
Concept explainers
Give the IUPAC name for each compounds.
a. 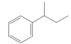 c.
c. 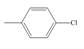 e.
e. 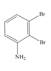 g.
g. 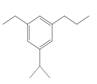
b. 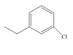 d.
d. 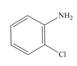 f.
f. 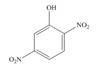 h.
h. 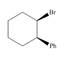
(a)
Interpretation: The IUPAC name of the given compound is to be stated.
Concept introduction: IUPAC nomenclature is a systematic way of naming the organic compounds. The basic principles of IUPAC naming for benzene derivatives are:
1. The compound consists of benzene ring is named as substituent followed by benzene.
2. When the ring is mono-substituted, then there is no need of numbering.
3. When the ring is substituted with same substituents, then numbering to one substituent is given and for other substituent, numbering proceed from clockwise or anticlockwise such that it gets lower number.
4. When the ring is substituted with different substituents, then the numbering is done according to priority.
5. Substituents on benzene ring is also indicated using ortho, meta, para prefix. The prefix ortho is used when substituents are on adjacent carbon, meta is used when substituents are separated by one carbon atom, para is used when substituents are across each other in benzene ring.
Answer to Problem 17.27P
The IUPAC name of the given compound is
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is,
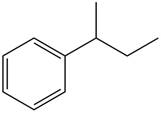
Figure 1
The parent ring is benzene. The substituent attached to the benzene ring is sec-butyl. Therefore, the IUPAC name of the given compound is
The IUPAC name of the given compound is
(b)
Interpretation: The IUPAC name of the given compound is to be stated.
Concept introduction: IUPAC nomenclature is a systematic way of naming the organic compounds. The basic principles of IUPAC naming for benzene derivatives are:
1. The compound consists of benzene ring is named as substituent followed by benzene.
2. When the ring is mono-substituted, then there is no need of numbering.
3. When the ring is substituted with same substituents, then numbering to one substituent is given and for other substituent, numbering proceed from clockwise or anticlockwise such that it gets lower number.
4. When the ring is substituted with different substituents, then the numbering is done according to priority.
5. Substituents on benzene ring is also indicated using ortho, meta, para prefix. The prefix ortho is used when substituents are on adjacent carbon, meta is used when substituents are separated by one carbon atom, para is used when substituents are across each other in benzene ring.
Answer to Problem 17.27P
The IUPAC name of the given compound is
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is,
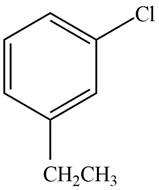
Figure 2
The parent ring is benzene. Chlorine atom is present on first carbon atom and ethyl group is present on third carbon atom. The two substituents are separated by one carbon atom. The IUPAC name of the given compound is
The IUPAC name of the given compound is
(c)
Interpretation: The IUPAC name of the given compound is to be stated.
Concept introduction: IUPAC nomenclature is a systematic way of naming the organic compounds. The basic principles of IUPAC naming for benzene derivatives are:
1. The compound consists of benzene ring is named as substituent followed by benzene.
2. When the ring is mono-substituted, then there is no need of numbering.
3. When the ring is substituted with same substituents, then numbering to one substituent is given and for other substituent, numbering proceed from clockwise or anticlockwise such that it gets lower number.
4. When the ring is substituted with different substituents, then the numbering is done according to priority.
5. Substituents on benzene ring is also indicated using ortho, meta, para prefix. The prefix ortho is used when substituents are on adjacent carbon, meta is used when substituents are separated by one carbon atom, para is used when substituents are across each other in benzene ring.
Answer to Problem 17.27P
The IUPAC name of the given compound is
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is,
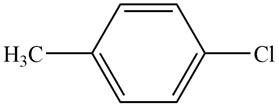
Figure 3
The parent ring is benzene. Chlorine atom is present on first carbon atom and methyl group is present on fourth carbon atom. The two substituents are across each other in benzene ring. The IUPAC name of the given compound is
The IUPAC name of the given compound is
(d)
Interpretation: The IUPAC name of the given compound is to be stated.
Concept introduction: IUPAC nomenclature is a systematic way of naming the organic compounds. The basic principles of IUPAC naming for benzene derivatives are:
1. The compound consists of benzene ring is named as substituent followed by benzene.
2. When the ring is mono-substituted, then there is no need of numbering.
3. When the ring is substituted with same substituents, then numbering to one substituent is given and for other substituent, numbering proceed from clockwise or anticlockwise such that it gets lower number.
4. When the ring is substituted with different substituents, then the numbering is done according to priority.
5. Substituents on benzene ring is also indicated using ortho, meta, para prefix. The prefix ortho is used when substituents are on adjacent carbon, meta is used when substituents are separated by one carbon atom, para is used when substituents are across each other in benzene ring.
Answer to Problem 17.27P
The IUPAC name of the given compound is
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is,
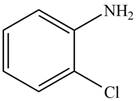
Figure 4
The parent ring is aniline. Chlorine atom and amine group are adjacent to each other in benzene ring. The IUPAC name of the given compound is
The IUPAC name of the given compound is
(e)
Interpretation: The IUPAC name of the given compound is to be stated.
Concept introduction: IUPAC nomenclature is a systematic way of naming the organic compounds. The basic principles of IUPAC naming for a benzene derivatives are:
1. The compound consists of benzene ring is named as substituent followed by benzene.
2. When the ring is mono-substituted, then there is no need of numbering.
3. When the ring is substituted with same substituents, then numbering to one substituent is given and for other substituent, numbering proceed from clockwise or anticlockwise such that it gets lower number.
4. When the ring is substituted with different substituents, then the numbering is done according to priority.
5. Substituents on benzene ring is also indicated using ortho, meta, para prefix. The prefix ortho is used when substituents are on adjacent carbon, meta is used when substituents are separated by one carbon atom, para is used when substituents are across each other in benzene ring.
Answer to Problem 17.27P
The IUPAC name of the given compound is
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is,
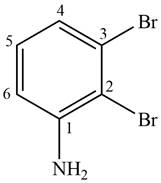
Figure 5
The parent ring is aniline. Two bromine atoms are present on second and third position. When same substituents are present then prefix depends on number of substituents are used. The IUPAC name of the given compound is
The IUPAC name of the given compound is
(f)
Interpretation: The IUPAC name of the given compound is to be stated.
Concept introduction: IUPAC nomenclature is a systematic way of naming the organic compounds. The basic principles of IUPAC naming for a benzene derivatives are:
1. The compound consists of benzene ring is named as substituent followed by benzene.
2. When the ring is mono-substituted, then there is no need of numbering.
3. When the ring is substituted with same substituents, then numbering to one substituent is given and for other substituent, numbering proceed from clockwise or anticlockwise such that it gets lower number.
4. When the ring is substituted with different substituents, then the numbering is done according to priority.
5. Substituents on benzene ring is also indicated using ortho, meta, para prefix. The prefix ortho is used when substituents are on adjacent carbon, meta is used when substituents are separated by one carbon atom, para is used when substituents are across each other in benzene ring.
Answer to Problem 17.27P
The IUPAC name of the given compound is
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is,
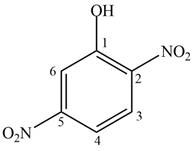
Figure 6
The parent ring is phenol. Two nitro groups are present on second and fifth position. When same substituents are present then prefix depends on number of substituents are used. The IUPAC name of the given compound is
The IUPAC name of the given compound is
(g)
Interpretation: The IUPAC name of the given compound is to be stated.
Concept introduction: IUPAC nomenclature is a systematic way of naming the organic compounds. The basic principles of IUPAC naming for a benzene derivatives are:
1. The compound consists of benzene ring is named as substituent followed by benzene.
2. When the ring is mono-substituted, then there is no need of numbering.
3. When the ring is substituted with same substituents, then numbering to one substituent is given and for other substituent, numbering proceed from clockwise or anticlockwise such that it gets lower number.
4. When the ring is substituted with different substituents, then the numbering is done according to priority.
5. Substituents on benzene ring is also indicated using ortho, meta, para prefix. The prefix ortho is used when substituents are on adjacent carbon, meta is used when substituents are separated by one carbon atom, para is used when substituents are across each other in benzene ring.
Answer to Problem 17.27P
The IUPAC name of the given compound is
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is,
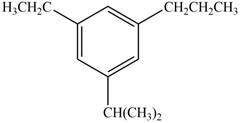
Figure 7
The parent ring is benzene. Ethyl group is present on second carbon atom, isopropyl group on third carbon atom and propyl group on fifth position. When same substituents are present then prefix depends on number of substituents are used. The IUPAC name of the given compound is
The IUPAC name of the given compound is
(h)
Interpretation: The IUPAC name of the given compound is to be stated.
Concept introduction: IUPAC nomenclature is a systematic way of naming the organic compounds. The basic principles of IUPAC naming for a cycloalkane are:
1. The cycloalkane is named after its parent hydrocarbon chain with a prefix cyclo.
2. When the ring is mono-substituted then there is no need of numbering.
3. When the ring is substituted with same substituents then numbering to one substituent is given and for other substituent numbering proceed from clockwise or anticlockwise such that it gets lower number.
4. When the ring is substituted with different substituents, then the numbering is done according to priority.
5. When alkyl chain has more carbon atoms than the cycloalkane then, the substituent is named as cycloalkyl group.
Answer to Problem 17.27P
The IUPAC name of the given compound is
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is,
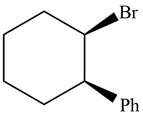
Figure 8
The number of carbon atoms in ring is six. Hence, its parent cycloalkane is cyclohexane.. Bromine atom is present on first carbon atom and phenyl group is present on second carbon atom. Both groups points in the same direction. The IUPAC name of the given compound is
The IUPAC name of the given compound is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
Package: Loose Leaf for Organic Chemistry with Biological Topics with Connect Access Card
- Quantum mechanics. In translational motion, the summation is replaced by an integral when evaluating the partition function. This is correct becausea) the spacing of the translational energy levels is very small compared to the product kTb) the spacing of the translational energy levels is comparable to the product kTc) the spacing of the translational energy levels is very large compared to the product kTarrow_forwardDon't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardPlease correct answer and don't used hand raiting don't used Ai solutionarrow_forward
- If the viscosity of hydrogen gas (at 0oC and 1 atm) is 8.83x10-5 P. If we assume that the molecular sizes are equal, calculate the viscosity of a gas composed of deuterium.arrow_forwardIf the viscosity of hydrogen gas (at 0oC and 1 atm) is 8.83x10-5 P. If we assume that the molecular sizes are equal, calculate the viscosity of a gas composed of deuterium.arrow_forwardLaser. Indicate the relationship between metastable state and stimulated emission.arrow_forward
- The table includes macrostates characterized by 4 energy levels (&) that are equally spaced but with different degrees of occupation. a) Calculate the energy of all the macrostates (in joules). See if they all have the same energy and number of particles. b) Calculate the macrostate that is most likely to exist. For this macrostate, show that the population of the levels is consistent with the Boltzmann distribution. macrostate 1 macrostate 2 macrostate 3 ε/k (K) Populations Populations Populations 300 5 3 4 200 7 9 8 100 15 17 16 0 33 31 32 DATO: k = 1,38×10-23 J K-1arrow_forwardDon't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardIn an experiment, the viscosity of water was measured at different temperatures and the table was constructed from the data obtained. a) Calculate the activation energy of viscous flow (kJ/mol). b) Calculate the viscosity at 30°C. T/°C 0 20 40 60 80 η/cpoise 1,972 1,005 0,656 0,469 0,356arrow_forward
- Don't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardLet's see if you caught the essentials of the animation. What is the valence value of carbon? a) 4 b) 2 c) 8 d) 6arrow_forwardA laser emits a line at 632.8 nm. If the cavity is 12 cm long, how many modes oscillate in the cavity? How long does it take for the radiation to travel the entire cavity? What is the frequency difference between 2 consecutive modes?(refractive index of the medium n = 1).arrow_forward
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning


