
Student Workbook for Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol 1. (Chs 1-21)
4th Edition
ISBN: 9780134110646
Author: Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus)
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 18, Problem 72EAP
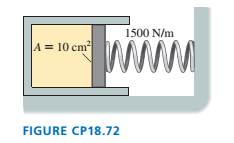
The cylinder in FIGURE CP18.72 has a moveable piston attached
to a spring. The cylinder's cross-section area is 10 cm2, it contains
0.0040 mol of gas, and the spring constant is 1500 N/m. At 20oC
the spring is neither compressed nor stretched. How far is the
spring compressed if the gas temperature is raised to 100oC?
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
A sky diver of mass 90 kg (with suit and gear) is falling at terminal speed. What is the upward force of air drag, and how do you know?
A car is traveling at top speed on the Bonneville salt flats while attempting a land speed record. The tires exert 25 kN of force in the backward direction on the ground. Why backwards? How large are the forces resisting the forward motion of the car, and why?
A bee strikes a windshield of a car on the freeway and gets crushed. What can you conclude about the force on the bee versus the force on the windshield, and on what principle is this based?
Chapter 18 Solutions
Student Workbook for Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol 1. (Chs 1-21)
Ch. 18 - Prob. 1CQCh. 18 - Prob. 2CQCh. 18 - Prob. 3CQCh. 18 - Prob. 4CQCh. 18 - Prob. 5CQCh. 18 - Prob. 6CQCh. 18 - Prob. 7CQCh. 18 - Prob. 8CQCh. 18 - Prob. 9CQCh. 18 - A gas undergoes the process shown in FIGURE...
Ch. 18 - Prob. 11CQCh. 18 - Prob. 12CQCh. 18 - Prob. 1EAPCh. 18 - Prob. 2EAPCh. 18 - What is the diameter of a copper sphere that has...Ch. 18 - Prob. 4EAPCh. 18 - Prob. 5EAPCh. 18 - How many atoms are in a 2.0 cm × 2.0 cm × 2.0 cm...Ch. 18 - Prob. 7EAPCh. 18 - An element in its solid phase has mass density...Ch. 18 - .0 mol of gold is shaped into a sphere. What is...Ch. 18 - What volume of aluminum has the same number of...Ch. 18 - Prob. 11EAPCh. 18 - Prob. 12EAPCh. 18 - Prob. 13EAPCh. 18 - A concrete bridge is built of 325-cm-long concrete...Ch. 18 - A surveyor has a steel measuring tape that is...Ch. 18 - Two students each build a piece of scientific...Ch. 18 - Prob. 17EAPCh. 18 -
18. What is the temperature in °F and the...Ch. 18 - Prob. 19EAPCh. 18 - .0 mol of gas at a temperature of -120°C fills a...Ch. 18 - Prob. 21EAPCh. 18 - Prob. 22EAPCh. 18 - Prob. 23EAPCh. 18 - Prob. 24EAPCh. 18 - Prob. 25EAPCh. 18 - Prob. 26EAPCh. 18 - Prob. 27EAPCh. 18 - Prob. 28EAPCh. 18 - A rigid, hollow sphere is submerged in boiling...Ch. 18 -
30. A rigid container holds hydrogen gas at a...Ch. 18 - Prob. 31EAPCh. 18 - Prob. 32EAPCh. 18 - Prob. 33EAPCh. 18 - Prob. 34EAPCh. 18 - Prob. 35EAPCh. 18 - Prob. 36EAPCh. 18 - Prob. 37EAPCh. 18 - .0050 mol of gas undergoes the process 1 2 3...Ch. 18 - Prob. 39EAPCh. 18 - Prob. 40EAPCh. 18 - Prob. 41EAPCh. 18 - Prob. 42EAPCh. 18 - Prob. 43EAPCh. 18 - A 15°C, 2.0-cm-diameter aluminum bar just barely...Ch. 18 - Prob. 45EAPCh. 18 - Prob. 46EAPCh. 18 - Prob. 47EAPCh. 18 - Prob. 48EAPCh. 18 - Prob. 49EAPCh. 18 - The 3.0-m-long pipe in FIGURE P18.50 is closed at...Ch. 18 - Prob. 51EAPCh. 18 - An electric generating plant boils water to...Ch. 18 - Prob. 53EAPCh. 18 - The air temperature and pressure in a laboratory...Ch. 18 - Prob. 55EAPCh. 18 - The mercury manometer shown in FIGURE P18.56 is...Ch. 18 - Prob. 57EAPCh. 18 - The 50 kg circular piston shown in FIGURE P18.58...Ch. 18 - Prob. 59EAPCh. 18 - .0 g of helium gas follows the process 1? 2 ?3...Ch. 18 - Prob. 61EAPCh. 18 - 62. FIGURE P18.62 shows two different processes...Ch. 18 - Prob. 63EAPCh. 18 - Prob. 64EAPCh. 18 - Prob. 65EAPCh. 18 - Prob. 66EAPCh. 18 - Prob. 67EAPCh. 18 - Prob. 68EAPCh. 18 - Prob. 69EAPCh. 18 - Prob. 70EAPCh. 18 - Prob. 71EAPCh. 18 - The cylinder in FIGURE CP18.72 has a moveable...Ch. 18 - Containers A and B in FIGURE CP18.73 hold the same...Ch. 18 - Prob. 74EAP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please help by: Use a free body diagram Show the equations State your assumptions Show your steps Box your final answer Thanks!arrow_forwardBy please don't use Chatgpt will upvote and give handwritten solutionarrow_forwardA collection of electric charges that share a common magnitude q (lower case) has been placed at the corners of a square, and an additional charge with magnitude Q (upper case) is located at the center of that square. The signs of the charges are indicated explicitly such that ∣∣+q∣∣∣∣+Q∣∣=∣∣−q∣∣==∣∣−Q∣∣=qQ Four unique setups of charges are displayed. By moving one of the direction drawings from near the bottom to the bucket beside each of the setups, indicate the direction of the net electric force on the charge with magnitude Q, located near the center, else indicate that the magnitude of the net electric force is zero, if appropriate.arrow_forward
- A number of electric charges has been placed at distinct points along a line with separations as indicated. Two charges share a common magnitude, q (lower case), and another charge has magnitude Q(upper case). The signs of the charges are indicated explicitly such that ∣∣+q∣∣∣∣+Q∣∣=∣∣−q∣∣==∣∣−Q∣∣=qQ Four different configurations of charges are shown. For each, express the net electric force on the charge with magnitude Q (upper case) as F⃗E=FE,xî where the positive x direction is towards the right. By repositioning the figures to the area on the right, rank the configurations from the most negative value to the most positive value of FE,x.arrow_forwardFor each part make sure to include sign to represent direction, with up being positive and down being negative. A ball is thrown vertically upward with a speed of 30.5 m/s. A) How high does it rise? y= B) How long does it take to reach its highest point? t= C) How long does it take the ball return to its starting point after it reaches its highest point? t= D) What is its velocity when it returns to the level from which it started? v=arrow_forwardFour point charges of equal magnitude Q = 55 nC are placed on the corners of a rectangle of sides D1 = 27 cm and D2 = 11cm. The charges on the left side of the rectangle are positive while the charges on the right side of the rectangle are negative. Use a coordinate system where the positive y-direction is up and the positive x-direction is to the right. A. Which of the following represents a free-body diagram for the charge on the lower left hand corner of the rectangle? B. Calculate the horizontal component of the net force, in newtons, on the charge which lies at the lower left corner of the rectangle.Numeric : A numeric value is expected and not an expression.Fx = __________________________________________NC. Calculate the vertical component of the net force, in newtons, on the charge which lies at the lower left corner of the rectangle.Numeric : A numeric value is expected and not an expression.Fy = __________________________________________ND. Calculate the magnitude of the…arrow_forward
- Point charges q1=50.0μC and q2=-35μC are placed d1=1.0m apart, as shown. A. A third charge, q3=25μC, is positioned somewhere along the line that passes through the first two charges, and the net force on q3 is zero. Which statement best describes the position of this third charge?1) Charge q3 is to the right of charge q2. 2) Charge q3 is between charges q1 and q2. 3) Charge q3 is to the left of charge q1. B. What is the distance, in meters, between charges q1 and q3? (Your response to the previous step may be used to simplify your solution.)Give numeric value.d2 = __________________________________________mC. Select option that correctly describes the change in the net force on charge q3 if the magnitude of its charge is increased.1) The magnitude of the net force on charge q3 would still be zero. 2) The effect depends upon the numeric value of charge q3. 3) The net force on charge q3 would be towards q2. 4) The net force on charge q3 would be towards q1. D. Select option that…arrow_forwardThe magnitude of the force between a pair of point charges is proportional to the product of the magnitudes of their charges and inversely proportional to the square of their separation distance. Four distinct charge-pair arrangements are presented. All charges are multiples of a common positive charge, q. All charge separations are multiples of a common length, L. Rank the four arrangements from smallest to greatest magnitude of the electric force.arrow_forwardA number of electric charges has been placed at distinct points along a line with separations as indicated. Two charges share a common magnitude, q (lower case), and another charge has magnitude Q (upper case). The signs of the charges are indicated explicitly such that ∣∣+q∣∣∣∣+Q∣∣=∣∣−q∣∣==∣∣−Q∣∣=qQ Four different configurations of charges are shown. For each, express the net electric force on the charge with magnitude Q (upper case) as F⃗E=FE,xî where the positive x direction is towards the right. By repositioning the figures to the area on the right, rank the configurations from the most negative value to the most positive value of FE,x.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
A Level Physics – Ideal Gas Equation; Author: Atomi;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=k0EFrmah7h0;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY