
(a)
To determine: The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with
Interpretation: The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with
Concept introduction: Friedel-Crafts alkylation permits the synthesis of alkylated products by the reaction of arenes with alkyl chlorides in the presence of aluminium chloride (Lewis acid). This alkylation reaction comes under the category of electrophilic aromatic substitution.
(a)
Answer to Problem 17.50SP
The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with
Explanation of Solution
The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with
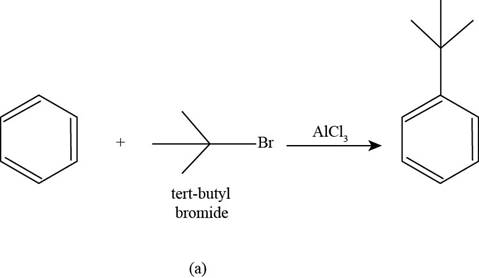
Figure
In the above reaction, benzene reacts with
(b)
To determine: The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with
Interpretation: The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with
Concept introduction: Friedel-Crafts alkylation permits the synthesis of alkylated products by the reaction of arenes with alkyl chlorides in the presence of aluminium chloride (Lewis acid). This alkylation reaction comes under the category of electrophilic aromatic substitution.
(b)
Answer to Problem 17.50SP
The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with
Explanation of Solution
The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with
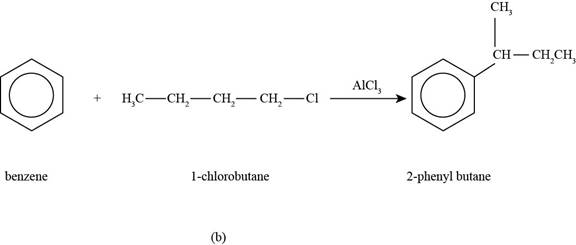
Figure
In the above reaction, benzene reacts with
(c)
To determine: The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with isobutyl alcohol in the presence of
Interpretation: The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with isobutyl alcohol in the presence of
Concept introduction: Friedel-Crafts alkylation permits the synthesis of alkylated products by the reaction of arenes with alcohol in the presence of
(c)
Answer to Problem 17.50SP
The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with isobutyl alcohol in the presence of
Explanation of Solution
The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with isobutyl alcohol in the presence of
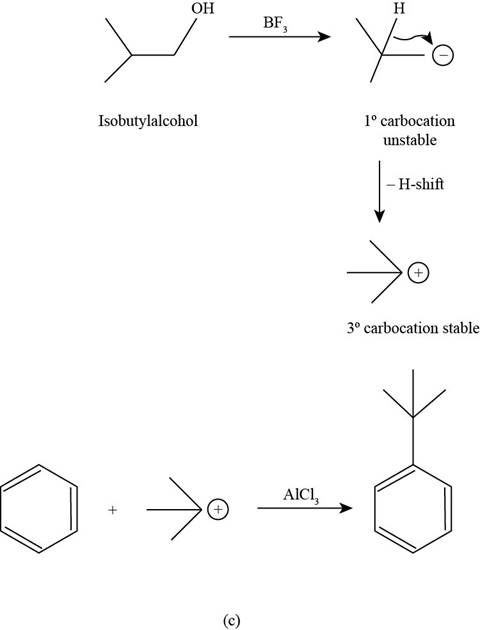
Figure
In the above reaction, the primary carbocation that is generated by the protonation of isobutyl alcohol by
In the second step, this electrophilic carbocation reacts with benzene in the presence of
(d)
To determine: The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with bromine in the presence of a nail.
Interpretation: The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with bromine in the presence of a nail is to be predicted.
Concept introduction: The reaction that includes the addition of one or more bromine atoms in a compound is known as bromination reaction. Bromination reaction is a type of halogenation reaction.
(d)
Answer to Problem 17.50SP
The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with bromine in the presence of a nail is shown as follows.
Explanation of Solution
The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with bromine in the presence of a nail is shown in Figure
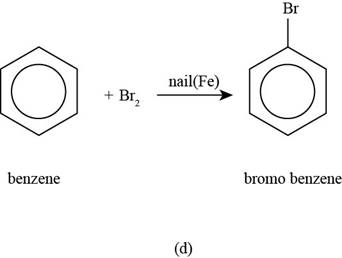
Figure
In the above reaction, bromination of benzene ring occurs to form bromobenzene as the desired product.
(e)
To determine: The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with isobutylene in the presence of
Interpretation: The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with isobutylene in the presence of
Concept introduction: Friedel-Crafts alkylation permits the synthesis of alkylated products by the reaction of arenes with
(e)
Answer to Problem 17.50SP
The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with isobutylene in the presence of
Explanation of Solution
The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with isobutylene in the presence of
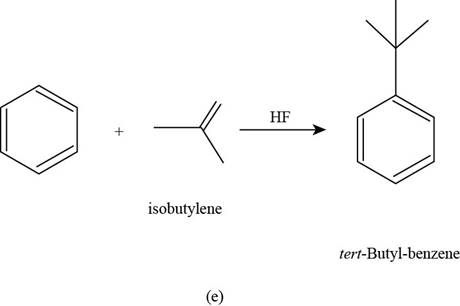
Figure
In the above reaction, benzene reacts with isobutylene in the presence of
(f)
To determine: The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with fuming sulphuric acid.
Interpretation: The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with fuming sulphuric acid is to be predicted.
Concept introduction: The process of attaching
(f)
Answer to Problem 17.50SP
The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with fuming sulphuric acid is shown as follows.
Explanation of Solution
The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with fuming sulphuric acid is shown in Figure
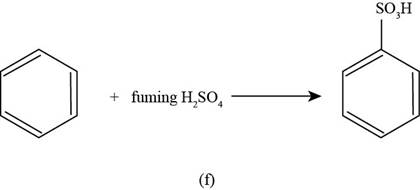
Figure
In the above reaction, benzene reacts with fuming sulphuric acid to form as the desired sulfonated product.
(g)
To determine: The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with
Interpretation: The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with
Concept introduction: Friedel-Crafts alkylation permits the synthesis of alkylated products by the reaction of arenes with alkyl chlorides in the presence of aluminium chloride (Lewis acid). This alkylation reaction comes under the category of electrophilic aromatic substitution.
(g)
Answer to Problem 17.50SP
The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with
Explanation of Solution
The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with
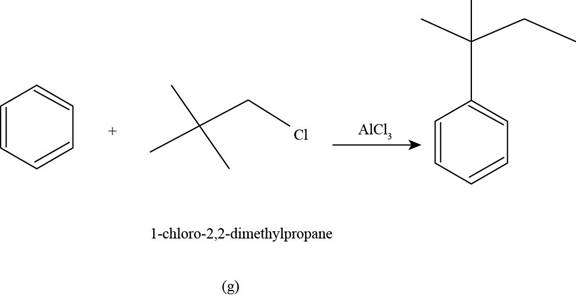
Figure
In the above reaction, benzene reacts with
(h)
To determine: The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with benzoyl chloride in the presence of
Interpretation: The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with benzoyl chloride in the presence of
Concept introduction: Friedel-Crafts alkylation permits the synthesis of alkylated products by the reaction of arenes with alkyl chlorides in the presence of aluminium chloride (Lewis acid). This alkylation reaction comes under the category of electrophilic aromatic substitution.
(h)
Answer to Problem 17.50SP
The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with benzoyl chloride in the presence of
Explanation of Solution
The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with benzoyl chloride in the presence of
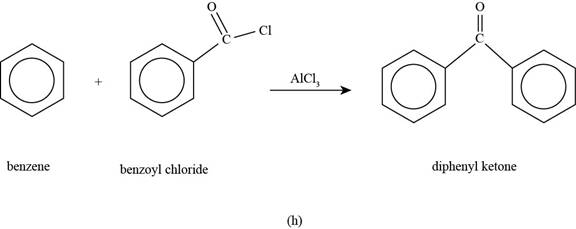
Figure
In the above reaction, benzene reacts with benzoyl chloride in the presence of
(i)
To determine: The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with iodine molecule in the presence of
Interpretation: The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with iodine molecule in the presence of
Concept introduction: The reaction that includes the addition of one or more than one halogen atoms in a compound is known as halogenation reaction.
(i)
Answer to Problem 17.50SP
The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with iodine molecule in the presence of
Explanation of Solution
The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with iodine molecule in the presence of
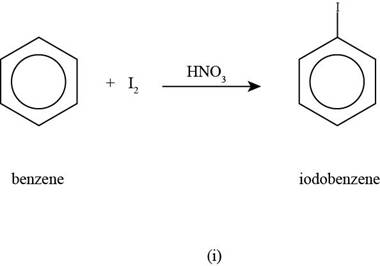
Figure
In the above halogenations reaction, benzene reacts with iodine molecule in the presence of
(j)
To determine: The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with nitric acid and sulphuric acid.
Interpretation: The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with nitric acid and sulphuric acid is to be predicted.
Concept introduction: The reaction that involves the addition of a nitro group on an alkyl or an aromatic compound in the presence of concentrated nitric acid and sulphuric acid is known as nitration reaction.
(j)
Answer to Problem 17.50SP
The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with nitric acid and sulphuric acid is shown as follows.
Explanation of Solution
The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene benzene with nitric acid and sulphuric acid is shown in Figure
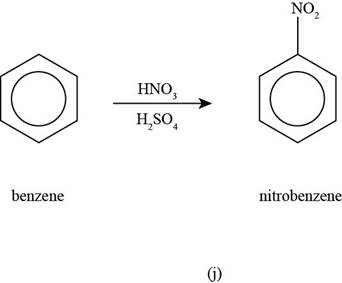
Figure
In the above nitration reaction, benzene reacts with concentrated nitric acid and sulphuric acid that forms nitrobenzene as the desired product.
(k)
To determine: The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with carbon monoxide in the presence of
Interpretation: The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with carbon monoxide in the presence of
Concept introduction: The synthesis in which
(k)
Answer to Problem 17.50SP
The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with carbon monoxide in the presence of
Explanation of Solution
The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with carbon monoxide in the presence of
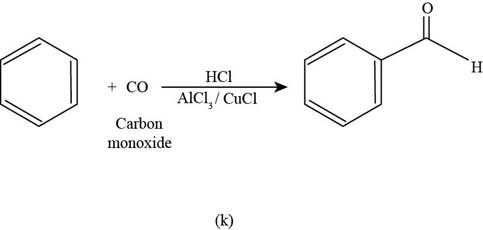
Figure
In the above reaction, benzene reacts with benzoyl carbon monoxide in the presence of
(l)
To determine: The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with
Interpretation: The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with
Concept introduction: Friedel-Crafts acylation permits the synthesis of acylated products by the reaction of arenes with acyl chlorides in the presence of
(l)
Answer to Problem 17.50SP
The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with
Explanation of Solution
The major product that is formed by reaction benzene with
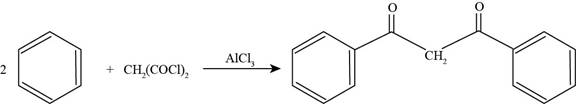
Figure
In the above reaction, benzene reacts with
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
Organic Chemistry Plus Masteringchemistry With Pearson Etext, Global Edition
- What is the pH of a 1.0 L buffer made with 0.300 mol of HF (Ka = 6.8 × 10⁻⁴) and 0.200 mol of NaF to which 0.160 mol of NaOH were added?arrow_forwardCan I please get help with this.arrow_forwardDetermine if the following salt is neutral, acidic or basic. If acidic or basic, write the appropriate equilibrium equation for the acid or base that exists when the salt is dissolved in aqueous solution. If neutral, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. N₂H₅ClO₄arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
