive diene and most reactive dienophile shown in part (a). (c) Draw a depiction of the orbital overlap involved in the pericyclic reaction that oc- curs between the diene and dienophile in part (b). (d) Is the major product formed in part (b) the endo or exo configuration? Explain your reasoning.arrow_forward20.40 The following compound undergoes an intramolecular Diels-Alder reaction to give a tricyclic product. Propose a structural formula for the product. CN heat An intramolecular Diels-Alder adductarrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

