
Concept explainers
Identify the
a. tyrosine (neutral, polar)
b. glutamate (acidic, polar)
c. methionine (neutral, nonpolar)
d. histidine (basic, polar)
e. cysteine (neutral, polar)
f. valine (neutral, nonpolar)
(a)
Interpretation:
The
Concept introduction:
Amino acids are organic compounds which combine sequentially to generate a protein. They are known as the building blocks of the human body. The main elements present in amino acids are carbon, nitrogen and oxygen while other elements are found in side chains.
Answer to Problem 19.3E
The
Explanation of Solution
Amino acids are formed by an amine and a carboxylic acid attached to a carbon atom with a characteristic side chain. The carboxylic acid in amino acids is usually in an ionic form and therefore is known as carboxylate group.
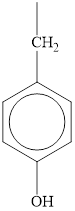
The structure of tyrosine is given below.
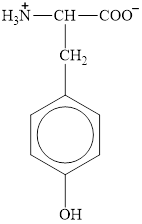
Figure 1
Therefore, the

Figure 2
The
(b)
Interpretation:
The
Concept introduction:
Amino acids are organic compounds which combine sequentially to generate a protein. They are known as the building blocks of the human body. The main elements present in amino acids are carbon, nitrogen and oxygen while other elements are found in side chains.
Answer to Problem 19.3E
The
![]()
Explanation of Solution
Amino acids are formed by an amine and a carboxylic acid attached to a carbon atom with a characteristic side chain. The carboxylic acid in amino acids is usually in an ionic form and therefore is known as carboxylate group.
The structure of glutamate is given below.
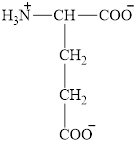
Figure 3
Therefore, the
![]()
Figure 4
The
(c)
Interpretation:
The
Concept introduction:
Amino acids are organic compounds which combine sequentially to generate a protein. They are known as the building blocks of the human body. The main elements present in amino acids are carbon, nitrogen and oxygen while other elements are found in side chains.
Answer to Problem 19.3E
The
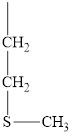
Explanation of Solution
Amino acids are formed by an amine and a carboxylic acid attached to a carbon atom with a characteristic side chain. The carboxylic acid in amino acids is usually in an ionic form and therefore is known as carboxylate group.
The structure of methionine is given below.
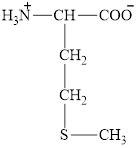
Figure 5
Therefore, the
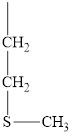
Figure 6
The
(d)
Interpretation:
The
Concept introduction:
Amino acids are organic compounds which combine sequentially to generate a protein. They are known as the building blocks of the human body. The main elements present in amino acids are carbon, nitrogen and oxygen while other elements are found in side chains.
Answer to Problem 19.3E
The
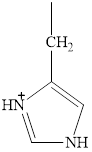
Explanation of Solution
Amino acids are formed by an amine and a carboxylic acid attached to a carbon atom with a characteristic side chain. The carboxylic acid in amino acids is usually in an ionic form and therefore is known as carboxylate group.
The structure of histidine is given below.
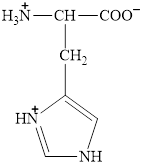
Figure 7
Therefore, the

Figure 8
The
(e)
Interpretation:
The
Concept introduction:
Amino acids are organic compounds which combine sequentially to generate a protein. They are known as the building blocks of the human body. The main elements present in amino acids are carbon, nitrogen and oxygen while other elements are found in side chains.
Answer to Problem 19.3E
The
![]()
Explanation of Solution
Amino acids are formed by an amine and a carboxylic acid attached to a carbon atom with a characteristic side chain. The carboxylic acid in amino acids is usually in an ionic form and therefore is known as carboxylate group.
The structure of cysteine is given below.
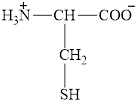
Figure 9
Therefore, the
![]()
Figure 10
The
(f)
Interpretation:
The
Concept introduction:
Amino acids are organic compounds which combine sequentially to generate a protein. They are known as the building blocks of the human body. The main elements present in amino acids are carbon, nitrogen and oxygen while other elements are found in side chains.
Answer to Problem 19.3E
The
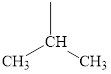
Explanation of Solution
Amino acids are formed by an amine and a carboxylic acid attached to a carbon atom with a characteristic side chain. The carboxylic acid in amino acids is usually in an ionic form and therefore is known as carboxylate group.
The structure of valine is given below.
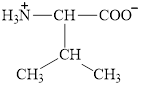
Figure 11
Therefore, the
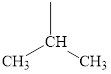
Figure 12
The
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
Bundle: Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Biochemistry, Loose-Leaf Version, 9th + LMS Integrated OWLv2, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card
- Differentiate between plastic deformation, elastic deformation, viscoelastic deformation and viscoplastic deformation.arrow_forward1.57 Draw all reasonable resonance structures for the following cation. Then draw the resonance hybrid.arrow_forwardFor the two questions below, draw the mechanism and form the major product.arrow_forward
- Indicate similarities and differences between natural, exchanged and pillared clays.arrow_forwardShow work. don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forwardIn intercalation compounds, their sheets can be neutral or have a negative or positive charge, depending on the nature of the incorporated species and its structure. Is this statement correct?arrow_forward
- This thermodynamic cycle describes the formation of an ionic compound MX2 from a metal element M and nonmetal element X in their standard states. What is the lattice enthalpy of MX2 ? What is the enthalpy formation of MX2 ? Suppose both the heat of sublimation of M and the ionization enthalpy of M were smaller. Would MX2 be more stable? Or less? or impossible to tell without more information?arrow_forward7. Draw the mechanism to describe the following transformation: Note: This is a base catalyzed reaction. So, the last steps must make [OH]- OH [OH]¯ OH Heat Oarrow_forwardShow work with explanation...don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forward
 World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,





