Concept explainers
Using the
a. 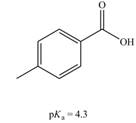 b.
b. 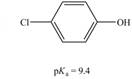 c.
c. 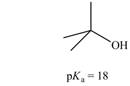
(a)
Interpretation: The correct
Concept introduction: Carboxylic acids are the carbon compounds that contain carboxyl group as a major functional group. They are polar due to electronegativity difference between the atoms in a compound. They sometimes exist as a dimer. Dimers are the compounds that consist of two monomer units connected by bonds or forces. Carboxylic acids are synthesized from alkynes, alkene, benzene derivatives, alcohol and allylic halides by using different reagents.
Answer to Problem 19.35P
The bases that are strong enough to deprotonate the given compounds are
Explanation of Solution
The given carboxylic acid is
The
Therefore, the bases that are strong enough to deprotonate the given compounds are
The bases that are strong enough to deprotonate the given compounds are
(b)
Interpretation: The correct
Concept introduction: Carboxylic acids are the carbon compounds that contain carboxyl group as a major functional group. They are polar due to electronegativity difference between the atoms in a compound. They sometimes exist as a dimer. Dimers are the compounds that consist of two monomer units connected by bonds or forces. Carboxylic acids are synthesized from alkynes, alkene, benzene derivatives, alcohol and allylic halides by using different reagents.
Answer to Problem 19.35P
The bases that are strong enough to deprotonate the given compounds are
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is
The
Therefore, the bases that are strong enough to deprotonate the given compounds are
The bases that are strong enough to deprotonate the given compounds are
(c)
Interpretation: The correct
Concept introduction: Carboxylic acids are the carbon compounds that contain carboxyl group as a major functional group. They are polar due to electronegativity difference between the atoms in a compound. They sometimes exist as a dimer. Dimers are the compounds that consist of two monomer units connected by bonds or forces. Carboxylic acids are synthesized from alkynes, alkene, benzene derivatives, alcohol and allylic halides by using different reagents.
Answer to Problem 19.35P
The bases that are strong enough to deprotonate the given compounds are
Explanation of Solution
The given carboxylic acid is
The
Therefore, the bases that are strong enough to deprotonate the given compounds are
The bases that are strong enough to deprotonate the given compounds are
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
PKG ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- 10. Complete the substitution reaction of 2 pentanol with these reagents. Reagents & Reaction Conditions use practice sheet. Please write only major products, minor product like water, other gases are not required. Hint: In substitution of alcohol, we generally substitute OH group with Halogens like cl, Br, F using some reagent containing halogens. Ensure to add halogens to the same carbon number where you are removing OH from Examples Alcohols can be converted to Alkyl Halides with HX acids HBr H₂O HCI + H₂O HI + H₂O CH,CH₂OH + SOCI₂ CH,CH₂OH + PCI₁₂ A BBYJU'S CH CHCI + SO₂+ HCI CH₂CH CIP(OH), + HCI CH,CH₂OH + PCI CHCHCI + POCI + HCI CH,CH₂OH + PBr, CH,CH,Br + P(OH), + HBr 1. Reaction with HBr with 2 Pentanol 2.Reaction with HI with 2 pentanol © Byjus.com 3.Reaction with HCI+ZnCl,, with 2 pentanol (Zncl2 is catalyst no role) 4.Reaction with SOCI,, with 2 Pentanol 5.Reaction with PBr; or PCl, with 2 pentanolarrow_forward3. Is 2-methyl-2-propanol a primary, secondary, or tertiary alcohol? Write out the structures of 2-methyl-2-propanol and also any oxidation products of 2- methyl-2- propanol. If there is more than one oxidation product, give the structure of each of the products. 4. 2-Propanol is the IUPAC systematic name of this alcohol. It has a common name by which it is much better known (You'll see it in the grocery store or pharmacy). Give that common name 5. Aldehydes can be synthesized by the oxidation of. Please choose from below choices A. Primary alcohols B. Secondary alcohols C. Organic acids D. Inorganic acids 6. Tertiary alcohol Can undergo oxidation. yes or no. ? If yes then answer the product.arrow_forwardFinish the reactions hand written pleasearrow_forward
- Part A Identify each alcohol as primary, secondary, or tertiary Drag the appropriate items to their respective bins. CH₂ H₂C- -C-OH HO CH₂ Primary Он OH CH₂ OH CCH₂OH CH₂ сн Secondary Tertiary Reset Help CH,CH₂ (CH)CHCH,OH CH,CH,CH,CCH, CHOH CH₂ Different types of alcohol groups Alcohol and its reaction: 8. Combing two alcohol molecules below and completing the reaction with Product .( Hint Reaction called etherification as ether is formed and name the ether once you complete the reaction. Hint.: R-O-H+H-O-RR-O-R Do the reaction: CH₂OH + CH₂OH---→ + H-O-H 9. Write the reaction of formation of alcohol from alkene by adding water: Addition reaction also called hydration reaction as we are adding water which occur always in presence of acid Hint: Break the double bond and add H and OH if symmetrical then add anywhere if unsymmetrical then follow Markovnikov rule H should go to that double bone carbon which has more hydrogen CH2=CH2 + H₂O-→arrow_forwardComplete the reaction hand written pleasearrow_forwardPredict the major products of this organic reaction: HBr (1 equiv) cold ? Some important notes: • Draw the major product, or products, of this reaction in the drawing area below. • You can draw the products in any arrangement you like. • Pay careful attention to the reaction conditions, and only include the major products. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. • Note that there is only 1 equivalent of HBr reactant, so you need not consider the case of multiple additions. dm Re Explanation Check ©2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Termarrow_forward
- b) Use curved arrows to show the reaction of the radical with hydrogen bromide. Br: Br H .. Answer Bankarrow_forwardIndicate the reaction products when CH3COCH2COOCH2COOC2H5 (ethyl acetoacetoacetate) reacts with 1º OH-/H2O and 2º H3O+arrow_forwardDraw the formula of the compound 4-cyclohexyl butanamide?arrow_forward
- What is the formula of the compound 3-isopropylcyclopentane-1-carbonyl chloride?arrow_forwardIndicate the products of the reaction between CH3COCH2COONa (Sodium acetoacetate) and BrCH2COOC2H5arrow_forwardIndicate whether the product of the reaction between Naphthalene and CrO3 in acetic acid at 25ºC is 1,4 naphthoquinone or phthalic anhydride.arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning


