
Concept explainers
A uniform slender rod is placed at corner B and is given a slight clockwise motion. Assuming that the corner is sharp and becomes slightly embedded in the end of the rod so that the coefficient of static friction at B is very large, determine (a) the angle β through which the rod will have rotated when it loses contact with the corner, (b) the corresponding velocity of end A.
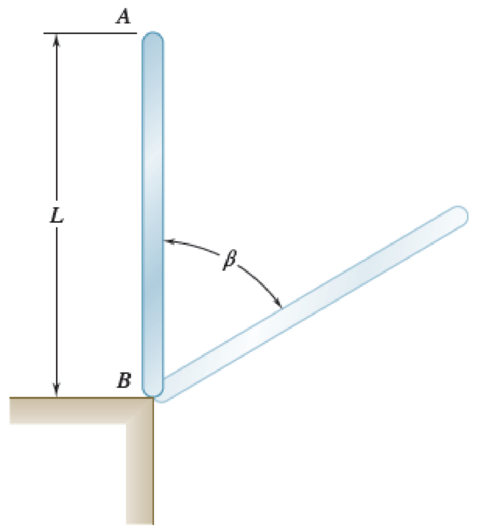
Fig. P17.139
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 17 Solutions
VECTOR MECHANIC
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects (7th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Elementary Surveying: An Introduction To Geomatics (15th Edition)
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Java How to Program, Early Objects (11th Edition) (Deitel: How to Program)
Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications
- Need helparrow_forwardY F1 α В X F2 You and your friends are planning to move the log. The log. needs to be moved straight in the x-axis direction and it takes a combined force of 2.9 kN. You (F1) are able to exert 610 N at a = 32°. What magnitude (F2) and direction (B) do you needs your friends to pull? Your friends had to pull at: magnitude in Newton, F2 = direction in degrees, ẞ = N degarrow_forwardProblem 1 8 in. in. PROBLEM 15.109 Knowing that at the instant shown crank BC has a constant angular velocity of 45 rpm clockwise, determine the acceleration (a) of Point A, (b) of Point D. 8 in. Answer: convert rpm to rad/sec first. (a). -51.2j in/s²; (b). 176.6 i + 50.8 j in/s²arrow_forward
- Problem 4 The semicircular disk has a radius of 0.4 m. At one instant, when 0-60°, it is rotating counterclockwise at 0-4 rad/s, which is increasing in the same direction at 1 rad/s². Find the velocity and acceleration of point B at this instant. (Suggestion: Set up relative velocity and relative acceleration that way you would for a no-slip disk; remember what I told you to memorize on the first day of class.) (Answer: B = −2.98î - 0.8ĵ m/s, ãB = 2.45î - 5.74ĵ m/s²) B 0.4 m y Xarrow_forwardA C C 2r A 2r B B (a) (b) Problem 3 Refer to (b) of the figure shown above. The disk OA is now rolling with no slip at a constant angular velocity of w. Find the angular velocity and angular acceleration of link AB and BC. (Partial Answers: WBC = 2wk, AB = w²k)arrow_forwardProblem 2 Refer to (a) of the figure shown below, where the disk OA rotates at a constant angular velocity of w. Find the angular velocity and angular acceleration of link AB and link BC. (Partial Answers: WBC = wk, AB = w²k) A 2r C B (a) A 2r B (b)arrow_forward
- Example Two rotating rods are connected by slider block P. The rod attached at A rotates with a constant clockwise angular velocity WA. For the given data, determine for the position shown (a) the angular velocity of the rod attached at B, (b) the relative velocity of slider block P with respect to the rod on which it slides. b = 8 in., w₁ = 6 rad/s. Given: b = 8 in., WA = 6 rad/s CW constant Find: (a). WBE (b). Vp/Frame E 60° 20° Barrow_forwardY F1 α В X F2 You and your friends are planning to move the log. The log. needs to be moved straight in the x-axis direction and it takes a combined force of 2.9 kN. You (F1) are able to exert 610 N at a = 32°. What magnitude (F2) and direction (B) do you needs your friends to pull? Your friends had to pull at: magnitude in Newton, F2 = direction in degrees, ẞ = N degarrow_forward100 As a spring is heated, its spring constant decreases. Suppose the spring is heated and then cooled so that the spring constant at time t is k(t) = t sin + N/m. If the mass-spring system has mass m = 2 kg and a damping constant b = 1 N-sec/m with initial conditions x(0) = 6 m and x'(0) = -5 m/sec and it is subjected to the harmonic external force f (t) = 100 cos 3t N. Find at least the first four nonzero terms in a power series expansion about t = 0, i.e. Maclaurin series expansion, for the displacement: • Analytically (hand calculations) Creating Simulink Model Plot solutions for first two, three and four non-zero terms as well as the Simulink solution on the same graph for the first 15 sec. The graph must be fully formatted by code.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





