
Concept explainers
Weighted-average method, assigning costs (continuation of 18-21).
Required
For the data in Exercise 18-21, summarize the total costs to account for; calculate the cost per equivalent unit for direct materials and conversion costs; and assign costs to units completed and transferred out (including normal spoilage), to abnormal spoilage, and to units in ending work-in-process inventory.
18-21 Weighted-average method, spoilage, equivalent units. (CMA, adapted) Consider the following data for November 2017 from MacLean Manufacturing Company, which makes silk pennants and uses a process-costing system. All direct materials are added at the beginning of the process, and conversion costs are added evenly during the process. Spoilage is detected upon inspection at the completion of the process. Spoiled units are disposed of at zero net disposal value. MacLean Manufacturing Company uses the weighted-average method of
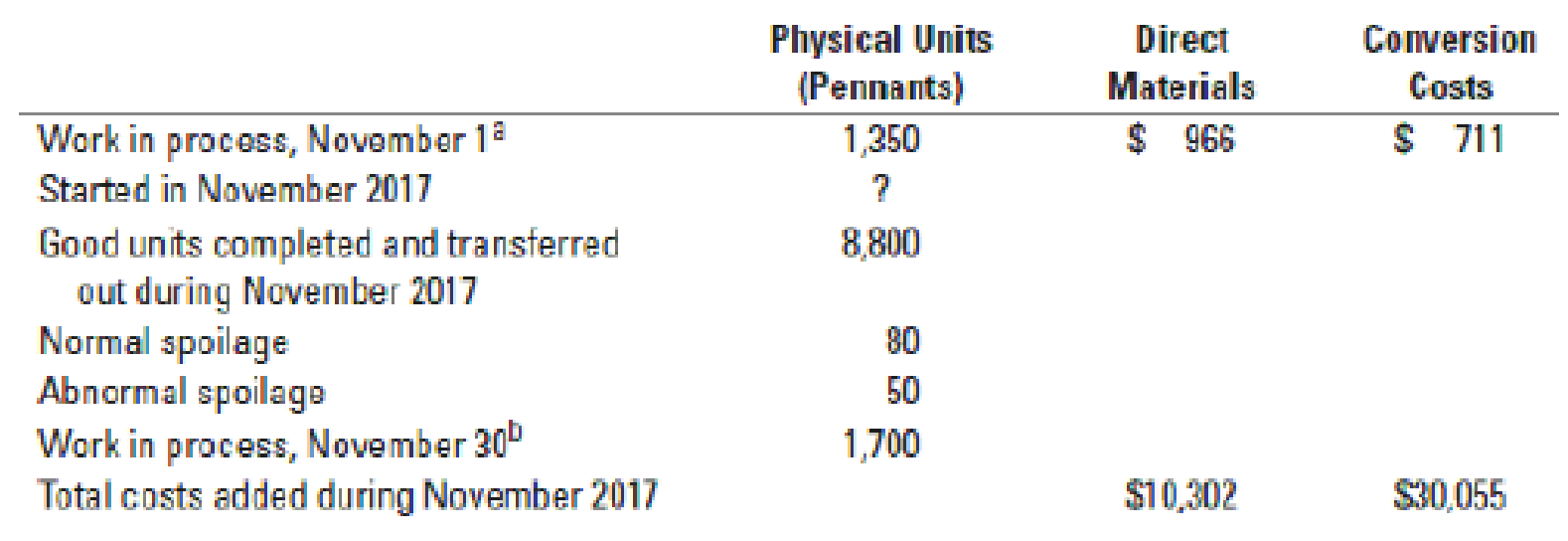
a Degree of completion: direct materials, 100%; conversion costs, 45%.
b Degree of completion: direct materials, 100%; conversion costs, 35%.
Required
Compute equivalent units for direct materials and conversion costs. Show physical units in the first column of your schedule.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

Chapter 18 Solutions
Horngren's Cost Accounting, Student Value Edition Plus MyLab Accounting with Pearson eText - Access Card Package (16th Edition)
Additional Business Textbook Solutions
Accounting Information Systems (14th Edition)
Foundations Of Finance
Principles of Operations Management: Sustainability and Supply Chain Management (10th Edition)
MARKETING:REAL PEOPLE,REAL CHOICES
Horngren's Accounting (12th Edition)
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis (16th Edition)
- As of July 1, 2022, the investee had assets with a book value of $3 million and liabilities of $74,400. At the time, Carter held equipment appraised at $364,000 more than book value; it was considered to have a seven-year remaining life with no salvage value. Carter also held a copyright with a five-year remaining life on its books that was undervalued by $972,000. Any remaining excess cost was attributable to an indefinite-lived trademark. Depreciation and amortization are computed using the straight-line method. Burrough applies the equity method for its investment in Carter. Carter's policy is to declare and pay a $1 per share cash dividend every April 1 and October 1. Carter's income, earned evenly throughout each year, was $598,000 in 2022, $639,600 in 2023, and $692,400 in 2024. In addition, Burrough sold inventory costing $91,200 to Carter for $152,000 during 2023. Carter resold $92,000 of this inventory during 2023 and the remaining $60,000 during 2024. Required: a. Determine…arrow_forwardFinancial Accountingarrow_forwardA company has an annual demand for.... please answer the financial accounting questionarrow_forward
- On July 1, 2022, Burrough Company acquired 88,000 of the outstanding shares of Carter Company for $13 per share. This acquisition gave Burrough a 25 percent ownership of Carter and allowed Burrough to significantly influence the investee's decisions. As of July 1, 2022, the investee had assets with a book value of $3 million and liabilities of $74,400. At the time, Carter held equipment appraised at $364,000 more than book value; it was considered to have a seven-year remaining life with no salvage value. Carter also held a copyright with a five-year remaining life on its books that was undervalued by $972,000. Any remaining excess cost was attributable to an indefinite-lived trademark. Depreciation and amortization are computed using the straight-line method. Burrough applies the equity method for its investment in Carter. Carter's policy is to declare and pay a $1 per share cash dividend every April 1 and October 1. Carter's income, earned evenly throughout each year, was $598,000 in…arrow_forwardCompute the materials variances on these financial accounting questionarrow_forwardSolve this general accounting questionarrow_forward
 Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College


