
(a)
Interpretation:
The reaction in which penta-2, 4-dienylmagnesium bromide reacts with deuterated water is to be completed.
Concept introduction:
Grignard reagents are
Answer to Problem 17.45AP
The complete reaction between penta-2, 4-dienylmagnesium bromide and D2O is shown below.
![]()
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is shown below.
![]()
Figure 1
The complete reaction is shown below.
![]()
Figure 2
The hydrolysis of Grignard reagent is shown in Figure 2 in the presence of a solvent D2O. Thus, penta-2, 4-dienylmagnesium bromide on treatment with deuterated water gives an
Therefore, the product formed is shown in Figure 2.
The complete reaction between penta-2, 4-dienylmagnesium bromide and D2O is shown in Figure 2.
(b)
Interpretation:
The reaction between penta-2, 4-dienylmagnesium bromide and
Concept introduction:
Grignard reagents are organometallic compounds which are prepared using alkyl halides in the presence of magnesium metal in dry ether. These reagents act as strong nucleophiles and bases.
Answer to Problem 17.45AP
The complete reaction between penta-2, 4-dienylmagnesium bromide and epoxide is shown below.
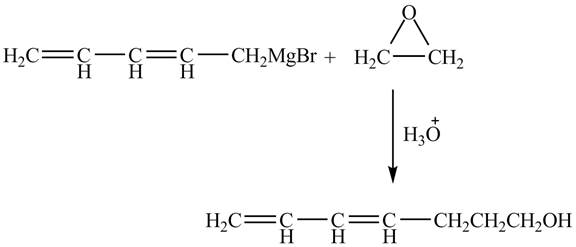
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is shown below.
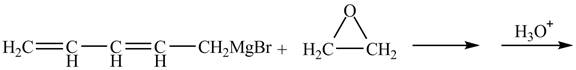
Figure 3
The complete reaction is shown below.
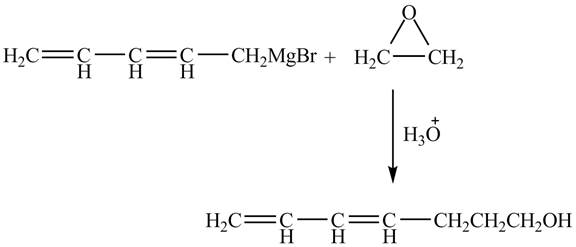
Figure 4
The Grignard reagent on treatment with epoxides in the presence of H3O+ gives primary alcohol as a product. The penta-2, 4-dienylmagnesium bromide on reaction with epoxide leads to the opening of epoxide ring. As a result, hepta-4, 6-dien-1-ol is formed as a product.
Therefore, the product formed is shown in Figure 4.
The complete reaction between penta-2, 4-dienylmagnesium bromide and epoxide is shown in Figure 4.
(c)
Interpretation:
The reaction between trans-1-bromo-4-methylpent-2-ene and sodium ethanethiolate is to be completed.
Concept introduction:
Nucleophiles are electron-rich species. The nucleophilic substitution reactions are the reactions in which nucleophile attacks the electrophilic center and eliminates another group.
Answer to Problem 17.45AP
The complete reaction between trans-1-bromo-4-methylpent-2-ene and sodium ethanethiolate is shown below.
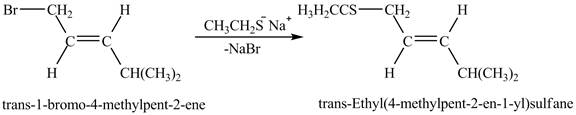
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is shown below.
![]()
Figure 5
The complete reaction is shown below.
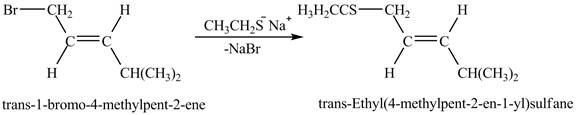
Figure 6
The above figure shows the reaction between ethyl sulfide ion and trans-1-bromo-4-methylpent-2-ene gives thioether as a product. The species, CH3CH2CH2S− acts as a nucleophile and attacks at the carbon adjacent to the double bond. As a result, Br leaves as a leaving group. Therefore, the product is formed by the removal of NaBr is shown in Figure 6.
The complete reaction between trans-1-bromo-4-methylpent-2-ene and sodium ethanethiolate is shown in Figure 6.
(d)
Interpretation:
The reaction between trans-1-bromo-4-methylpent-2-ene and ethanol is to be completed.
Concept introduction:
Nucleophiles are electron-rich species. The nucleophilic substitution reactions are the reactions in which nucleophile attacks the electrophilic center and eliminates another group.
Answer to Problem 17.45AP
The complete reaction between trans-1-bromo-4-methylpent-2-ene and ethanol is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
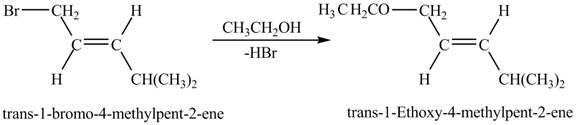
The given reaction is shown below.

Figure 7
The complete reaction is shown below.
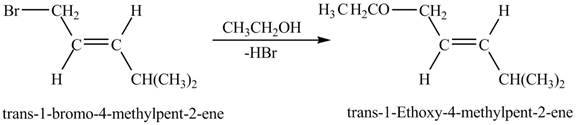
Figure 8
Figure 8 shows the reaction between trans-1-bromo-4-methylpent-2-ene and ethanol which gives trans-1-ethoxy-4-methylpent-2-ene as a product by the removal of hydrogen bromide. The species, CH3CH2O− acts as a nucleophile and attacks at the carbon adjacent to the double bond. As a result, Br leaves as a leaving group. Therefore, the product is formed by the removal of HBr which is shown in Figure 8.
The complete reaction between trans-1-bromo-4-methylpent-2-ene and ethanol is shown in Figure 8.
(e)
Interpretation:
The reaction of a given compound with NBS is to be completed.
Concept introduction:
Cyclic alkenes on reaction with N-Bromosuccinimide (NBS) forms allyl bromide, that is, bromine is substituted at the allylic position. NBS is a rich source of free radical of Br. The mechanism followed by NBS is a radical substitution reaction.
Answer to Problem 17.45AP
The complete reaction of a given compound with NBS is shown below.
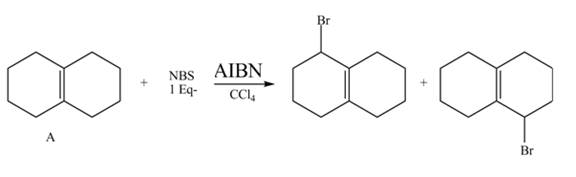
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is shown below.
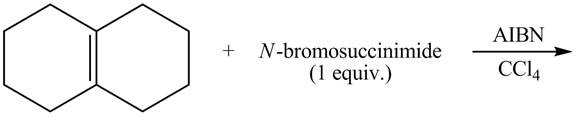
Figure 9
The complete reaction is shown below.

Figure 10
The NBS is used for allylic bromination that is it substitutes Br at allylic positions. The compound A contains two allylic positions. Therefore, two different products are formed in the presence of AIBN and CCl4.
Therefore, the products formed are shown in Figure 10.
The complete reaction of given compound with NBS is shown in Figure 10.
(f)
Interpretation:
The reaction between p-cymene and NBS is shown is to be completed.
Concept introduction:
Cyclic alkenes on reaction with N-Bromosuccinimide (NBS) forms allyl bromide, that is, bromine is substituted at the allylic position. NBS is a rich source of free radical of Br. The mechanism followed by NBS is a radical substitution reaction.
Answer to Problem 17.45AP
The complete reaction between p-cymene and NBS is shown below.

Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is shown below.
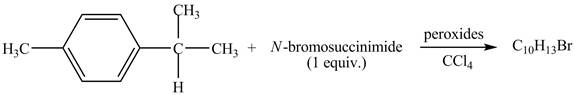
Figure 11
The complete reaction is shown below.

Figure 12
The molecular formula of the product is C10H13Br. This reaction is a free radical substitution reaction. The stable free radical is formed at benzylic position.
Due to the addition of NBS, benzylic bromination of p-cymene takes places which leads to the formation of 1-(2-bromopropan-2-yl)-4-methylbenzene.
Therefore, the product formed is shown in Figure 12.
The complete reaction between p-cymene and NBS is shown in Figure 12.
(g)
Interpretation:
The complete reaction in which 1, 4-dihydronaphthalene reacts with Br2 followed by treatment with KOH and ethanol is to be completed.
Concept introduction:
The elimination reaction of alkyl halide, β-elimination, involves removal of the halogen atom and a hydrogen atom from the adjacent carbon atom, which leads to the formation of the alkene.
Answer to Problem 17.45AP
The complete reaction in which 1, 4-dihydronaphthalene reacts with Br2 followed by treatment with KOH and ethanol is shown below.
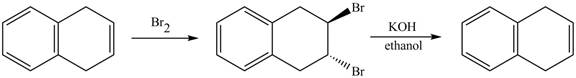
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is shown below.
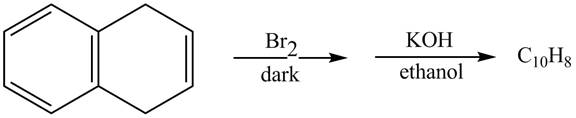
Figure 13
The complete reaction is shown below.

Figure 14
The addition of Br2 takes place at the double bond of 1, 4-dihydronaphthalene. Furthermore, the product formed undergoes β-elimination reaction takes place in presence of KOH and ethanol which leads to the formation of naphthalene as a product.
Therefore, the product formed is shown in Figure 14.
The complete reaction in which 1, 4-dihydronaphthalene reacts with Br2 followed by treatment with KOH and ethanol is shown in Figure 14.
(h)
Interpretation:
The reaction between buta-1, 3-dienylbenzene and HBr is to be completed.
Concept introduction:
When an alkene reacts with water in the acidic medium the reaction follows Markovnikov rule which states that the negative part of the reagent attacks the carbon with the least number of hydrogen atoms attached to it.
Answer to Problem 17.45AP
The complete reaction between buta-1, 3-dienylbenzene and HBr is shown below.
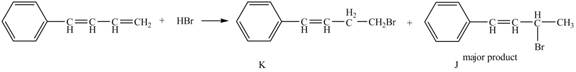
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is shown below.
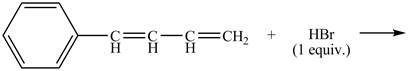
Figure 15
The complete reaction is shown below.

Figure 16
The compound, buta-1, 3-dienylbenzene, on treatment with HBr gives two products. The product which follows Markovnikov rule will be obtained as a major product. Therefore compound J is obtained as a major product as Br− gets attached to that carbon which contains less number of the hydrogen atom.
Therefore, the products formed are shown in Figure 16.
The complete reaction between buta-1, 3-dienylbenzene and HBr is shown in Figure 16.
(i)
Interpretation:
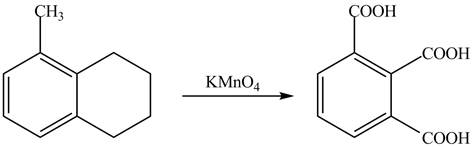
The reaction between 5-methyl-1, 2, 3, 4-tetrahydronaphthalene and potassium permanganate is to be completed.
Concept introduction:
The substance which gets easily reduced is termed as a strong oxidizing agent. It is also defined as the substances which oxidize other substances by accepting their electrons. Examples of strong oxidizing agents are potassium permanganate, hydrogen peroxide and many more.
Answer to Problem 17.45AP
The complete reaction between 5-methyl-1, 2, 3, 4-tetrahydronaphthalene and potassium permanganate is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is shown below.
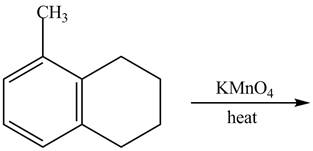
Figure 17
The complete reaction is shown below.

Figure 18
The compound, KMnO4 is a strong oxidizing agent. Therefore, it will convert the alkyl side chain of 5-methyl-1, 2, 3, 4-tetrahydronaphthalene into
Therefore, the product formed is shown in Figure 18.
The complete reaction between 5-methyl-1, 2, 3, 4-tetrahydronaphthalene and potassium permanganate is shown in Figure 18.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEM +SG +SAPLING >IP<
- What is the product of the reaction? F3C. CF3 OMe NaOH / H₂Oarrow_forwardWhat would you expect to be the major product obtained from the following reaction? Please explain what is happening here. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing showing how the reaction occurs. The correct answer to this question is V.arrow_forwardPlease answer the question for the reactions, thank youarrow_forward
- What is the product of the following reaction? Please include a detailed explanation of what is happening in this question. Include a drawing showing how the reagent is reacting with the catalyst to produce the correct product. The correct answer is IV.arrow_forwardPlease complete the reactions, thank youarrow_forwardConsider the synthesis. What is compound Y? Please explain what is happening in this question. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing to show how the compound Y creates the product. The correct answer is D.arrow_forward
- What would be the major product of the following reaction? Please include a detailed explanation of what is happening in this question. Include steps and a drawing to show this reaction proceeds and how the final product is formed. The correct answer is B. I put answer D and I don't really understand what is going on in the question.arrow_forwardWhat is the product of the following reaction? Please explain what is happening in this question. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing showing how the reagent is reacting with the catalysts to product the correct product. The correct answer is B.arrow_forwardWhat is the missing intermediate 1 and the final product 2. Please include a detailed explanation explaining the steps of malonic ester synthesis. Please include drawings of the intermediate and how it occurs and how the final product is former.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
