
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The concentration of acid has to be explained before and after dissociation of a concentrated solution of a strong acid.
Concept introduction:
Increasing acid strength:
Acids strength is mainly depending on the dissociation of ions, strong acids dissociates completely and weak acid dissociate slightly.
The acid strength is depending on the
Conjugate acid-Base pairs:
The acid donates the proton to form its conjugate base and the base accepts a proton to form its conjugate acid.
When an acid is dissolved in water, the acid
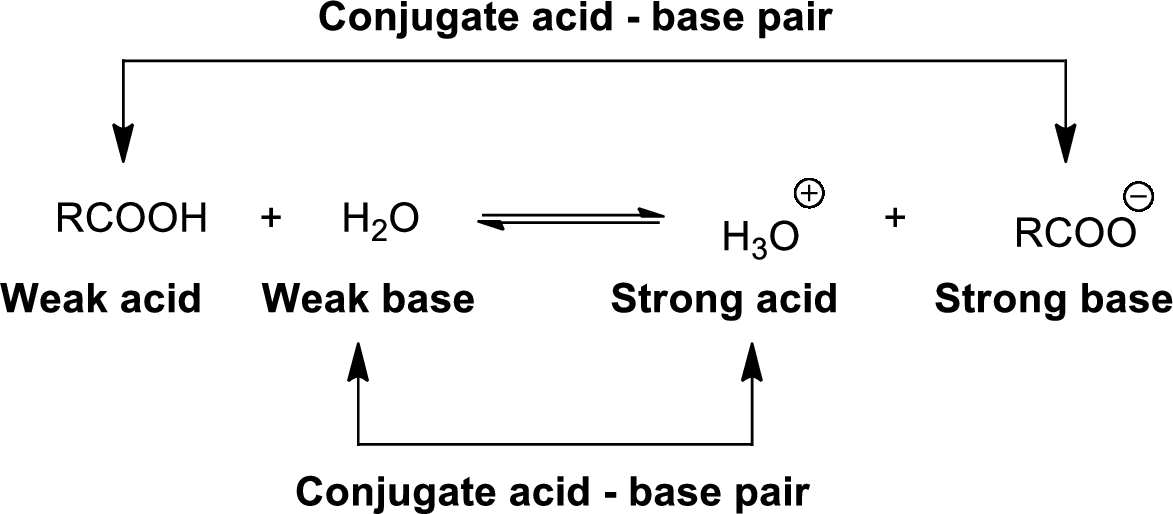
The pair of an Acid –Base differs by a proton called conjugated Acid-Base pair.
(b)
Interpretation:
The concentration of acid has to be explained before and after dissociation of a concentrated solution of a weak acid.
Concept introduction:
Increasing acid strength:
Acids strength is mainly depending on the dissociation of ions, strong acids dissociate completely and weak acid dissociate slightly.
The acid strength is depending on the
Conjugate acid-Base pairs:
The acid donates the proton to form its conjugate base and the base accepts a proton to form its conjugate acid.
When an acid is dissolved in water, the acid
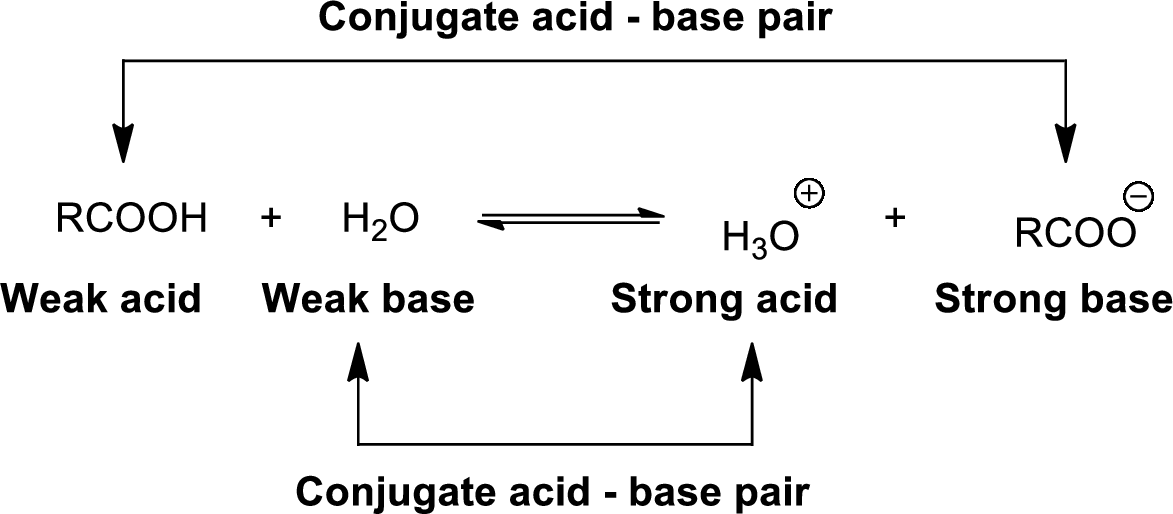
The pair of an Acid –Base differs by a proton called conjugated Acid-Base pair.
(c)
Interpretation:
The concentration of acid has to be explained before and after dissociation of a diluted solution of a weak acid.
Concept introduction:
Increasing acid strength:
Acids strength is mainly depending on the dissociation of ions, strong acids dissociates completely and weak acid dissociate slightly.
The acid strength is depending on the
Conjugate acid-Base pairs:
The acid donates the proton to form its conjugate base and the base accepts a proton to form its conjugate acid.
When an acid is dissolved in water, the acid
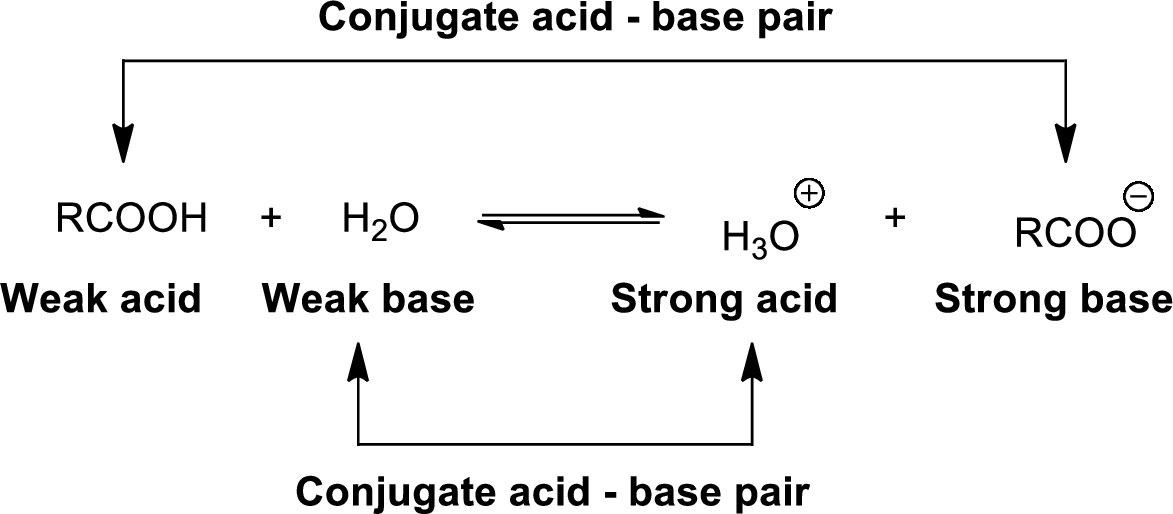
The pair of an Acid –Base differs by a proton called conjugated Acid-Base pair.
(d)
Interpretation:
The concentration of acid has to be explained before and after dissociation of a diluted solution of a strong acid.
Concept introduction:
Increasing acid strength:
Acids strength is mainly depending on the dissociation of ions, strong acids dissociates completely and weak acid dissociate slightly.
The acid strength is depending on the
Conjugate acid-Base pairs:
The acid donates the proton to form its conjugate base and the base accepts a proton to form its conjugate acid.
When an acid is dissolved in water, the acid
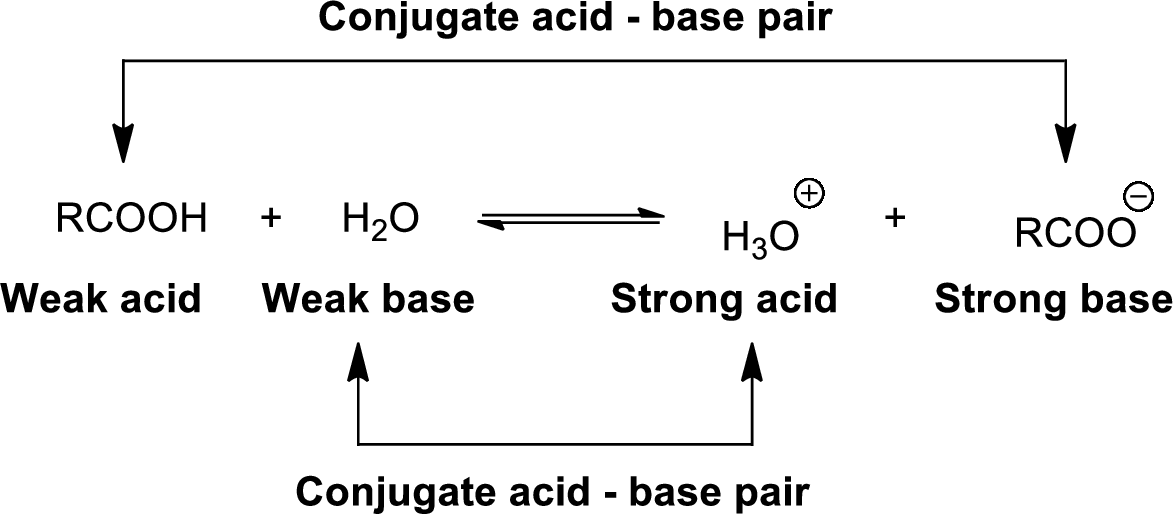
The pair of an Acid –Base differs by a proton called conjugated Acid-Base pair.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 18 Solutions
CHEMISTRY >CUSTOM<
- Determine if the following salt is neutral, acidic or basic. If acidic or basic, write the appropriate equilibrium equation for the acid or base that exists when the salt is dissolved in aqueous solution. If neutral, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction LiNO3arrow_forwardAn unknown weak acid with a concentration of 0.410 M has a pH of 5.600. What is the Ka of the weak acid?arrow_forward(racemic) 19.84 Using your reaction roadmaps as a guide, show how to convert 2-oxepanone and ethanol into 1-cyclopentenecarbaldehyde. You must use 2-oxepanone as the source of all carbon atoms in the target molecule. Show all reagents and all molecules synthesized along the way. & + EtOH H 2-Oxepanone 1-Cyclopentenecarbaldehydearrow_forward
- R₂ R₁ R₁ a R Rg Nu R₂ Rg R₁ R R₁₂ R3 R R Nu enolate forming R₁ R B-Alkylated carbonyl species or amines Cyclic B-Ketoester R₁₁ HOB R R₁B R R₁₂ B-Hydroxy carbonyl R diester R2 R3 R₁ RB OR R₂ 0 aB-Unsaturated carbonyl NaOR Aldol HOR reaction 1) LDA 2) R-X 3) H₂O/H₂O ketone, aldehyde 1) 2°-amine 2) acid chloride 3) H₂O'/H₂O 0 O R₁ R₁ R R₁ R₁₂ Alkylated a-carbon R₁ H.C R₁ H.C Alkylated methyl ketone acetoacetic ester B-Ketoester ester R₁ HO R₂ R B-Dicarbonyl HO Alkylated carboxylic acid malonic ester Write the reagents required to bring about each reaction next to the arrows shown. Next, record any regiochemistry or stereochemistry considerations relevant to the reaction. You should also record any key aspects of the mechanism, such as forma- tion of an important intermediate, as a helpful reminder. You may want to keep track of all reactions that make carbon-carbon bonds, because these help you build large molecules from smaller fragments. This especially applies to the reactions in…arrow_forwardProvide the reasonable steps to achieve the following synthesis.arrow_forwardIdentify which compound is more acidic. Justify your choice.arrow_forward
- Provide the reasonable steps to achieve the following synthesis.arrow_forwardWhen anisole is treated with excess bromine, the reaction gives a product which shows two singlets in 1H NMR. Draw the product.arrow_forward(ii) Draw a reasonable mechanism for the following reaction: CI NaOH heat OH (hint: SNAr Reaction) :arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





