
Electronics Fundamentals: Circuits, Devices & Applications
8th Edition
ISBN: 9780135072950
Author: Thomas L. Floyd, David Buchla
Publisher: Prentice Hall
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 17, Problem 35P
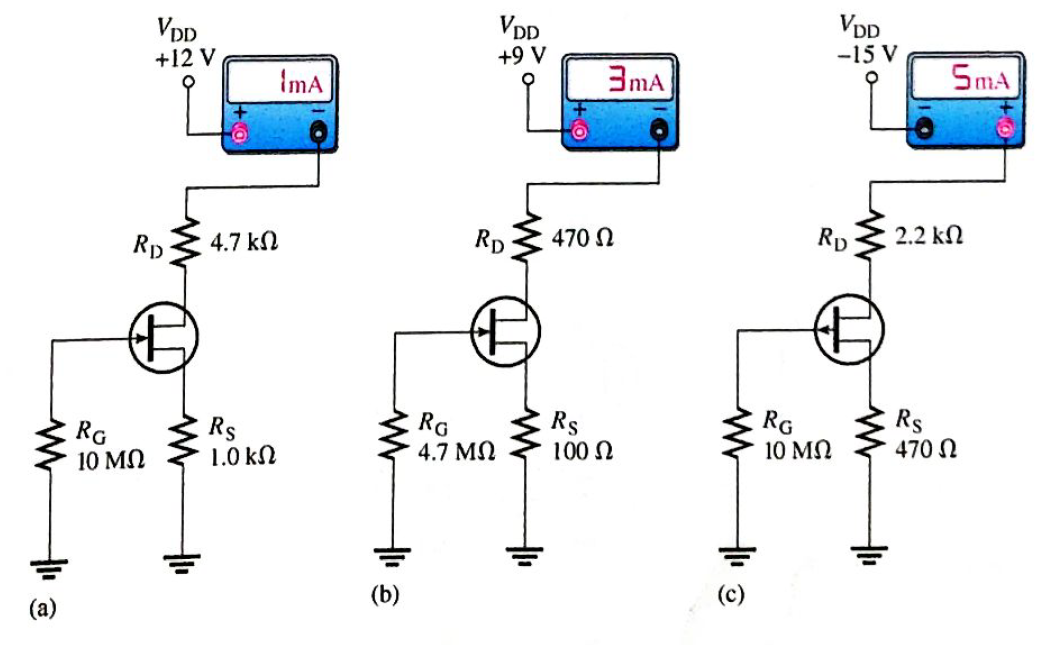
For each circuit in Figure 17-81, determine
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Can you rewrite the solution because it is
unclear?
AM
(+) = 8(1+0.5 cos 1000kt +0.5 ros 2000 thts)
=
cos 10000 πt.
8 cos wat + 4 cos wit + 4 cos Wat coswet.
J4000 t
j11000rt
$14+) = 45
jqooort
+4e
+ e
+ e
j 12000rt.
12000 kt
+ e
+e
+e
Le
jsoort
-; goon t
te
+e
Dcw>
= 885(W- 100007) + 8 IS (W-10000) -
USB
Can you rewrite the solution because it is
unclear?
Q2
AM
①(+) = 8 (1+0.5 cos 1000πt +0.5 ros 2000kt)
$4+) = 45
=
*cos 10000 πt.
8 cos wat + 4 cosat + 4 cos Wat coswet.
j1000016
+4e
-j10000πt j11000Rt
j gooort -j 9000 πt
+
e
+e
j sooort
te
+e
J11000 t
+ e
te
j 12000rt.
-J12000 kt
+ с
= 8th S(W- 100007) + 8 IS (W-10000)
<&(w) =
USB
-5-5
-4-5-4
b) Pc 2² = 64
PSB =
42
+ 4
2
Pt Pc+ PSB =
y = Pe
c) Puss =
PLSB =
= 32
4² = 8 w
32+ 8 =
× 100% = 140
(1)³×2×2
31
= 20%
x 2 = 3w
302
USB
4.5 5 5.6 6
ms Ac = 4 mi
= 0.5
mz Ac = 4
५
M2
=
=0.5
A. Draw the waveform for the following binary sequence using Bipolar RZ, Bipolar NRZ, and
Manchester code.
Data sequence= (00110100)
B. In a binary PCM system, the output signal-to-quantization ratio is to be hold to a minimum of
50 dB. If the message is a single tone with fm-5 kHz. Determine:
1) The number of required levels, and the corresponding output signal-to-quantizing noise ratio.
2) Minimum required system bandwidth.
Chapter 17 Solutions
Electronics Fundamentals: Circuits, Devices & Applications
Ch. 17 - In a bipolar transistor, if the base-emitter...Ch. 17 - When a transistor is saturated. an increase in...Ch. 17 - Prob. 3TFQCh. 17 - The power gain of a CC amplifier is the same as...Ch. 17 - A class B amplifier is more efficient than a class...Ch. 17 - A JFET is always operated with the gate-source...Ch. 17 - Prob. 7TFQCh. 17 - The transconductance of a FET is the ratio of ac...Ch. 17 - Prob. 9TFQCh. 17 - The input to a feedback oscillator is only the...
Ch. 17 - The n-type regions in an npn bipolar junction...Ch. 17 - The n-region in a pnp transistor is the base...Ch. 17 - Prob. 3STCh. 17 - Prob. 4STCh. 17 - Prob. 5STCh. 17 - Alpha () is the ratio of collector current to...Ch. 17 - If the beta of a certain transistor operating in...Ch. 17 - If the base current of a transistor operating in...Ch. 17 - Prob. 9STCh. 17 - When the gate-to-source voltage of an n-channel...Ch. 17 - When a negative gate-to-source voltage is applied...Ch. 17 - Prob. 12STCh. 17 - If the capacitor from emitter to ground in a CE...Ch. 17 - When the collector resistor in a CE amplifier is...Ch. 17 - The input resistance of a CE amplifier is affected...Ch. 17 - The output signal of a CE amplifier is always in...Ch. 17 - The output signal of a common-collector amplifier...Ch. 17 - The largest theoretical voltage gain obtainable...Ch. 17 - In a class A amplifier, the output signal is...Ch. 17 - A class A amplifier conducts for 90 of input cycle...Ch. 17 - Prob. 21STCh. 17 - Feedback oscillators operate on the principle of...Ch. 17 - What is the value of IC for IE=5.34mA and IB=475A?Ch. 17 - Prob. 2PCh. 17 - Prob. 3PCh. 17 - In a certain transistor circuit, the base current...Ch. 17 - Find IB,IE, and in Figure 17-70 given that DC=0.98...Ch. 17 - The transistor in Figure 17-70 is replaced with...Ch. 17 - Prob. 7PCh. 17 - Prob. 8PCh. 17 - Determine IB,IC, and VC in Figure 17-72.Ch. 17 - For the circuit in Figure 17-73, find VB,VE,IE,IC,...Ch. 17 - In Figure 17-73, what is VCE? What are the Q-point...Ch. 17 - A transistor amplifier has a voltage gain of 50....Ch. 17 - To achieve an output of 10 V with an input of300...Ch. 17 - A 50 mV signal is applied to the base of a...Ch. 17 - Determine the voltage gain for Figure 17-74.Ch. 17 - Determine each of the dc voltages, VB,VC, and VE,...Ch. 17 - Determine the following dc values for the...Ch. 17 - Determine the following ac values for the...Ch. 17 - The amplifier in Figure 17-76 has a variable gain...Ch. 17 - If a load resistance of 600 is placed on the...Ch. 17 - Determine the voltage gain for the...Ch. 17 - What is the total input resistance in Figure...Ch. 17 - A load resistance is capacitively coupled in the...Ch. 17 - Prob. 24PCh. 17 - Determine the maximum peak output voltage and peak...Ch. 17 - The efficiency of a certain class B push-pull...Ch. 17 - Prob. 27PCh. 17 - The transistor in Figure 17-80 has a DC of 150....Ch. 17 - The VGS of ap-channel JFET is increased from 1 V...Ch. 17 - Why must the gate-to-source voltage of an...Ch. 17 - Draw the schematic symbols for n-channel and...Ch. 17 - Explain why both types of MOSFETs have an...Ch. 17 - In what mode is an n-channel D-MOSFET operating...Ch. 17 - A certain E-MOSFET has a VGS(th)=3V. What is the...Ch. 17 - For each circuit in Figure 17-81, determine VDS...Ch. 17 - Prob. 36PCh. 17 - Each E-MOSFET in Figure 17-83 has a VGS(th) of +5...Ch. 17 - Prob. 38PCh. 17 - Find the gain of each amplifier in Figure 17-85.Ch. 17 - Determine the gain of each amplifier in Figure...Ch. 17 - If the voltage gain of the amplifier portion of a...Ch. 17 - Generally describe the change required to the...Ch. 17 - Prob. 43PCh. 17 - Prob. 44PCh. 17 - Prob. 47PCh. 17 - Prob. 48PCh. 17 - Prob. 49PCh. 17 - Prob. 50PCh. 17 - Prob. 51PCh. 17 - Prob. 52PCh. 17 - Open file P17-53. Determine if the circuit is...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Find Io using Mesh analysisarrow_forwardFM station of 100 MHz carrier frequency modulated by a 20 kHz sinusoid with an amplitude of 10 volt, so that the peak frequency deviation is 25 kHz determine: 1) The BW of the FM signal. 2) The approximated BW if the modulating signal amplitude is increased to 50 volt. 3) The approximated BW if the modulating signal frequency is increased by 70%. 4) The amplitude of the modulating signal if the BW is 65 kHz.arrow_forwardAn FDM is used to multiplex two groups of signals using AM-SSB, the first group contains 25 speech signals, each has maximum frequency of 4 kHz, the second group contains 15 music signals, each has maximum frequency of 10 kHz. A guard bandwidth of 500 Hz is used bety each two signals and before the first one. 1. Find the BWmultiplexing 2. Find the BWtransmission if the multiplexing signal is modulated using AM-DSB-LC.arrow_forward
- An FM signal with 75 kHz deviation, has an input signal-to-noise ratio of 18 dB, with a modulating frequency of 15 kHz. 1) Find SNRO at demodulator o/p. 2) Find SNRO at demodulator o/p if AM is used with m=0.3. 3) Compare the performance in case 1) and 2).. Hint: for single tone AM-DSB-LC, SNR₁ = (2m²) (4)arrow_forwardFind Va and Vb using Nodal analysisarrow_forwardCalculate the nodal voltage in the circuitarrow_forward
- Calculate the mesh currents, find Ia, Ib, Ic. Apply mesh analysisarrow_forwardFind Va and Vb using Nodal analysisarrow_forward4. A battery operated sensor transmits to a receiver that is plugged in to a power outlet. The device is continuously operated. The battery is a 3.6 V coin-cell battery with a 245mAHr capacity. The application requires a bit rate of 36 Mbps and an error rate of less than 10^-3. The channel has a center frequency of 2.4 GHz, a bandwidth of 10 MHz and a noise power spectral density of 10^-14 W/Hz. The maximum distance is 36 meters and the losses in the channel attenuates the signal by 0.25 dB/meter. Your company has two families of chips that you can use. An M-ary ASK and an M-ary QAM chip. The have very different power requirements as shown in the table below. The total current for the system is the current required to achieve the desired Eb/No PLUS the current identified below: Hokies PSK Chip Set Operating Current NOT Including the required Eb/No for the application Hokies QAM Chip Set Operating Current NOT Including the required Eb/No for the application Chip ID M-ary Voltage (volts)…arrow_forward
- Using the 802.11a specifications given below, in Matlab (or similar tool) create the time domain signal for one OFDM symbol using QPSK modulation. See attached plot for the QPSK constellation. Your results should include the power measure in the time and frequency domain and comment on those results. BW 802.11a OFDM PHY Parameters 20 MHZ OBW Subcarrer Spacing Information Rate Modulation Coding Rate Total Subcarriers Data Subcarriers Pilot Subcarriers DC Subcarrier 16.6 MHZ 312.5 Khz (20MHz/64 Pt FFT) 6/9/12/18/24/36/48/54 Mbits/s BPSK, QPSK, 16QAM, 64QAM 1/2, 2/3, 3/4 52 (Freq Index -26 to +26) 48 4 (-21, -7, +7, +21) *Always BPSK Null (0 subcarrier) 52 subarriers -7 (48 Data, 4 Pilot (BPSK), 1 Null) -26 -21 0 7 21 +26 14 One Subcarrier 1 OFDM symbol 1 OFDM Burst -OBW 16.6 MHz BW 20 MHZ 1 constellation point = 52 subcarriers = one or more OFDM symbols 802.11a OFDM Physical Parameters Show signal at this point x bits do Serial Data d₁ S₁ Serial-to- Input Signal Parallel Converter IFFT…arrow_forwardFind Vb and Va using Mesh analysisarrow_forward1. The communication channel bandwidth is 25 MHz centered at 1GHz and has a noise power spectral density of 10^-9 W/Hz. The channel loss between the transmitter and receiver is 25dB. The application requires a bit rate of 200Mbps and BER of less than 10^-4. Excluding Mary FSK, Determine the minimum transmit power required.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Random Variables and Probability Distributions; Author: Dr Nic's Maths and Stats;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lHCpYeFvTs0;License: Standard Youtube License