
Chemistry and Chemical Reactivity - AP Edition
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781337399203
Author: Kotz
Publisher: CENGAGE L
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 18, Problem 105SCQ
The Haber-Bosch process for the production of ammonia is one of the key industrial processes in developed countries.
N2(g) + 3H2(g) ⇄ 2NH3(g)
(a) Calculate ΔrG° for the reaction at 298 K, 800 K, and 1300 K. Data at 298 K are given in Appendix L Data for the other temperatures are as follows:
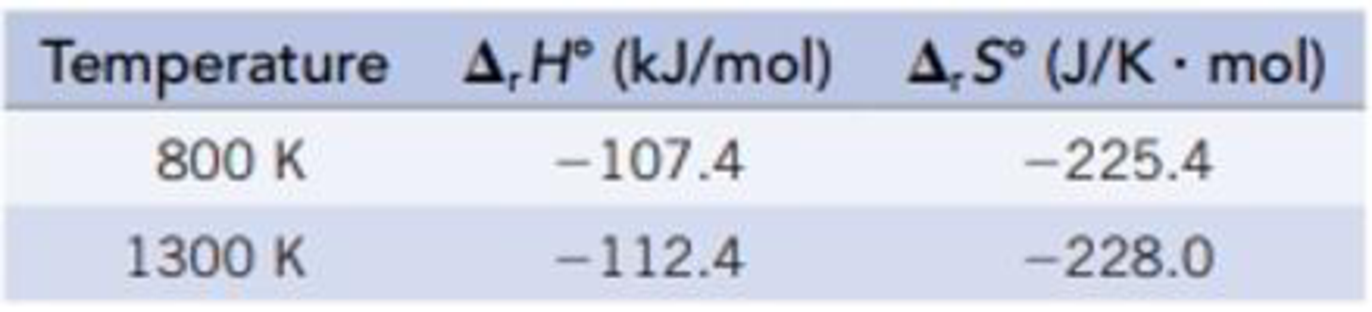
How does the ΔrG° change with temperature?
(b) Calculate the equilibrium constant for the reaction at 298 K, 800 K, and 1300 K.
(c) At what temperature (298 K, 800 K, or 1300 K) is the mole fraction of NH3 the greatest?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
There is an instrument in Johnson 334 that measures total-reflectance x-ray fluorescence (TXRF) to do elemental analysis (i.e., determine what elements are present in a sample). A researcher is preparing a to measure calcium content in a series of well water samples by TXRF with an internal standard of vanadium (atomic symbol: V). She has prepared a series of standard solutions to ensure a linear instrument response over the expected Ca concentration range of 40-80 ppm. The concentrations of Ca and V (ppm) and the instrument response (peak area, arbitrary units) are shown below. Also included is a sample spectrum. Equation 1 describes the response factor, K, relating the analyte signal (SA) and the standard signal (SIS) to their respective concentrations (CA and CIS).
Ca, ppm
V, ppm
SCa, arb. units
SV, arb. units
20.0
10.0
14375.11
14261.02
40.0
10.0
36182.15
17997.10
60.0
10.0
39275.74
12988.01
80.0
10.0
57530.75
14268.54
100.0…
A mixture of 0.568 M H₂O, 0.438 M Cl₂O, and 0.710 M HClO are enclosed in a vessel at 25 °C.
H₂O(g) + C₁₂O(g) = 2 HOCl(g)
K = 0.0900 at 25°C
с
Calculate the equilibrium concentrations of each gas at 25 °C.
[H₂O]=
[C₁₂O]=
[HOCI]=
M
Σ
M
What units (if any) does the response factor (K) have? Does the response factor (K) depend upon how the concentration is expressed (e.g. molarity, ppm, ppb, etc.)?
Chapter 18 Solutions
Chemistry and Chemical Reactivity - AP Edition
Ch. 18.3 - Predict which substance in each pair has the...Ch. 18.3 - Prob. 18.2CYUCh. 18.4 - Based on rH and rS, predict the spontaneity of the...Ch. 18.6 - Prob. 18.4CYUCh. 18.6 - Prob. 18.5CYUCh. 18.6 - Oxygen was first prepared by Joseph Priestley...Ch. 18.6 - Prob. 18.7CYUCh. 18.6 - Prob. 18.8CYUCh. 18.6 - Prob. 18.9CYUCh. 18.7 - Consider the hydrolysis reactions of creatine...
Ch. 18.7 - Prob. 1.2ACPCh. 18.7 - The decomposition of diamond to graphite...Ch. 18.7 - It has been demonstrated that buckminsterfullerene...Ch. 18 - Solid NH4NO3 is placed in a beaker containing...Ch. 18 - Acetic acid, a weak acid, was added to a beaker...Ch. 18 - Identify the following processes as either...Ch. 18 - Identify the following processes as either...Ch. 18 - Prob. 5PSCh. 18 - Predict whether each of the following processes...Ch. 18 - Indicate which of the following processes are...Ch. 18 - Prob. 8PSCh. 18 - Prob. 9PSCh. 18 - Prob. 10PSCh. 18 - Prob. 11PSCh. 18 - Calculate the entropy change that occurs when 1.00...Ch. 18 - Prob. 13PSCh. 18 - Calculate the change in entropy of a system with...Ch. 18 - The third law of thermodynamics says that a...Ch. 18 - Identify trends in S values: (a) For the halogens:...Ch. 18 - Which substance has the higher entropy? (a) dry...Ch. 18 - Which substance has the higher entropy? (a) a...Ch. 18 - Use S values to calculate the standard entropy...Ch. 18 - Use S values to calculate the standard entropy...Ch. 18 - Calculate the standard entropy change for the...Ch. 18 - Calculate the standard entropy change for the...Ch. 18 - Calculate the standard entropy change for the...Ch. 18 - Calculate the standard entropy change for the...Ch. 18 - Is the reaction Si(s) + 2 Cl2(g) SiCl4(g)...Ch. 18 - Is the reaction Si(s) + 2 H2(g) SiH4(g)...Ch. 18 - Calculate S(universe) for the decomposition of 1...Ch. 18 - Calculate S(universe) for the formation of 1 mol...Ch. 18 - Classify each of the reactions according to one of...Ch. 18 - Classify each of the reactions according to one of...Ch. 18 - Using values of fH and S, calculate rG for each of...Ch. 18 - Using values of fH and S, calculate rG for each of...Ch. 18 - Using values of fH and S, calculate the standard...Ch. 18 - Using values of fH and S, calculate the standard...Ch. 18 - Using values of fG, calculate rG for each of the...Ch. 18 - Using values of fG, calculate rG for each of the...Ch. 18 - For the reaction BaCO3(s) BaO(s) + CO2(g), rG =...Ch. 18 - For the reaction TiCl2(s) + Cl2(g) TiCl4(), rG =...Ch. 18 - Determine whether the reactions listed below are...Ch. 18 - Determine whether the reactions listed below are...Ch. 18 - Heating some metal carbonates, among them...Ch. 18 - Calculate rH and rS for the reaction of tin(IV)...Ch. 18 - The ionization constant, Ka, for acetic acid is...Ch. 18 - Prob. 44PSCh. 18 - The standard free energy change, rG, for the...Ch. 18 - Prob. 46PSCh. 18 - Calculate rG at 25 C for the formation of 1.00 mol...Ch. 18 - Prob. 48PSCh. 18 - Prob. 49PSCh. 18 - Prob. 50PSCh. 18 - Compare the compounds in each set below and decide...Ch. 18 - Using standard entropy values, calculate rS for...Ch. 18 - About 5 billion kilograms of benzene, C6H6, are...Ch. 18 - Hydrogenation, the addition of hydrogen to an...Ch. 18 - Is the combustion of ethane, C2H6, product-favored...Ch. 18 - Prob. 56GQCh. 18 - When vapors from hydrochloric acid and aqueous...Ch. 18 - Calculate S(system), S(surroundings), and...Ch. 18 - Methanol is now widely used as a fuel in race...Ch. 18 - The enthalpy of vaporization of liquid diethyl...Ch. 18 - Calculate the entropy change, rS, for the...Ch. 18 - Using thermodynamic data, estimate the normal...Ch. 18 - Prob. 63GQCh. 18 - When calcium carbonate is heated strongly, CO2 gas...Ch. 18 - Sodium reacts violently with water according to...Ch. 18 - Yeast can produce ethanol by the fermentation of...Ch. 18 - Elemental boron, in the form of thin fibers, can...Ch. 18 - Prob. 68GQCh. 18 - Prob. 69GQCh. 18 - Estimate the boiling point of water in Denver,...Ch. 18 - The equilibrium constant for the butane ...Ch. 18 - A crucial reaction for the production of synthetic...Ch. 18 - Calculate rG for the decomposition of sulfur...Ch. 18 - Prob. 74GQCh. 18 - A cave in Mexico was recently discovered to have...Ch. 18 - Wet limestone is used to scrub SO2 gas from the...Ch. 18 - Sulfur undergoes a phase transition between 80 and...Ch. 18 - Calculate the entropy change for dissolving HCl...Ch. 18 - Some metal oxides can be decomposed to the metal...Ch. 18 - Prob. 80ILCh. 18 - Prob. 81ILCh. 18 - Prob. 82ILCh. 18 - Titanium(IV) oxide is converted to titanium...Ch. 18 - Cisplatin [cis-diamminedichloroplatinum(II)] is a...Ch. 18 - Prob. 85ILCh. 18 - Explain why each of the following statements is...Ch. 18 - Decide whether each of the following statements is...Ch. 18 - Under what conditions is the entropy of a pure...Ch. 18 - Prob. 89SCQCh. 18 - Consider the formation of NO(g) from its elements....Ch. 18 - Prob. 91SCQCh. 18 - The normal melting point of benzene, C6H6, is 5.5...Ch. 18 - Prob. 93SCQCh. 18 - For each of the following processes, predict the...Ch. 18 - Heater Meals are food packages that contain their...Ch. 18 - Prob. 96SCQCh. 18 - Prob. 97SCQCh. 18 - Prob. 98SCQCh. 18 - Iodine, I2, dissolves readily in carbon...Ch. 18 - Prob. 100SCQCh. 18 - Prob. 101SCQCh. 18 - Prob. 102SCQCh. 18 - Prob. 103SCQCh. 18 - Prob. 104SCQCh. 18 - The Haber-Bosch process for the production of...Ch. 18 - Prob. 106SCQCh. 18 - Prob. 107SCQ
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Provide the structure, circle or draw, of the monomeric unit found in the biological polymeric materials given below. HO OH amylose OH OH 행 3 HO cellulose OH OH OH Ho HOarrow_forwardWhat units (if any) does K have? Does K depend upon how the concentration is expressed (e.g. molarity, ppm, ppb, etc.)? in calculating the response factorarrow_forwardDon't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forward
- Don't used Ai solution and don't used hand raitingarrow_forwardOA. For the structure shown, rank the bond lengths (labeled a, b and c) from shortest to longest. Place your answer in the box. Only the answer in the box will be graded. (2 points) H -CH3 THe b Нarrow_forwardDon't used hand raitingarrow_forward
- Quizzes - Gen Organic & Biological Che... ☆ myd21.lcc.edu + O G screenshot on mac - Google Search savings hulu youtube google disney+ HBO zlib Homework Hel...s | bartleby cell bio book Yuzu Reader: Chemistry G periodic table - Google Search b Home | bartleby 0:33:26 remaining CHEM 120 Chapter 5_Quiz 3 Page 1: 1 > 2 > 3 > 6 ¦ 5 > 4 > 7 ¦ 1 1 10 8 ¦ 9 a ¦ -- Quiz Information silicon-27 A doctor gives a patient 0.01 mC i of beta radiation. How many beta particles would the patient receive in I minute? (1 Ci = 3.7 x 10 10 d/s) Question 5 (1 point) Saved Listen 2.22 x 107 222 x 108 3.7 x 108 2.22 x 108 none of the above Question 6 (1 point) Listen The recommended dosage of 1-131 for a test is 4.2 μCi per kg of body mass. How many millicuries should be given to a 55 kg patient? (1 mCi = 1000 μСi)? 230 mCiarrow_forwardDon't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardDon't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forward
- Q3: Arrange each group of compounds from fastest SN2 reaction rate to slowest SN2 reaction rate. CI Cl H3C-Cl CI a) A B C D Br Br b) A B C Br H3C-Br Darrow_forwardQ4: Rank the relative nucleophilicity of halide ions in water solution and DMF solution, respectively. F CI Br | Q5: Determine which of the substrates will and will not react with NaSCH3 in an SN2 reaction to have a reasonable yield of product. NH2 Br Br Br .OH Brarrow_forwardClassify each molecule as optically active or inactive. Determine the configuration at each H соон Chirality center OH 애 He OH H3C Ноос H H COOH A K B.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079113
Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:Cengage Learning

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580343
Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:9780534420123
Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337398909
Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399074
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:Cengage Learning
The Laws of Thermodynamics, Entropy, and Gibbs Free Energy; Author: Professor Dave Explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8N1BxHgsoOw;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY