
Concept explainers
Superior Construction, Inc. is a home builder in Arizona. Superior uses a
- a. Purchased materials on account, $400,000.
- b. Requisitioned direct materials and used direct labor in construction. Recorded the materials requisitioned.
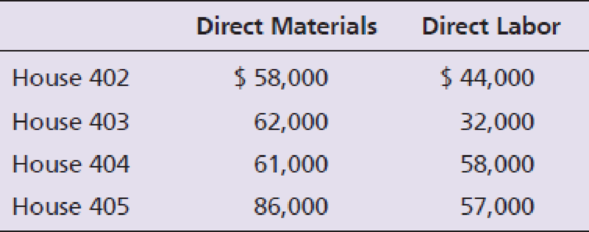
- c. The company incurred total wages of $300,000. Use the data from Item b to assign the wages. Wages are not yet paid.
- d.
Depreciation of construction equipment, $6,700. - e. Other overhead costs incurred: Equipment rentals paid in cash, $30,000; Worker liability insurance expired, $7,000.
- f. Allocated overhead to jobs.
- g. Houses completed: 402, 404.
- h. House sold on account: 404 for $250,000.
Requirements
- 1. Calculate Superior’s predetermined overhead allocation rate for the year.
- 2. Prepare
journal entries to record the events in the general journal. - 3. Open T-accounts for Work-in-Process Inventory and Finished Goods Inventory.
Post the appropriate entries to these accounts, identifying each entry by letter. Determine the ending account balances, assuming that the beginning balances were zero. - 4. Add the costs of the unfinished houses, and show that this total amount equals the ending balance in the Work-in-Process Inventory account.
- 5. Add the costs of the completed house that has not yet been sold, and show that this equals the ending balance in Finished Goods Inventory.
- 6. Compute gross profit on the house that was sold. What costs must gross profit cover for Superior Construction?
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

Chapter 17 Solutions
Horngren's Financial & Managerial Accounting, The Managerial Chapters (6th Edition)
Additional Business Textbook Solutions
Managerial Accounting (5th Edition)
Operations Management
Horngren's Financial & Managerial Accounting, The Financial Chapters (Book & Access Card)
MARKETING:REAL PEOPLE,REAL CHOICES
Foundations of Financial Management
- Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning  Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub



