
(a)
Interpretation:
The product when acetone reacts with
Concept introduction:
The replacement or substitution of one
Answer to Problem 19.40AP
The gem-
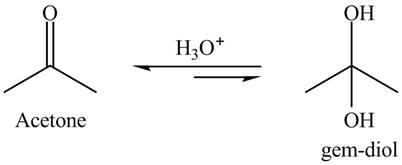
Explanation of Solution
The hydrated product is formed known as gem-diol. The gem-diol is an unstable compound. Therefore, the reaction is always is in a backward direction. The overall reaction is shown below.

Figure 1
The product of hydration of acetone is shown in Figure 1.
(b)
Interpretation:
The product when acetone reacts with
Concept introduction:
Sodium borohydride is a reducing agent which is selective in nature. It selectively reduces the carbonyl compounds into corresponding alcohols. It converts
Answer to Problem 19.40AP
The
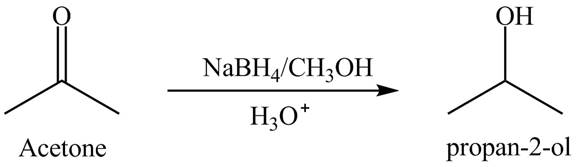
Explanation of Solution
Sodium borohydride is selective in nature which is used as a reducing agent. The conversion of acetone into

Figure 2
The product of reduction of acetone is shown in Figure 2.
(c)
Interpretation:
The product when acetone reacts with
Concept introduction:
Chromium trioxide is the acidic anhydride of chromic acid. It is used as an oxidizing agent which is an inorganic compound. It resists oxidizing the ketones in the presence of pyridine. It shows that chromium trioxide is selective in nature.
Answer to Problem 19.40AP
The product is not formed when acetone reacts with
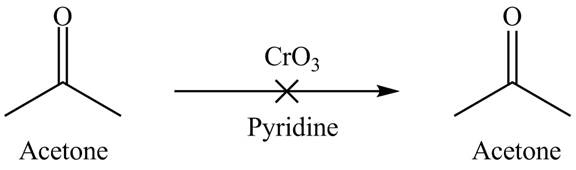
Explanation of Solution
Chromium trioxide is used as an oxidizing agent which is an inorganic compound. It resists oxidizing the ketones in the presence of pyridine. Therefore, acetone is not oxidized. It shows that chromium trioxide is selective in nature. The reactant is unreacted due to the inertness of the chromium trioxide. The overall reaction is shown below.

Figure 3
The reaction of acetone with the chromium trioxide is shown in Figure 3.
(d)
Interpretation:
The product when acetone reacts with
Concept introduction:
Sodium cyanide solution in water acts as a base. It is corrosive in nature. As well as reacts very rapidly with acid. It also reacts with water, moisture, carbon dioxide. The
Answer to Problem 19.40AP
The product formed is
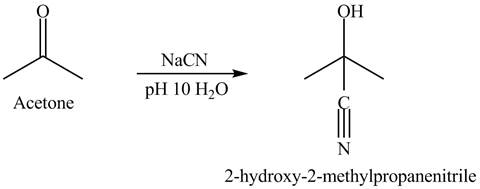
Explanation of Solution
The acetone reacts with sodium cyanide solution in water. The pH is maintained at
There is a nucleophilic addition where cyanide is act as a nucleophile. The overall reaction is given below.
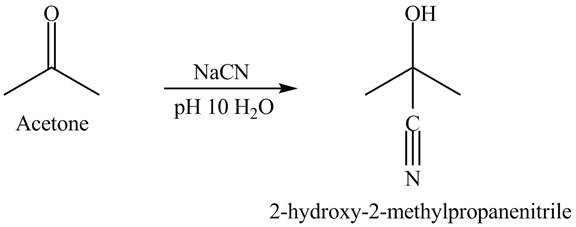
Figure 4
Acetone and sodium cyanide reacts to give the product as shown in Figure 4.
(e)
Interpretation:
The expected product when acetone reacts with
is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
A dehydration reaction is defined as the removal of
There are several dehydrating agents in the chemistry some of them are sulfuric acid and ammonia.
Answer to Problem 19.40AP
The product formed is
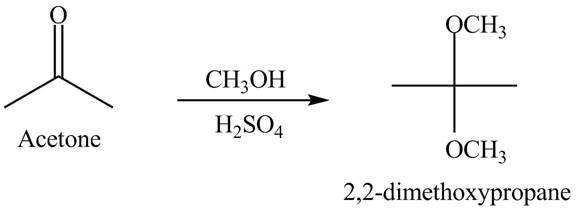
Explanation of Solution
When acetone reacts with excess of

Figure 5
The acetone reacts with excess of
(f)
Interpretation:
The expected product when acetone reacts with pyrrolidine and a trace of acid is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Pyrrolidine is a colorless water-soluble. It is a heterocyclic compound. Enamine is formed by the condensation process of an
Answer to Problem 19.40AP
The product formed is
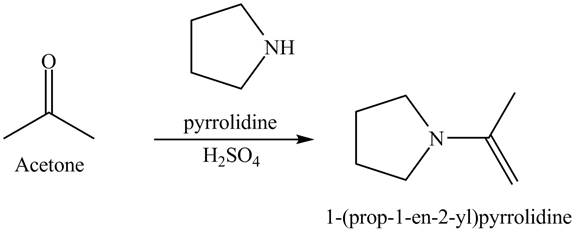
Explanation of Solution
When acetone reacts with pyrrolidine in the presence of acid. This reaction is a nucleophilic addition reaction. Pyrrolidine acts as a nucleophile which attacks at the electron-deficient site that is carbonyl carbon. In the final step, protonation takes place. The overall reaction is shown below.

Figure 6
The reaction is shown in Figure 6.
(g)
Interpretation:
The expected product when acetone reacts with semicarbazide with diluted acid is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Semicarbazide is the derivative of urea. Semicarbazide is water-soluble and white in color. Protonation takes place by using acid in the reaction. This reaction is a nucleophilic addition reaction. Semicarbazide is used to convert ketone into amides.
Answer to Problem 19.40AP
The product formed is
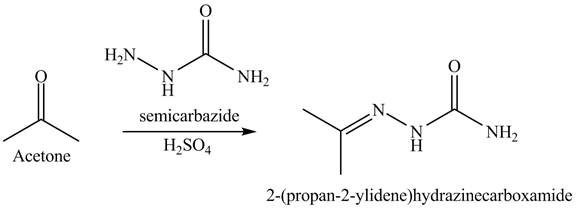
Explanation of Solution
The acetone reacts with semicarbazide with diluted acid. This reaction is a nucleophilic addition reaction. Semicarbazide is used to convert ketone into amides. In the first step, the nitrogen of semicarbazide is act as a nucleophile which attacks on the electrophilic site of ketone that is carbonyl carbon. In the second step, rearrangements take place. In the final step, the protonation takes place. The overall reaction is shown below.

Figure 7
The rection is shown in Figure 7.
(h)
Interpretation:
The expected product when acetone reacts with
Concept introduction:
Grignard reagents are
Answer to Problem 19.40AP
The product formed is
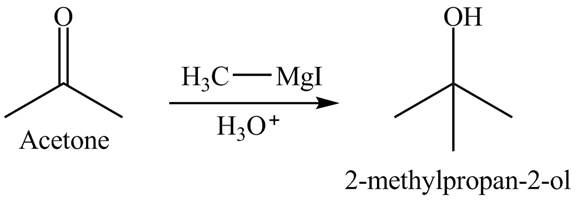
Explanation of Solution
The acetone reacts with the Grignard reagent. The Grignard reagent acts as a nucleophile. This reaction is a nucleophilic addition reaction. In the first step, the nucleophile attacks on the electrophilic part of the ketone which is carbonyl carbon. In the final step, protonation takes place. The overall reaction is shown below.

Figure 8
The product formed is
(i)
Interpretation:
The expected product obtained when
Concept introduction:
Oxidation is the process of addition of oxygen. Oxidation is also be defined as loosing of electrons. In the oxidation process, there is increasing in the oxidation state. The acid is added in the reaction for protonation.
The oxidizing agent is defined as the species which oxidizes others and itself gets reduced.
Answer to Problem 19.40AP
The product formed is acetone when
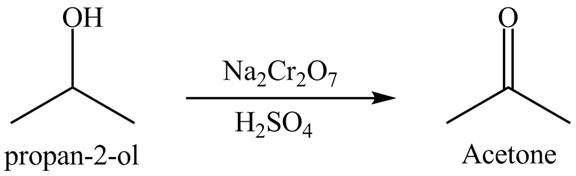
Explanation of Solution
The product

Figure 9
The product formed is acetone when
(j)
Interpretation:
The expected product obtained when
Concept introduction:
A dehydration reaction is defined as the removal of
There are several dehydrating agents in the chemistry some of are like sulfuric acid and ammonia.
Answer to Problem 19.40AP
The product formed is acetone when
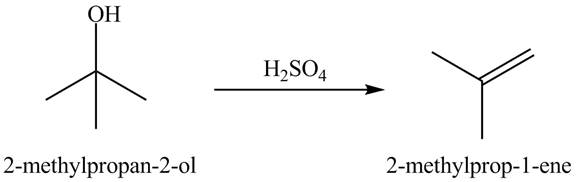
Explanation of Solution
In the dehydration process, the alcohol is converted into an alkene. The double bond formation takes place in this reaction. In the first step, the hydroxyl group attracts one proton of an acid. In the second step, the proton is taken by ![]()
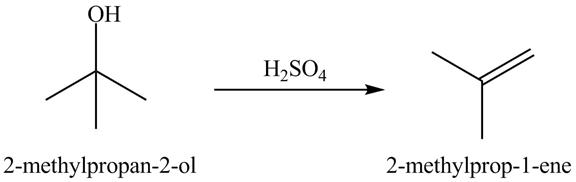
Figure 10
The dehydrated product of
(k)
Interpretation:
The expected product obtained when acetone reacts with
Concept introduction:
Hydrogenation is defined as the addition of hydrogen. Platinum is used as a surface catalyst. Mostly, catalysts are insoluble in metals like
Answer to Problem 19.40AP
The product formed is
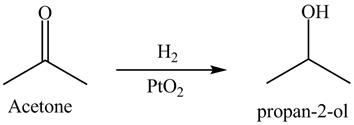
Explanation of Solution
Hydrogenation is defined as the addition of hydrogen. Platinum is used as a surface catalyst.
The product formed is
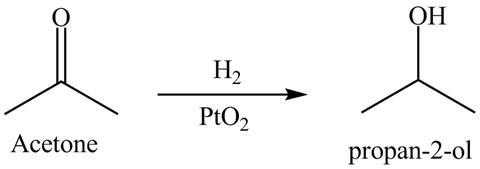
Figure 11
The reductive product of acetone is shown in Figure 11.
(l)
Interpretation:
The expected product obtained when acetone reacts with
Concept introduction:
The Wittig reaction is the chemical reaction involves a change in an aldehyde or ketone converted into an alkene. The chemical name of Wittig reagent is triphenyl phosphonium ylide. In the Wittig reaction, aldehydes or a ketone reacts with triphenyl phosphonium ylide to generate an alkene and triphenylphosphine oxide. The Wittig reagent gives good yields of alkene even when other functional groups are present on the aldehydes or ketone. However, as the steric hindrance of the aldehydes or ketone increases, the yield of alkene decreases.
Answer to Problem 19.40AP
The product formed is
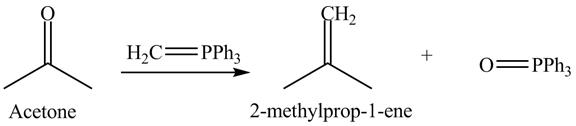
Explanation of Solution
In the Wittig reaction, acetone reacts with triphenyl phosphonium ylide to generate an alkene and triphenylphosphine oxide. The Wittig reagent gives good yields of alkene even when other functional groups are present on the aldehydes or ketone. However, as the steric hindrance of the aldehydes or ketone increases, the yield of alkene decreases. The overall reaction is shown below.
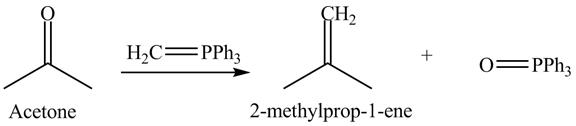
Figure 12
The treatment of Wittig reagent with acetone is shown in Figure 12.
(m)
Interpretation:
The expected product obtained when acetone reacts with
Concept introduction:
Clemmensen reduction is defined as the reduction in which aldehydes or ketones are converted into alkane or hydrocarbon. The catalyst is used in this reaction is zinc amalgam in the presence of concentrated hydrochloric acid. This is one of the easy methods to convert aldehydes or ketones into hydrocarbon.
Answer to Problem 19.40AP
The product formed is propane with the help of
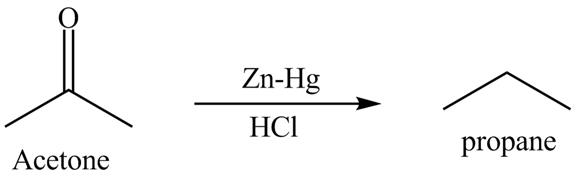
Explanation of Solution
The acetone is converted into propane with the help of zinc-amalgam in the presence of concentrated hydrochloric acid. Zinc,

Figure 13
The reduction of acetone with the help of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
Organic Chemistry Study Guide and Solutions
- What is the name of the following compound? SiMe3arrow_forwardK Draw the starting structure that would lead to the major product shown under the provided conditions. Drawing 1. NaNH2 2. PhCH2Br 4 57°F Sunny Q Searcharrow_forward7 Draw the starting alkyl bromide that would produce this alkyne under these conditions. F Drawing 1. NaNH2, A 2. H3O+ £ 4 Temps to rise Tomorrow Q Search H2arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning


