
EBK PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEER
9th Edition
ISBN: 8220100581557
Author: Jewett
Publisher: Cengage Learning US
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 18, Problem 18.85AP
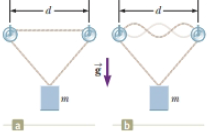
Review. A 12.0-kg object hangs in equilibrium from a string with a total length of L = 5.00 m and a linear mass density of μ = 0.001 00 kg/m. The string is wrapped around two light, frictionless pulleys that are separated by a distance of d = 2.00 m (Fig. P17.47a). (a) Determine the tension in the string. (b) At what frequency must the string between the pulleys vibrate to form the standing-wave pattern shown in Figure P 17.47b?
Figure P17.47 Problem 47 and 48.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
A system consists of a vertical spring with force constant k = 1250 N/m, length L = 1.50 m, and object of mass m = 5.00 kg attached to the end (Fig. P13.76). The object is placed at the level of the point of attachment with the spring unstretched, at position yi = L, and then it is released so that it swings like a pendulum. (a) Write Newton’s second law symbolically for the system as the object passes through its lowest point. (Note that at the lowest point, r = L - yf.) (b) Write the conservation of energy equation symbolically, equating the total mechanical energies at the initial point and lowest point. (c) Find the coordinate position of the lowest point. (d) Will this pendulum’s period be greater or less than the period of a simple pendulum with the same mass m and length L? Explain.
A system consists of a vertical spring with force constant k = 1 250 N/m, length L = 1.50 m, and object of mass m = 5.00 kg attached to the end (Fig. P13.76). The object is placed at the level of the point of attachment with the spring unstretched, at position yi = L, and then it is released so that it swings like a pendulum. (a) Write Newton’s second law symbolically for the system as the object passes through its lowest point. (Note that at the lowest point, r = L − yf.) (b) Write the conservation of energy equation symbolically, equating the total mechanical energies at the initial point and lowest point. (c) Find the coordinate position of the lowest point. (d) Will this pendulum’s period be greater or less than the period of a simple pendulum with the same mass m and length L? Explain.
A 13.0-kg object hangs in equilibrium from a string with a total length of
5.20 m
and a linear mass density of
? = 0.00300 kg/m.
The string is wrapped around two light frictionless pulleys that are separated by a distance of
d = 2.00 m.
udistance d.
(a) Determine the tension in the string.N(b) At what frequency must the string between the pulleys vibrate in order to form the standing-wave pattern shown in Figure b?
Chapter 18 Solutions
EBK PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEER
Ch. 18 - Prob. 18.1QQCh. 18 - Consider the waves in Figure 17.8 to be waves on a...Ch. 18 - When a standing wave is set up on a string fixed...Ch. 18 - Prob. 18.4QQCh. 18 - Balboa Park in San Diego has an outdoor organ....Ch. 18 - In figure OQ18.1 (page 566), a sound wave of...Ch. 18 - A string of length L, mass pet unit length , and...Ch. 18 - In Example 18.1, we investigated an oscillator at...Ch. 18 - Prob. 18.4OQCh. 18 - A flute has a length of 58.0 cm. If the speed of...
Ch. 18 - When two tuning forks are sounded at the same...Ch. 18 - A tuning fork is known to vibrate with frequency...Ch. 18 - An archer shoots an arrow horizontally from the...Ch. 18 - As oppositely moving pulses of the same shape (one...Ch. 18 - Prob. 18.10OQCh. 18 - Suppose all six equal-length strings of an...Ch. 18 - Assume two identical sinusoidal waves are moving...Ch. 18 - Prob. 18.1CQCh. 18 - When two waves interfere constructively or...Ch. 18 - Prob. 18.3CQCh. 18 - What limits the amplitude of motion of a real...Ch. 18 - Prob. 18.5CQCh. 18 - An airplane mechanic notices that the sound from a...Ch. 18 - Despite a reasonably steady hand, a person often...Ch. 18 - Prob. 18.8CQCh. 18 - Does the phenomenon of wave interference apply...Ch. 18 - Two waves are traveling in the same direction...Ch. 18 - Two wave pulses A and B are moving in opposite...Ch. 18 - Two waves on one string are described by the wave...Ch. 18 - Two pulses of different amplitudes approach each...Ch. 18 - A tuning fork generates sound waves with a...Ch. 18 - The acoustical system shown in Figure OQ18.1 is...Ch. 18 - Two pulses traveling on the same string are...Ch. 18 - Two identical loudspeakers are placed on a wall...Ch. 18 - Two traveling sinusoidal waves are described by...Ch. 18 - Why is the following situation impossible? Two...Ch. 18 - Two sinusoidal waves on a string are defined by...Ch. 18 - Two identical sinusoidal waves with wavelengths of...Ch. 18 - Two identical loudspeakers 10.0 m apart are driven...Ch. 18 - Prob. 18.14PCh. 18 - Two sinusoidal waves traveling in opposite...Ch. 18 - Verify by direct substitution that the wave...Ch. 18 - Two transverse sinusoidal waves combining in a...Ch. 18 - A standing wave is described by the wave function...Ch. 18 - Two identical loudspeakers are driven in phase by...Ch. 18 - Prob. 18.20PCh. 18 - A string with a mass m = 8.00 g and a length L =...Ch. 18 - The 64.0-cm-long string of a guitar has a...Ch. 18 - The A string on a cello vibrates in its first...Ch. 18 - A taut string has a length of 2.60 m and is fixed...Ch. 18 - A certain vibrating string on a piano has a length...Ch. 18 - A string that is 30.0 cm long and has a mass per...Ch. 18 - In the arrangement shown in Figure P18.27, an...Ch. 18 - In the arrangement shown in Figure P17.14, an...Ch. 18 - Review. A sphere of mass M = 1.00 kg is supported...Ch. 18 - Review. A sphere of mass M is supported by a...Ch. 18 - Prob. 18.31PCh. 18 - Review. A solid copper object hangs at the bottom...Ch. 18 - Prob. 18.33PCh. 18 - The Bay of Fundy, Nova Scotia, has the highest...Ch. 18 - An earthquake can produce a seiche in a lake in...Ch. 18 - High-frequency sound can be used to produce...Ch. 18 - Prob. 18.37PCh. 18 - Prob. 18.38PCh. 18 - Calculate the length of a pipe that has a...Ch. 18 - The overall length of a piccolo is 32.0 cm. The...Ch. 18 - The fundamental frequency of an open organ pipe...Ch. 18 - Prob. 18.42PCh. 18 - An air column in a glass tube is open at one end...Ch. 18 - Prob. 18.44PCh. 18 - Prob. 18.45PCh. 18 - A shower stall has dimensions 86.0 cm 86.0 cm ...Ch. 18 - Prob. 18.47PCh. 18 - Prob. 18.48PCh. 18 - As shown in Figure P17.27, water is pumped into a...Ch. 18 - As shown in Figure P17.27, water is pumped into a...Ch. 18 - Two adjacent natural frequencies of an organ pipe...Ch. 18 - Why is the following situation impossible? A...Ch. 18 - A student uses an audio oscillator of adjustable...Ch. 18 - An aluminum rod is clamped one-fourth of the way...Ch. 18 - Prob. 18.55PCh. 18 - Prob. 18.56PCh. 18 - In certain ranges of a piano keyboard, more than...Ch. 18 - Prob. 18.58PCh. 18 - Review. A student holds a tuning fork oscillating...Ch. 18 - An A-major chord consists of the notes called A,...Ch. 18 - Suppose a flutist plays a 523-Hz C note with first...Ch. 18 - A pipe open at both ends has a fundamental...Ch. 18 - Prob. 18.63APCh. 18 - Two strings are vibrating at the same frequency of...Ch. 18 - Prob. 18.65APCh. 18 - A 2.00-m-long wire having a mass of 0.100 kg is...Ch. 18 - The fret closest to the bridge on a guitar is 21.4...Ch. 18 - Prob. 18.68APCh. 18 - A quartz watch contains a crystal oscillator in...Ch. 18 - Review. For the arrangement shown in Figure...Ch. 18 - Prob. 18.71APCh. 18 - Two speakers are driven by the same oscillator of...Ch. 18 - Review. Consider the apparatus shown in Figure...Ch. 18 - Review. The top end of a yo-yo string is held...Ch. 18 - On a marimba (Fig. P18.75), the wooden bar that...Ch. 18 - A nylon siring has mass 5.50 g and length L = 86.0...Ch. 18 - Two train whistles have identical frequencies of...Ch. 18 - Review. A loudspeaker at the front of a room and...Ch. 18 - Prob. 18.79APCh. 18 - Prob. 18.80APCh. 18 - Prob. 18.81APCh. 18 - A standing wave is set up in a string of variable...Ch. 18 - Two waves are described by the wave functions...Ch. 18 - Prob. 18.84APCh. 18 - Review. A 12.0-kg object hangs in equilibrium from...Ch. 18 - Review. An object of mass m hangs in equilibrium...Ch. 18 - Review. Consider the apparatus shown in Figure...Ch. 18 - Prob. 18.88CP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- An object of mass m1 = 9.00 kg is in equilibrium when connected to a light spring of constant k = 100 N/m that is fastened to a wall as shown in Figure P12.67a. A second object, m2 = 7.00 kg, is slowly pushed up against m1, compressing the spring by the amount A = 0.200 m (see Fig. P12.67b). The system is then released, and both objects start moving to the right on the frictionless surface. (a) When m1 reaches the equilibrium point, m2 loses contact with m1 (see Fig. P12.67c) and moves to the right with speed v. Determine the value of v. (b) How far apart are the objects when the spring is fully stretched for the first time (the distance D in Fig. P12.67d)? Figure P12.67arrow_forwardReview. A system consists of a spring with force constant k = 1 250 N/m, length L = 1.50 m, and an object of mass m = 5.00 kg attached to the end (Fig. P15.49). The object is placed at the level of the point of attachment with the spring unstretched, at position yi = L, and then it is released so that it swings like a pendulum. (a) Find the y position of the object at the lowest point. (b) Will the pendulums period be greater or less than the period of a simple pendulum with the same mass m and length L? Explain. Figure PI 5.49arrow_forwardA nylon string has mass 5.50 g and length L = 86.0 cm. The lower end is tied to the floor, and the upper end is tied to a small set of wheels through a slot in a track on which the wheels move (Fig. P14.56). The wheels have a mass that is negligible compared with that of the string, and they roll without friction on the track so that the upper end of the string is essentially free. At equilibrium, the string is vertical and motionless. When it is carrying a small-amplitude wave, you may assume the string is always under uniform tension 1.30 N. (a) Find the speed of transverse waves on the string. (b) The strings vibration possibilities are a set of standing-wave states, each with a node at the fixed bottom end and an anti-node at the free top end. Find the nodeantinode distances for each of the three simplest states. (c) Find the frequency of each of these states. Figure P14.56arrow_forward
- A lightweight spring with spring constant k = 225 N/m is attached to a block of mass m1 = 4.50 kg on a frictionless, horizontal table. The blockspring system is initially in the equilibrium configuration. A second block of mass m2 = 3.00 kg is then pushed against the first block, compressing the spring by x = 15.0 cm as in Figure P16.77A. When the force on the second block is removed, the spring pushes both blocks to the right. The block m2 loses contact with the springblock 1 system when the blocks reach the equilibrium configuration of the spring (Fig. P16.77B). a. What is the subsequent speed of block 2? b. Compare the speed of block 1 when it again passes through the equilibrium position with the speed of block 2 found in part (a). 77. (a) The energy of the system initially is entirely potential energy. E0=U0=12kymax2=12(225N/m)(0.150m)2=2.53J At the equilibrium position, the total energy is the total kinetic energy of both blocks: 12(m1+m2)v2=12(4.50kg+3.00kg)v2=(3.75kg)v2=2.53J Therefore, the speed of each block is v=2.53J3.75kg=0.822m/s (b) Once the second block loses contact, the first block is moving at the speed found in part (a) at the equilibrium position. The energy 01 this spring-block 1 system is conserved, so when it returns to the equilibrium position, it will be traveling at the same speed in the opposite direction, or v=0.822m/s. FIGURE P16.77arrow_forwardReview. For the arrangement shown in Figure P14.60, the inclined plane and the small pulley are frictionless; the string supports the object of mass M at the bottom of the plane; and the string has mass m. The system is in equilibrium, and the vertical part of the string has a length h. We wish to study standing waves set up in the vertical section of the string. (a) What analysis model describes the object of mass M? (b) What analysis model describes the waves on the vertical part of the string? (c) Find the tension in the string. (d) Model the shape of the string as one leg and the hypotenuse of a right triangle. Find the whole length of the string. (e) Find the mass per unit length of the string. (f) Find the speed of waves on the string. (g) Find the lowest frequency for a standing wave on the vertical section of the string. (h) Evaluate this result for M = 1.50 kg, m = 0.750 g, h = 0.500 m, and θ = 30.0°. (i) Find the numerical value for the lowest frequency for a standing wave on the sloped section of the string. Figure P14.60arrow_forwardA spherical bob of mass m and radius R is suspended from a fixed point by a rigid rod of negligible mass whose length from the point of support to the center of the bob is L (Fig. P16.75). Find the period of small oscillation. N The frequency of a physical pendulum comprising a nonuniform rod of mass 1.25 kg pivoted at one end is observed to be 0.667 Hz. The center of mass of the rod is 40.0 cm below the pivot point. What is the rotational inertia of the pendulum around its pivot point?arrow_forward
- As shown in Figure P14.37, water is pumped into a tall, vertical cylinder at a volume flow rate R. The radius of the cylinder is r, and at the open top of the cylinder a tuning fork is vibrating with a frequency f. As the water rises, what time interval elapses between successive resonances? Figure P14.37 Problems 37 and 38.arrow_forwardA block of mass m rests on a frictionless, horizontal surface and is attached to two springs with spring constants k1 and k2 (Fig. P16.22). It is displaced to the right and released. Find an expression for the angular frequency of oscillation of the resulting simple harmonic motion. FIGURE P16.22 Problems 22 and 81.arrow_forwardP13.195 A 500 g block is released from rest after a spring of constant k=800 N/m has been compressed 200 mm. Determine the force exerted by the loop ABCD on the block as the block passes through (a) point A, (b) point B, (c) point C. Assume no friction. B 600 mm сarrow_forward
- A steel propeller shaft is to transmit 4.5 MW at 3 Hz without exceeding a sheering stress of 50 MPa or twisting through more than 1 degree in a length of 26 diameter (G= 83 GPa) A. Find the maximum torque applied in the steel propeller shaft? B. What is the proper diameter for the steel shaft?arrow_forwardA homogeneous rod with a length of L = 1 m and a mass of m = 0.5 kg is fixed in the middle so that it can rotate. Two springs with a constant k = 12 N / m are connected at both ends of the rod. The other ends of the bow are fixed and the springs are unstretched. The rod is rotated from its equilibrium position to Ɵ << and released. What is the angular frequency of the rod (rad / s)? g = 10 m / s2arrow_forwardA block of mass m = 2.00 kg is attached to a spring of force constant k = 5.00 × 102 N/m that lies on a horizontal frictionless surface as shown in Figure P13.8. The block is pulled to a position xi = 5.00 cm to the right of equilibrium and released from rest. Find (a) the work required to stretch the spring and (b) the speed the block has as it passes through equilibrium.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Wave Speed on a String - Tension Force, Intensity, Power, Amplitude, Frequency - Inverse Square Law; Author: The Organic Chemistry Tutor;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vEzftaDL7fM;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Vibrations of Stretched String; Author: PhysicsPlus;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BgINQpfqJ04;License: Standard Youtube License