
Concept explainers
Weighted-average method, assigning costs (continuation of 17-24).
For the data in Exercise 17-24, summarize the total costs to account for calculate the cost per equivalent unit for direct materials and conversion costs, and assign costs to the units completed (and transferred out) and units in ending work in process.
17-24 Weighted-average method, equivalent units. The assembly division of Quality Time Pieces, Inc. uses the weighted-average method of
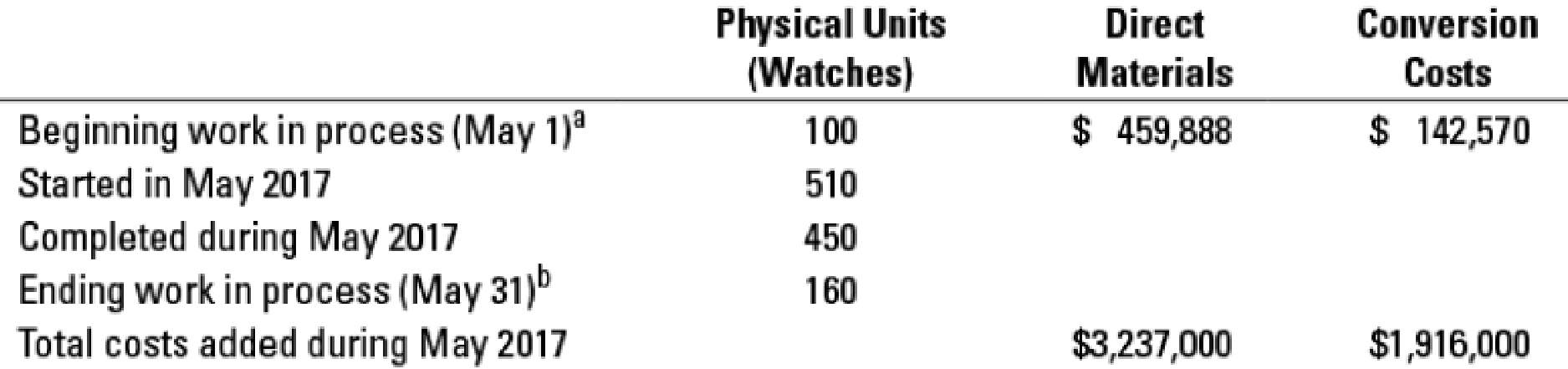
a Degree of completion: direct materials. 80%: conversion costs, 35%.
b Degree of completion: direct materials, 80%; conversion costs, 40%.
Compute equivalent units for direct materials and conversion costs. Show physical units in the first column of your schedule.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

Chapter 17 Solutions
Horngren's Cost Accounting, Student Value Edition (16th Edition)
Additional Business Textbook Solutions
Operations Management: Processes and Supply Chains (12th Edition) (What's New in Operations Management)
Macroeconomics
Intermediate Accounting (2nd Edition)
Financial Accounting, Student Value Edition (5th Edition)
Foundations Of Finance
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis (16th Edition)
 Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College PubPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College PubPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning




