
Concept explainers
Transferred-in costs, weighted-average method. Spelling Sports, which produces basketballs, has two departments: cutting and stitching. Each department has one direct-cost category (direct materials) and one indirect-cost category (conversion costs). This problem focuses on the stitching department.
Basketballs that have undergone the cutting process are immediately transferred to the stitching department. Direct material is added when the stitching process is 70% complete. Conversion costs are added evenly during stitching operations. When those operations are done, the basketballs are immediately transferred to Finished Goods.
Spelling Sports uses the weighted-average method of
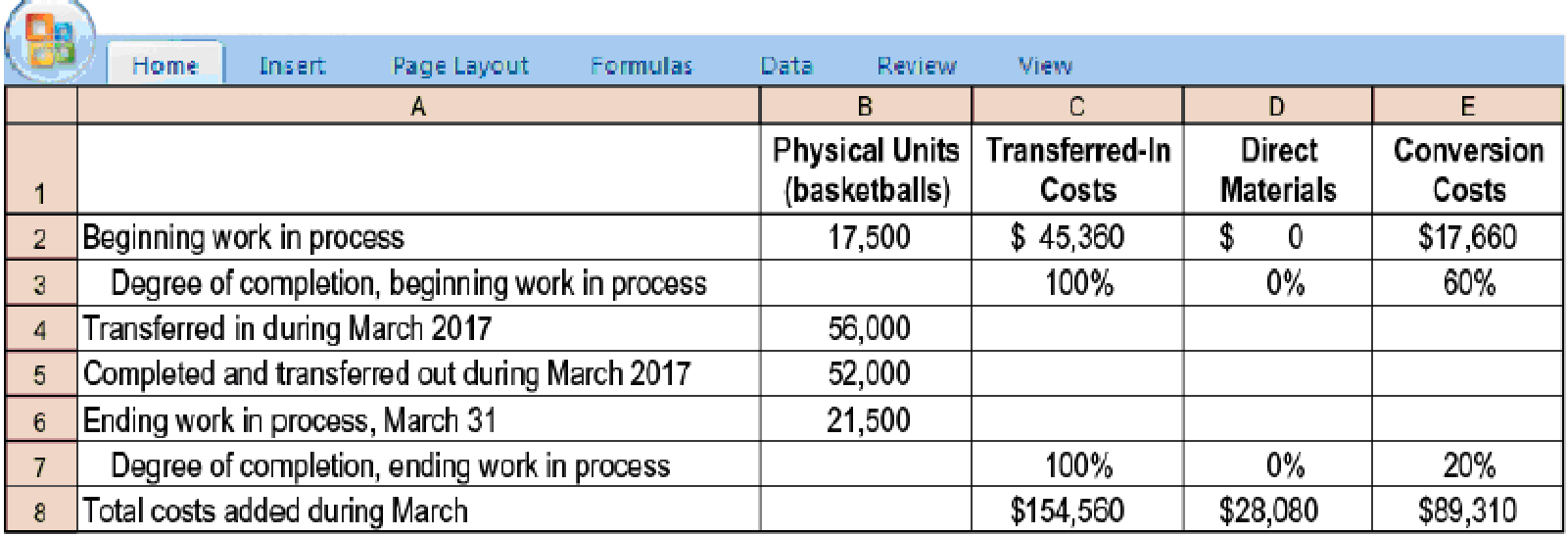
- 1. Summarize total stitching department costs for March 2017, and assign these costs to units completed (and transferred out) and to units in ending work in process.
Required
- 2. Prepare
journal entries for March transfers from the cutting department to the stitching department and from the stitching department to Finished Goods.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 17 Solutions
Horngren's Cost Accounting, Student Value Edition (16th Edition)
- McKnight Handcraft is a manufacturer of picture frames for large retailers. Every picture frame passes through two departments: the assembly department and the finishing department. This problem focuses on the assembly department. The process-costing system at McKnight has a single direct-cost category (direct materials) and a single indirect-cost category (conversion costs). Direct materials are added when the assembly department process is 10% complete. Conversion costs are added evenly during the assembly department's process. McKnight uses the weighted-average method of process costing. Consider the following data for the assembly department in April 2017 E (Click the icon to view the data.) Read the requirements. Requirement 1. Summarize total assembly department costs for April 2017, and assign total costs to units completed (and transferred out) and to units in ending work in process. Begin by calculating the physical units and equivalent units. Equivalent Units Data table…arrow_forwardMcKnight Handcraft is a manufacturer of picture frames for large retailers. Every picture frame passes through two departments: the assembly department and the finishing department. This problem focuses on the assembly department. The process-costing system at McKnight has a single direct-cost category (direct materials) and a single indirect-cost category (conversion costs). Direct materials are added when the assembly department process is 10% complete. Conversion costs are added evenly during the assembly department's process. McKnight uses the weighted-average method of process costing. Consider the following data for the assembly department in April: (Click the icon to view the data.) Required Work in process, ending Accounted for Equivalent units of work done to date Now summarize the total costs to account for. Work in process, beginning Costs added in current period Total costs to account for Completed and transferred out Work in process, ending IZU 570 Total costs accounted…arrow_forwarddisc uses activity-based costing. two of discs production activinarrow_forward
- Assign costs to units completed (and transferred out) and to units in ending work in process.arrow_forwardWeighted-average method. Hoffman Company manufactures car seats in its Boise plant. Each car seat passes through the assembly department and the testing department. This problem focuses on the assembly department. The process-costing system at Hoffman Company has a single direct-cost category (direct materials) and a single indirect-cost category (conversion materials are added at the costs). Direct beginning of the process. Conversion costs are added evenly during the process. When the assembly department finishes work on each car seat, it is immediately transferred to testing. Hoffman Company uses the weighted-average method of process costing. Data for the assembly department for October 2019 are as follows: Physical Units (Car Seats) Direct Materials Conversion Costs Work in process, October 1ª 4,000 $1,248,000 $ 241,650 Started during October 2019 22,500 Completed during October 2019 26,000 Work in process, October 31b 500 Total costs added during October $4,635,000 $2,575,125…arrow_forwardcan you solve itarrow_forward
- Complete Problem using the FIFO method of process costing.arrow_forwardKeyboard uses activity-based costing. Two of Keyboard's production activities are kitting (assembling the raw materials needed for each computer in one kit) and boxing the completed products for shipment to customers. Assume that Keyboard spends $10,000,000per month on kitting and $18,000,000 per month on boxing.Keyboardallocates the following: •Kitting costs based on the number of parts used in the computer •Boxing costs based on the cubic feet of space the computer requires Suppose Keyboard estimates it will use 250,000,000 parts per month and ship products with a total volume of 22,500,000 cubic feet per month. Assume that each desktop computer requires 175 parts and has a volume of 7 cubic feet. The predetermined overhead allocation rate for kitting is $0.04 per part and the predetermined overhead allocation rate for boxing is $0.80 per cubic foot. What are the kitting and boxing costs assigned to one desktop computer?arrow_forwardI need helparrow_forward
- Lens Care Inc. (LCI) manufactures specialized equipment for polishing optical lenses. There are two models - one mainly used for fine eyewear (F-32) and another for lenses used in binoculars, cameras, and similar equipment (B-13).The manufacturing cost of each unit is calculated using activity-based costing, using the following manufacturing cost pools: Cost Pools Allocation Base Costing Rate Materials handling Number of parts $ 2.50 per part Manufacturing supervision Hours of machine time $ 14.81 per hour Assembly Number of parts $ 3.35 per part Machine setup Each setup $ 56.55 per setup Inspection and testing Logged hours $ 45.55 per hour Packaging Logged hours $ 19.55 per hour LCI currently sells the B-13 model for $2,000 and the F-32 model for $1,500. Manufacturing costs and activity usage for the two products are as follows: B-13 F-32 Direct materials $ 164.55 $ 75.64 Number of parts 161 121 Machine hours 7.95 4.21…arrow_forwardLens Care Inc. (LCI) manufactures specialized equipment for polishing optical lenses. There are two models - one mainly used for fine eyewear (F-32) and another for lenses used in binoculars, cameras, and similar equipment (B-13).The manufacturing cost of each unit is calculated using activity-based costing, using the following manufacturing cost pools: Cost Pools Allocation Base Costing Rate Materials handling Number of parts $ 2.50 per part Manufacturing supervision Hours of machine time $ 14.81 per hour Assembly Number of parts $ 3.35 per part Machine setup Each setup $ 56.55 per setup Inspection and testing Logged hours $ 45.55 per hour Packaging Logged hours $ 19.55 per hour LCI currently sells the B-13 model for $2,000 and the F-32 model for $1,500. Manufacturing costs and activity usage for the two products are as follows: B-13 F-32 Direct materials $ 164.55 $ 75.64 Number of parts 161 121 Machine hours 7.95 4.21…arrow_forwardThe following product costs are available for Stellis Company on the production of erasers: direct materials, $22,000; direct labor, $35,000; manufacturing overhead, $17,500; selling expenses, $17,600; and administrative expenses; $13,400. What are the prime costs? What are the conversion costs? What is the total product cost? What is the total period cost? If 13,750 equivalent units are produced, what is the equivalent material cost per unit? If 17,500 equivalent units are produced, what is the equivalent conversion cost per unit?arrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College

