Concept explainers
Draw all resonance structures of the conjugate bases formed by removal of the labeled protons
a.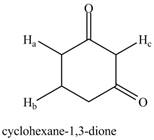 b.
b.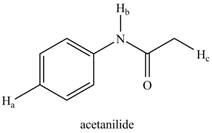
(a)
Interpretation: The resonance structure of the conjugate bases formed by the removal of the labeled protons
Concept introduction: Most of the organic structures cannot be represented using single Lewis structure. Therefore, there exists more than one Lewis structure for representing a molecule or ion. These structures are known as resonance structures. These are the hypothetical structures and do not specify the exact structure. These resonance structure combine together to give resonance hybrid that is lower in energy and is the most stable structure.
The delocalization of electrons results in the formation resonance structure.
Answer to Problem 19.50P
The resonance structure of the conjugate bases formed by the removal of the labeled protons
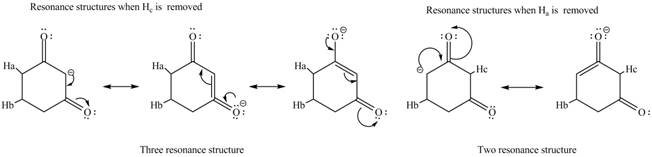
Figure 1
The increasing order of acidity of protons is
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is,
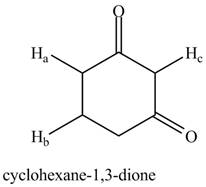
Figure 2
The conjugate base formed by the removal of
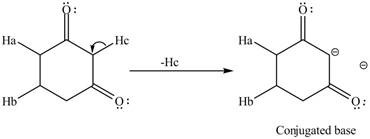
Figure 3
Therefore, the resonance structure of the conjugate base formed by the removal of the
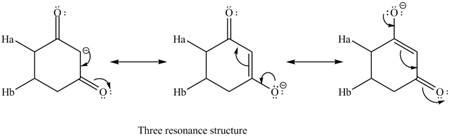
Figure 4
The conjugate base formed by the removal of
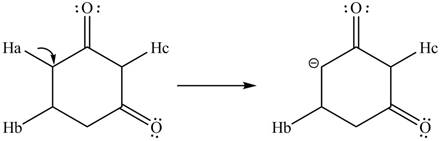
Figure 5
Therefore, the resonance structure of the conjugate base formed by the removal of the
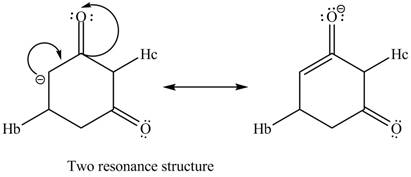
Figure 6
The stability of resonance structures depends upon the following rules:
• The stability of resonance structure is more if it possesses more bonds and fewer charges.
• Resonance structure will be more stable if atoms of the resonance structure have complete octet.
• The stability of resonance structure is more if negative charge is on more electronegative atom
The removal of
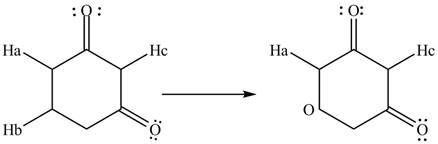
Figure 7
Proton acidity depends upon the stability of conjugated bases. More the number of resonance structures more will be the stability of molecule. Therefore, the increasing order of acidity of protons is
The resonance structures of the conjugate bases formed by the removal of the labeled protons
(b)
Interpretation: The resonance structure of the conjugate bases formed by the removal of the labeled protons
Concept introduction: Most of the organic structures cannot be represented using single Lewis structure. Therefore, there exists more than one Lewis structure for representing a molecule or ion. These structures are known as resonance structures. These are the hypothetical structures and do not specify the exact structure. These resonance structure combine together to give resonance hybrid that is lower in energy and is the most stable structure.
The delocalization of electrons results in the formation resonance structure.
Answer to Problem 19.50P
The resonance structure of the conjugate bases formed by the removal of the labeled protons
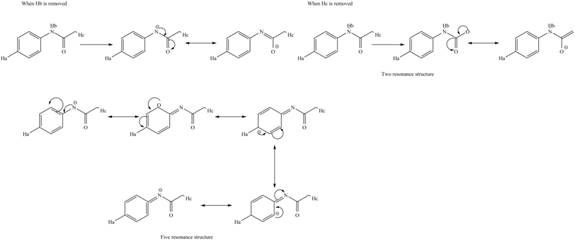
Figure 8
The increasing order of acidity of protons is
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is,
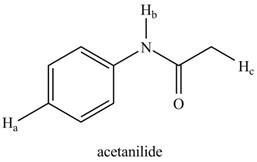
Figure 9
The conjugate base formed by the removal of
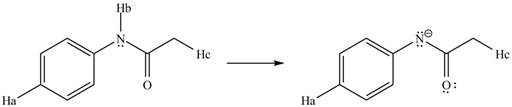
Figure 10
Therefore, the resonance structure of the conjugate base formed by the removal of the
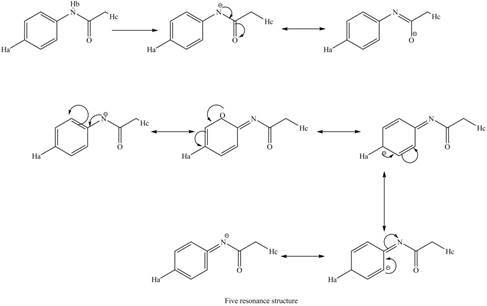
Figure 11
Similarly, the resonance structure of the conjugate base formed by the removal of the
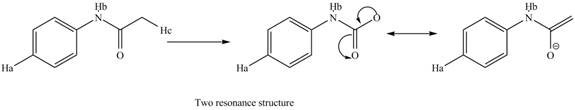
Figure 12
The stability of resonance structures depends upon the following rules:
• The stability of resonance structure is more if it possesses more bonds and fewer charges.
• Resonance structure will be more stable if atoms of the resonance structure have complete octet.
• The stability of resonance structure is more if negative charge is on more electronegative atom
The removal of
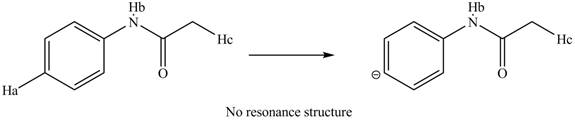
Figure 13
Proton acidity depends upon the stability of conjugated bases. More the number of resonance structures more will be the stability of molecule. Therefore, the increasing order of acidity of protons is
The resonance structures of the conjugate bases formed by the removal of the labeled protons
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
PKG ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- Using the chart describe the change from cystine to tyrosine and its impact on the protein. Using the chart describe the change from histidine to aspartic acid and its impact on the protein.arrow_forwardHow to get the predicted product of this reaction belowarrow_forwardPlease help me fill out the chart then using the chart describe the change from cystine to tyrosine and its impact on the protein. Then using the chart describe the change from histidine to aspartic acid.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning


