
The
To find: The frequency of light wave is higher, lower or the same after the light enters a piece of glass.
Answer to Problem 1CQ
The frequency of light wave is same after the light enters a piece of glass.
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
The frequency of light wave is
Formula used:
Write the expression for refractive index.
Here,
Write the expression for speed.
Here,
Explanation:
Draw the light wave travels from air to glass as shown in Figure 1.
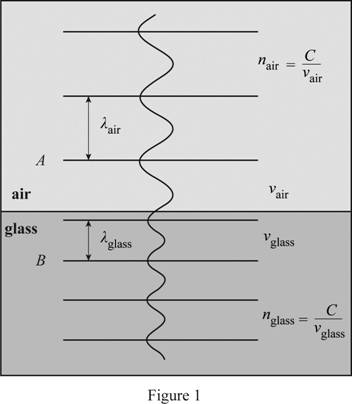
Refer to Table 17.1 in the textbook, the value of index of refraction for glass and air is
Modify equation (1) for air as follows.
Modify equation (2) for air as follows.
Substitute
Rearrange the equation.
Modify equation (1) for glass as follows.
Modify equation (2) for air as follows.
Substitute
Rearrange the equation as follows.
Here, the value of
Substitute
Substitute
Find the value of
Find the value of
Write the relation between
Re-arrange equation (4) as follows.
Re-arrange equation (6) as follows.
Divide equation (7) by (8).
Substitute
Conclusion:
Hence, the frequency of light wave is same after the light enters a piece of glass.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Concepts of Genetics (12th Edition)
Chemistry: A Molecular Approach (4th Edition)
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
- In the movie Fast X, a 10100 kg round bomb is set rolling in Rome. The bomb gets up to 17.6 m/s. To try to stop the bomb, the protagonist Dom swings the counterweight of a crane, which has a mass of 354000 kg into the bomb at 3.61 m/s in the opposite direction. Directly after the collision the crane counterweight continues in the same direction it was going at 2.13 m/s. What is the velocity (magnitude and direction) of the bomb right after the collision?arrow_forwardDon't use aiarrow_forwardMake sure to draw a sketch with scale pleasearrow_forward
- Make sure to draw a sketch with scalearrow_forwardUltimate Byleth and Little Mac fight. Little Mac, who is a boxer, dashes forward at 26.6 m/s, fist first. Byleth moves in the opposite direction at 3.79 m/s, where they collide with Little Mac’s fist. After the punch Byleth flies backwards at 11.1 m/s. How fast, and in what direction, is Little Mac now moving? Little Mac has a mass of 48.5 kg and Byleth has a mass of 72.0 kg.arrow_forwardMake sure to draw a sketch with scale as wellarrow_forward
- Make sure to draw a sketch with scale pleasearrow_forwardKirby jumps towards his enemy/ally, Meta Knight, at 2.06 m/s while Meta Knight glides in the opposite direction (toward Kirby) at 5.06 m/s. Kirby then begins to inhale, swallowing Meta Knight. What is Kirby/Meta Knight’s velocity immediately after being swallowed? Please put the magnitude of the velocity and then mark direction using dropdown menu. Kirby has a mass of 0.283 kg and Meta Knight has a mass of 0.538 kg.arrow_forwardNo Aiarrow_forward
 Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning





