
Concept explainers
a)
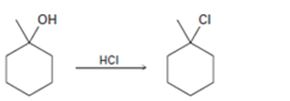
Interpretation:
The complete mechanism for the conversion of 30 alcohol given to 30
Concept introduction:
Alcohols get protonated in the presence of strong acids. The protonated intermediate will lose a molecule of water to yield a carbocation. The nucleophilic attack by the halide ion will lead to the formation of the alkyl halide.
To propose:
The complete mechanism for the conversion of 30 alcohol given to 30 alkyl halide by treating with HCl involving two cationic intermediates.
b)
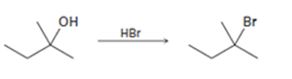
Interpretation:
The complete mechanism for the conversion of 30 alcohol given to 30 alkyl halide by treating with HBr involving two cationic intermediates is to be proposed.
Concept introduction:
Alcohols get protonated in the presence of strong acids. The protonated intermediate will lose a molecule of water to yield a carbocation. The nucleophilic attack by the halide ion will lead to the formation of the alkyl halide.
To propose:
The complete mechanism for the conversion of 30 alcohol given to 30 alkyl halide by treating with HBr involving two cationic intermediates.
c)
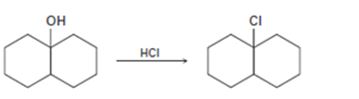
Interpretation:
The complete mechanism for the conversion of 30 alcohol given to 30 alkyl halide by treating with HCl involving two cationic intermediates is to be proposed.
Concept introduction:
Alcohols get protonated in the presence of strong acids. The protonated intermediate will lose a molecule of water to yield a carbocation. The nucleophilic attack by the halide ion will lead to the formation of the alkyl halide.
To propose:
The complete mechanism for the conversion of 30 alcohol given to 30 alkyl halide by treating with HCl involving two cationic intermediates.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 17 Solutions
Organic Chemistry - With Access (Custom)
- Steps and explanations. Also provide, if possible, ways to adress this kind of problems in general.arrow_forwardFor a complex reaction with the rate equation v = k1[A] + k2[A]2, we can say(A) that it is of order 1.(B) that it is of order 1.5.(C) that it is of order 2.(D) that for certain values of [A] it can behave as if it were of order 1, and for other values as if it were of order 2.arrow_forwarda. Draw a complete arrow pushing mechanism for the following. Is this the thermodynamic or the kinetic product? Use your mechanism to explain your choice. Draw all the resonance. HBr Brarrow_forward
- Which, if any, of the substances had resonance structures? How many resonance structures did each substance have from the following list: CCl4 H2O CO2 C2H4 NH3 SF6 ICl5arrow_forwardSteps and explanation pleasearrow_forwardSteps and explanation please. Add how to solve or target similar problems.arrow_forward
- Steps and explanation please. Add how to solve or target similar problems.arrow_forwardSteps and explanation please. Add how to solve or target similar problems.arrow_forwardWould the following organic synthesis occur in one step? Add any missing products, required catalysts, inorganic reagents, and other important conditions. Please include a detailed explanation and drawings showing how the reaction may occur in one step.arrow_forward
