
FIFO method, spoilage, equivalent units. Refer to the information in Exercise 18-21. Suppose MacLean Manufacturing Company uses the FIFO method of
18-21 Weighted-average method, spoilage, equivalent units. (CMA, adapted) Consider the following data for November 2017 from MacLean Manufacturing Company, which makes silk pennants and uses a process-costing system. All direct materials are added at the beginning of the process, and conversion costs are added evenly during the process. Spoilage is detected upon inspection at the completion of the process. Spoiled units are disposed of at zero net disposal value. MacLean Manufacturing Company uses the weighted-average method of process costing.
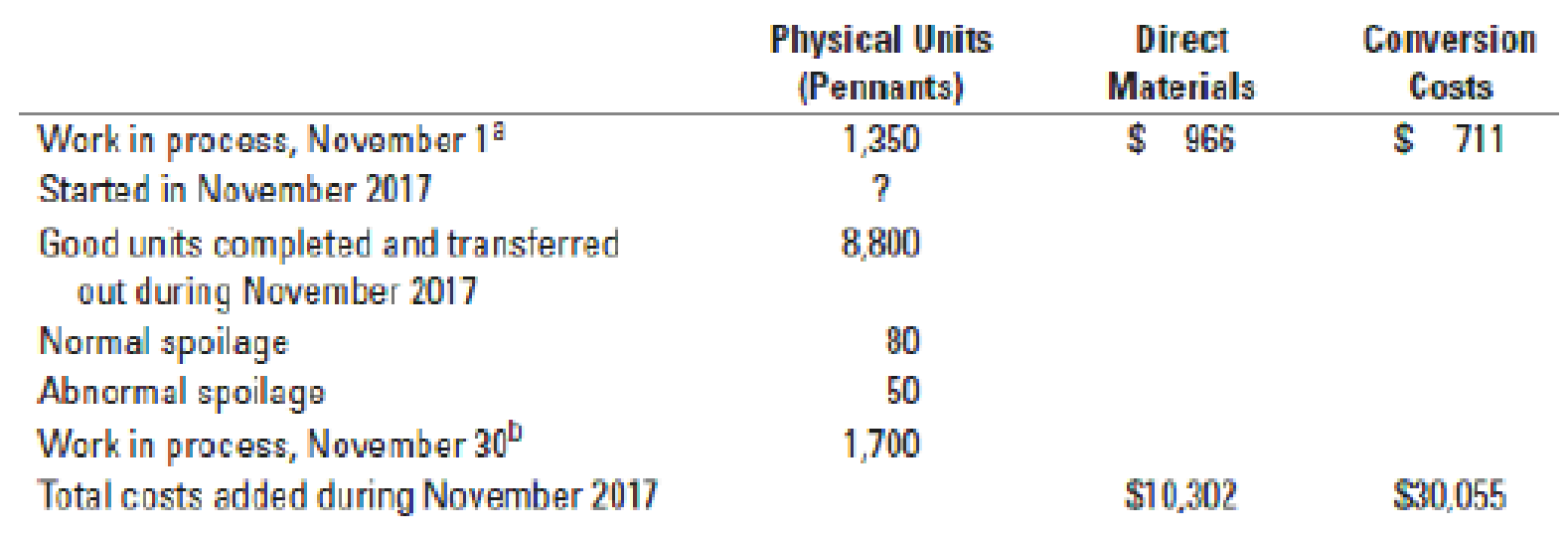
a Degree of completion: direct materials, 100%; conversion costs, 45%.
b Degree of completion: direct materials, 100%; conversion costs, 35%.
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

Chapter 18 Solutions
Horngren's Cost Accounting, Student Value Edition Plus MyLab Accounting with Pearson eText - Access Card Package (16th Edition)
Additional Business Textbook Solutions
Financial Accounting, Student Value Edition (4th Edition)
Horngren's Financial & Managerial Accounting, The Managerial Chapters (6th Edition)
Managerial Accounting (5th Edition)
Construction Accounting And Financial Management (4th Edition)
Intermediate Accounting (2nd Edition)
Horngren's Accounting (12th Edition)
- The assembly division of Fenton Watches, Inc. uses the FIFO method of process costing. Consider the following data for May 2020: (Click the icon to view the data.) (Click the icon to view the equivalent unit computation.) Requirement Summarize total costs to account for, calculate cost per equivalent unit for direct materials and conversion costs, and assign costs to units completed (and transferred out) and to units in ending work-in-process inventory. Begin by summarizing total costs to account for. Total costs to account for Total CH Production Costs Direct Materials Conversion Costsarrow_forwardThe assembly division of Gannett Watches,Inc. uses the FIFO method of process costing. Consider the following data for the month of May 2017: the icon to view the equivalent unit computation.) Requirement Summarize the total costs to account for, calculate the cost per equivalent unit for direct materials and conversion costs, and assign costs to units completed (and transferred out) and to units in ending work in process. Begin by summarizing the total costs to account for. Total Direct Conversion Production Costs Materials Costs (1) (2) Total costs to account for Next, calculate cost per equivalent unit for direct materials and conversion costs. Direct Conversion Materials Costs (3) Divide by (4) Cost per equivalent unit Finally, assign total costs to units…arrow_forwarduse the FIFO method to summarize the total costs to account for; calculate the cost per equivalent unit for direct materials and conversion costs; and assign costs to units completed and transferred out (including normal spoilage), to abnormal spoilage, and to units in ending work in process.arrow_forward
- Please refer to the pictures for parts A and B. Part C is below: Cost assignment—Weighted average EUP Cost per EUP Total cost Completed and transferred out Direct materials Conversion Total Completed and transferred out Ending work in process Direct materials Conversion Total ending work in process Total costs accounted for HI-T Company.arrow_forwardConsider the following data for the assembly division of Stiles Watches Company: The assembly division uses the weighted-average method of process costing. (Click the icon to view the data) Requirement Summarise total costs to account for calculate cost per equivalent unit for direct materials and conversion costs, and assign total costs to units completed (and transferred out) and to units in ending work-in-process. Begin by summarising the total costs to account for. (Complete the necessary drop downs. Fill in the relevant cells with its corresponding figures) Total Direct Materials Conversion Costs Production Costs Total costs to account for Data table Beginning work-in-process (1 May) Started in May, this year Completed during May, this year Ending work-in-process (31 May) Total costs added during May, this year (Click the icon to view the equivalent unit computation.) Physical Units (Watches) 100 525 480 145 "Degree of completion direct materials, 90%; conversion costs, 40% Degree…arrow_forward[The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Victory Company uses weighted average process costing. The company has two production processes. Conversion cost is added evenly throughout each process. Direct materials are added at the beginning of the first process. Additional information for the first process follows. Beginning work in process inventory Units started this period Units completed and transferred out Ending work in process inventory. Beginning work in process inventory. Direct materials Conversion Costs added this period Direct materials Conversion Total costs to account for Cost per equivalent unit of production Units Total costs + Equivalent units of production (from part 1) Cost per equivalent unit of production 78,000 876,000 760,000 194,000 $ 496,080 87,640 3,319,920 1,665, 160 Direct Materials. Percent Complete 100% 100% 2. Compute cost per equivalent unit of production for both direct materials and conversion. Costs EUP $ 583,7: 4,985,0…arrow_forward
- please, look at image.arrow_forwardClassic Clothing, Inc., is a manufacturer of winter clothes. It has a knitting department and a finishing department. This exercise focuses on the finishing department. Direct materials are added at the end of the process. Conversion costs are added evenly during the process. Classic uses the weighted-average method of process costing. The following information for June 2017 is available. Read the requirements2. Requirement 1. Calculate equivalent units of transferred-in costs, direct materials, and conversion costs. (Enter a "0" for any zero balances.) Equivalent Units Physical Units Transferred-In Direct Conversion (tons) Costs Materials Costs Work in process, beginning inventory (June 1) 100 Transferred in during June 165 To account for Completed and transferred out during June 200 Work in process, ending inventory (June 30) 65…arrow_forwardI couldn't attached the full thing but the picture contains parts A and B. Please refer to part C below. Cost assignment—Weighted average EUP Cost per EUP Total cost Completed and transferred out Direct materials Conversion Total Completed and transferred out Ending work in process Direct materials Conversion Total ending work in process Total costs accounted forarrow_forward
- The assembly division of Quality Time Pieces, Inc. uses the weighted-average method of process costing. Consider the following data for May 2020: (Click the icon to view the data.) Requirement Compute equivalent units for direct materials and conversion costs. Show physical units in the first column of your schedule. Enter the physical units first, then calculate the equivalent units. Flow of Production Work in process beginning Started during current period To account for Completed and transferred out during current period Work in process, ending Accounted for Equivalent units of work done to date Physical Units Data table Beginning work in process (May 1)ª Started in May 2020 Completed during May 2020 Ending work in process (May 31) Total costs added during May 2020 Physical Units Direct (Watches) Materials 100 $459,888 Print 510 450 160 $3,237,000 aDegree of completion: direct materials, 80%; conversion costs, 35%. bDegree of completion: direct materials, 80%; conversion costs, 40%.…arrow_forwardAlpesharrow_forwardCentral Perk, LLC, a manufacturer of coffee beans, is considering switching its operations to an Activity Based Costing system. The following manufacturing overhead activities and cost drivers have been identified: Activity. Machine setup Machine assembly Product inspection Product movement General factory Cost Driver Number of machine setups Machine hours logged Inspection hours logged Number of moves Machine hours logged Based on the above descriptions, which of the following correctly pairs the activity with its appropriate cost level? O A. Product Inspection... batch level cost OB. Product Movement... facility level cost O C. Machine Assembly... unit level cost O D. General Factory... batch level cost O E. Machine Setup... unit level costarrow_forward
 Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning
Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning

