
Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics (14th Edition)
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780133915389
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
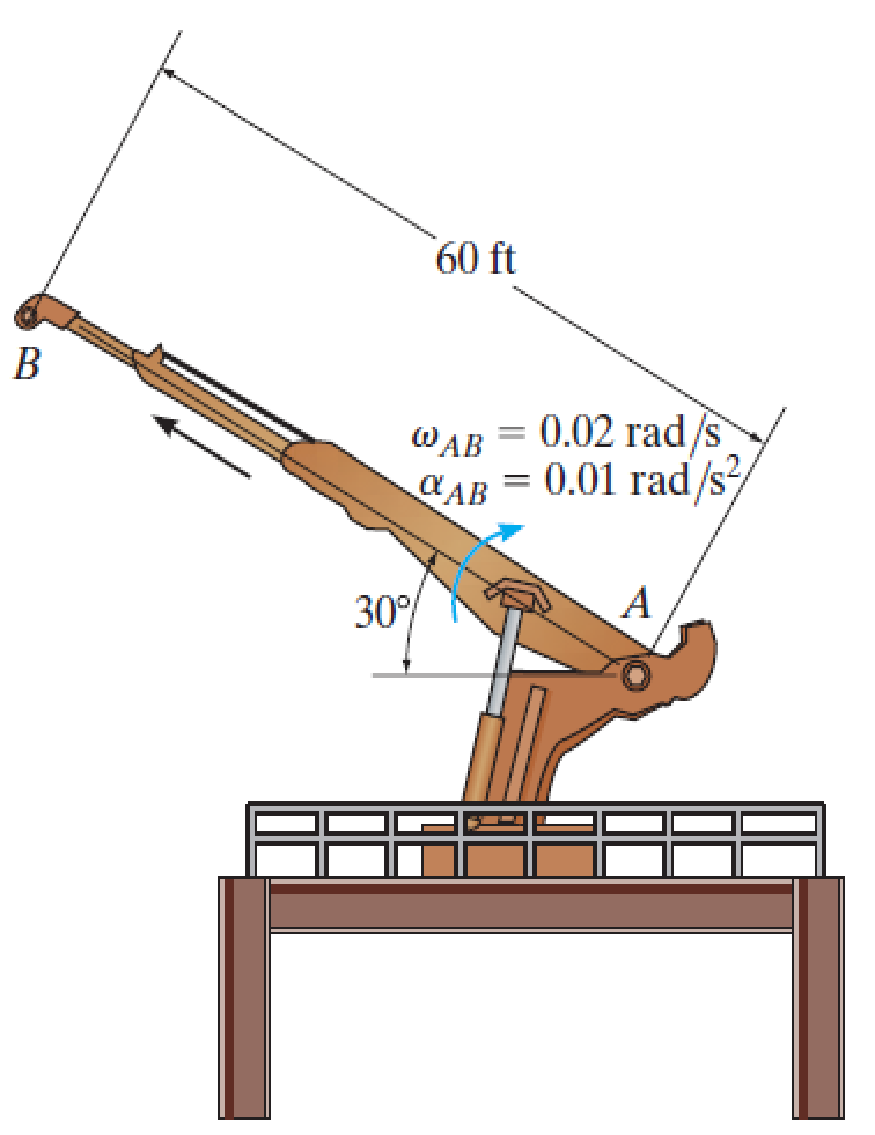
Chapter 16.8, Problem 130P
At the same instant, the boom is extending with a constant speed of 0.5 ft/s, measured relative to the boom. Determine the magnitudes of the velocity and acceleration of point B at this instant.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
The hinged rod is rotating counterclockwise at a rate of 1rad/s. The slider moves with
respect to the rod at a rate of 1m/s in the direction shown. At this moment, the slider
is located 1m from the rod's hinge, and the rod is at the angle shown. Find the x
component of the slider's total velocity.
35°
1 m/s
1 radis
X
Answer(s):
The bent flat bar rotates about a fixed axis through point O. The angle can be found at any instant
according to this relation 8 = sin(t), where 0 is in rad and t is in seconds. At this instant, determine
the instantaneous velocity and acceleration of point A. Note: w=0, a = 0. Also, you must change the
angle from (Degree) to (Rad)
a
I
0.5 m
A
0.3 m
105⁰
30°
Thex-and y-motions of guides A and Bwith right-angle slots control the curvilinear mation of the connecting pin P. which slides in
bath slots. For a short interval, the motions are governed byx- 19+0.47 and y - 19 - 0.90P. wherexand y are in millimeters and tis
in seconds. Calculate the magnitudes of the velocity v and acceleration a of the pin for t-23s. Sketch the direction of the path and
indicate its curvature for this instant.
Calculate the x- and y-components of the acceleration.
Answers:
mm/s?
0.94
a,-
-12.42
mm/s?
Calculate the x- and y-components of the velocity.
Answers:
2.162
mm/s
Vy"
-14.283
mm/s
Chapter 16 Solutions
Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics (14th Edition)
Ch. 16.3 - Determine its constant angular acceleration and...Ch. 16.3 - Determine the angular acceleration when it has...Ch. 16.3 - Determine the time it takes to achieve an angular...Ch. 16.3 - If the angular displacement of the wheel is =...Ch. 16.3 - Determine the magnitude of the velocity and...Ch. 16.3 - Determine the velocity of the cylinder and the...Ch. 16.3 - Determine the magnitudes of the velocity and...Ch. 16.3 - If the disk is originally rotating at 0 = 12...Ch. 16.3 - It it is subjected to a constant angular...Ch. 16.3 - If it is subjected to a constant angular...
Ch. 16.3 - Determine the number of revolutions, the angular...Ch. 16.3 - Determine the number of revolutions it must...Ch. 16.3 - Also, find the number of revolutions of gear D to...Ch. 16.3 - Gears A, B, C, and D have radii of 15 mm, 50 mm,...Ch. 16.3 - Determine the magnitude of acceleration of point B...Ch. 16.3 - pulley A is given a constant angular acceleration...Ch. 16.3 - Starting from rest, determine the angular...Ch. 16.3 - If the engine turns pulley A at A = (20t + 40)...Ch. 16.3 - If the engine turns pulley A at A = 60 rad/s,...Ch. 16.3 - Determine the angular velocity of the disk and its...Ch. 16.3 - Determine the magnitudes of the normal and...Ch. 16.3 - Determine the magnitudes of the normal and...Ch. 16.3 - If this gear is initially turning at A = 15 rad/s,...Ch. 16.3 - If this gear is initially turning at A = 15 rad/s,...Ch. 16.3 - Determine the brushs angular velocity when t = 4...Ch. 16.3 - If this gear is initially turning at (A)0 = 20...Ch. 16.3 - Determine the magnitudes of the velocity and the n...Ch. 16.3 - If the motor turns gear A with an angular...Ch. 16.3 - If the motor turns gear A with an angular...Ch. 16.3 - and the meshed pinion gear B on the propeller...Ch. 16.3 - determine the magnitude of the velocity and...Ch. 16.3 - If the gears A and have the dimensions shown,...Ch. 16.3 - and the meshed pinion gear B on the propeller...Ch. 16.3 - and the meshed pinion gear B on the propeller...Ch. 16.3 - If the canisters are centered 200 mm apart on the...Ch. 16.3 - Determine the largest angular velocity of gear B...Ch. 16.3 - The shaft of the motor M turns with an angular...Ch. 16.3 - If A has a constant angular acceleration of A = 30...Ch. 16.3 - If the angular displacement of A it A = (5t3 +...Ch. 16.3 - This gear is connected to gear B, which is fixed...Ch. 16.3 - Express the result in Cartesian vector form.Ch. 16.3 - Determine the velocity and acceleration of point D...Ch. 16.3 - At the instant shown it is rotating about the y...Ch. 16.3 - Determine the magnitudes of the velocity and...Ch. 16.4 - Determine the angular velocity and angular...Ch. 16.4 - Determine the angular acceleration and angular...Ch. 16.4 - Determine the angular acceleration and angular...Ch. 16.4 - Determine the angular velocity and angular...Ch. 16.4 - Determine the angular velocity of the connecting...Ch. 16.4 - The cam rotates with a constant counterclockwise...Ch. 16.4 - The pin connection at O does not cause an...Ch. 16.4 - Determine the velocity of the follower rod AB as...Ch. 16.4 - The pin connection at O does not cause an...Ch. 16.4 - Determine the velocity and acceleration of the peg...Ch. 16.4 - Determine the velocity and acceleration of block...Ch. 16.4 - Determine the angular velocity and angular...Ch. 16.4 - If the slotted arm is causing A to move downward...Ch. 16.4 - If the wedge moves to the left with a constant...Ch. 16.4 - If the rollers do not slip, determine their...Ch. 16.4 - If no slipping occurs between the disk D and the...Ch. 16.4 - Determine the velocity and acceleration of...Ch. 16.5 - If roller A moves to the right with a constant...Ch. 16.5 - Determine the magnitude of the velocity of point B...Ch. 16.5 - The cable wraps around the inner core, and the...Ch. 16.5 - If crank OA rotates with an angular velocity of =...Ch. 16.5 - If rod AB slides along the horizontal slot with a...Ch. 16.5 - Determine the velocity of the peg at B at this...Ch. 16.5 - Determine the velocity of point B at this instant.Ch. 16.5 - If the block at C is moving downward at 4 ft/s,...Ch. 16.5 - Determine the velocity of block C and the angular...Ch. 16.5 - Determine the angular velocities of links A B and...Ch. 16.5 - Also, sketch the position of link BC when = 55,...Ch. 16.5 - Link BC rotates clockwise with an angular velocity...Ch. 16.5 - If the angular velocity of link AB is AB = 3...Ch. 16.5 - Determine the velocity of the gear rack C.Ch. 16.5 - If B is moving to the right at 8 ft/s and C is...Ch. 16.5 - Determine the angular velocity of the gear and the...Ch. 16.5 - Determine the velocity of point A on the rim of...Ch. 16.5 - Link CB is horizontal at this instant.Ch. 16.5 - Determine the velocity of the slider C at the...Ch. 16.5 - Determine the velocity of block C and the angular...Ch. 16.5 - If AB has an angular velocity AB = 8 rad/s,...Ch. 16.5 - If the slider block A is moving downward at vA = 4...Ch. 16.5 - If the slider block A is moving downward at A = 4...Ch. 16.5 - This gear has an inner hub C which is fixed to B...Ch. 16.5 - If link AB is rotating at AB =3 rad/s, determine...Ch. 16.5 - If link CD is rotating at CD = 5 rad/s, determine...Ch. 16.5 - By locking or releasing certain gears, it has the...Ch. 16.5 - If the ring gear A rotates clockwise with an...Ch. 16.5 - It consists of a driving piston A, three links,...Ch. 16.5 - Because of the rotational motion of lint AB and...Ch. 16.6 - Establish the location of the instantaneous center...Ch. 16.6 - Determine the angular velocity of the rod and the...Ch. 16.6 - Determine the angular velocity of link BC and...Ch. 16.6 - The gear rack B is fixed.Ch. 16.6 - If cable AB is unwound with a speed of 3 m/s, and...Ch. 16.6 - Determine the angular velocity of link BC and the...Ch. 16.6 - Determine the angular velocity of links BC and CD...Ch. 16.6 - Assume the geometry is known.Ch. 16.6 - Determine the angular velocity of link AB at the...Ch. 16.6 - Determine the angular velocity of the link CB at...Ch. 16.6 - Determine the velocities of the cylinders center C...Ch. 16.6 - Determine the velocities of points A and B on the...Ch. 16.6 - Determine the velocities of points A and B.Ch. 16.6 - If rod CD is rotating with an angular velocity CD...Ch. 16.6 - If bar AB has an angular velocity AB = 6 rad/s,...Ch. 16.6 - Under these conditions, what is the speed at A if...Ch. 16.6 - Due to slipping, points A and B on the rim of the...Ch. 16.6 - Determine the velocities of the center point C and...Ch. 16.6 - Determine the velocity of point D and the angular...Ch. 16.6 - Determine the velocity of point P, and the angular...Ch. 16.6 - If connected bar CD is rotating with an angular...Ch. 16.6 - Determine the speeds of points A, B, and C caused...Ch. 16.6 - Determine the velocity of the gear rack C.Ch. 16.6 - If the hub gear H and ring gear R have angular...Ch. 16.6 - What is the angular velocity of the spur gear?Ch. 16.6 - Determine the angular velocity of rod CD at the...Ch. 16.6 - If bar CD is rotating with an angular velocity of...Ch. 16.6 - If the link rotates about the fixed point B at 4...Ch. 16.7 - if the sun gear D is rotating clockwise at D = 5...Ch. 16.7 - The angular velocity is given.Ch. 16.7 - Determine the angular acceleration of the rod and...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the acceleration of point A.Ch. 16.7 - At the instant shown, the center O of the gear...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the angular acceleration of the gear at...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the angular acceleration of link BC at...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the angular acceleration of link BC and...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the velocity sod acceleration of the...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the acceleration of the top of the...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the acceleration of the bottom A of the...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the velocity and acceleration of the...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the velocity and acceleration of the...Ch. 16.7 - At the instant shown, point A has the motion...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the angular velocity and angular...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the angular velocity and angular...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the angular acceleration of link AB and...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the angular acceleration of link CD if...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the velocity and acceleration of point A...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the velocity and acceleration of point B...Ch. 16.7 - If it is pulled with a constant velocity v,...Ch. 16.7 - If it does not slip at A, determine the...Ch. 16.7 - If it does not slip at A, determine the...Ch. 16.7 - As cord CF unwinds from the inner rim of the...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the velocity and acceleration of point B...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the angular velocity and angular...Ch. 16.7 - If link DE has the angular motion shown, determine...Ch. 16.7 - If member AB has the angular motion shown,...Ch. 16.7 - If member AB has the angular motion shown,...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the acceleration of points A and B on...Ch. 16.7 - At a given instant, A has a velocity of vA = 4...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the angular acceleration of rod AB at...Ch. 16.8 - Determine the acceleration of A at the instant...Ch. 16.8 - If at the same instant the disk has the angular...Ch. 16.8 - At the same instant, the boom is extending with a...Ch. 16.8 - Prob. 131PCh. 16.8 - Prob. 132PCh. 16.8 - Determine the velocity and acceleration of a water...Ch. 16.8 - At the instant shown, the cord is pulled down...Ch. 16.8 - Prob. 135PCh. 16.8 - Determine the velocity and acceleration of point C...Ch. 16.8 - Prob. 137PCh. 16.8 - Determine the magnitudes of the velocity and...Ch. 16.8 - If link AD is rotating at a constant rate of AD =...Ch. 16.8 - Determine the angular velocity and angular...Ch. 16.8 - If rod AB has an angular velocity of 2 rad/s and...Ch. 16.8 - Prob. 142PCh. 16.8 - If the gears center O moves with the velocity and...Ch. 16.8 - Prob. 144PCh. 16.8 - Prob. 145PCh. 16.8 - Also at this instant the car mounted at the end of...Ch. 16.8 - If the slider block C is fixed to the disk that...Ch. 16.8 - Determine the velocity and acceleration of car A...Ch. 16.8 - Determine the velocity and acceleration of car B...Ch. 16.8 - Link AB has a pin at B which is confined to move...Ch. 16.8 - Prob. 151PCh. 16.8 - The star wheel A makes one sixth of a revolution...Ch. 16.8 - If the tires do not slip on the pavement,...Ch. 16.8 - Determine the velocity and deceleration of the...Ch. 16.8 - Determine the speed of block B when it has risen s...Ch. 16.8 - At the instant shown, it has an acceleration of...Ch. 16.8 - If bar AB has an angular velocity AB = 6 rad/s,...Ch. 16.8 - If the cable does not slip on the pulley's...Ch. 16.8 - Determine the acceleration of the pin at C and the...Ch. 16.8 - If it does not slip at A, determine the...Ch. 16.8 - Determine the velocity and acceleration of the...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The jet plane travels along the vertical parabolic path. When it is at point A it has a speed of 200 m/s, which is increasing at the rate of 0.8 m/s^2 . Determine the magnitude of acceleration of the plane when it is at point Aarrow_forwardA car moving with constant speed from point A and sinks to point B of the hump. The radius of curvature of the road at point A is KA=120m and acceleration at A is 0.5g. Determine the car speed V if at point B acceleration is limited to 0.3g. Find the minimum radius of curvature ( KB) of road at point B.arrow_forwardAn airplane is flying in a straight line with a velocity of 200 mi/h and an acceleration of 3 mi/h^2. If the propeller has a diameter of 6 ft and is rotating at a constant angular rate of 120 rad/s, determine the magnitudes of velocity and acceleration of a particle located on the tip of the propeller.arrow_forward
- A car is traveling around a circular track of 840-ft radius. If the magnitude of its total acceleration is 6.2 ft/sec2 at the instant when its speed is 42 mi/hr, determine the rate at at which the car is changing its speed. Answer: at = ± ft/sec2arrow_forwardAt the instant shown, the truck moves to the right at 3 m/s, while the tube rolls counterclockwise at 6 rad/without sliding on B. Determine the speed of the center G of the tube. G1.5 m 3 m/s Вarrow_forwardThe collar A slides along the rod OB, which is rotating counterclockwise.Determine the velocity vector of A when OB is vertical, given that the speedof end B is 0.4 m/s in that position.arrow_forward
- On a curvy road, a motorist applies breaks and the speed of the vehicle is reduced uniformly from 60 km/h at point A to 40 km/h at point B; points A and B are 120 m apart. If the vehicle has a resultant acceleration of 2.5 m/s2 at point A, calculate the radius of the curvature of the road at this point. Calculate also the acceleration of the vehicle at point B where the road has a radius of curvature equal to 90 m. (complete steps)arrow_forwardThe slider P can be moved inward by means of the string S, while the slotted arm rotates about point O. The angular position of the arm is given by 0 = 0.65t - 0.057t2, where 0 is in radians and t is in seconds. The slider is at r = 1.26 m when t = 0 and thereafter is drawn inward at the constant rate of 0.13 m/s. Determine the velocity v and acceleration a of the slider whent = 3.6 s. Express your answers in the x-y coordinate system.arrow_forwardThe slider P can be moved inward by means of the string S, while the slotted arm rotates about point O. The angular position of the arm is given by 0 = 0.53t - 0.036t², where is in radians and t is in seconds. The slider is at r = 1.29 m when t = 0 and thereafter is drawn inward at the constant rate of 0.12 m/s. Determine the velocity v and acceleration a of the slider when t = 3.1 s. Express your answers in the x-y coordinate system. S Answers: At t = 3.1 s, v = ( i -0.12 0.2816 j) m/s a = ( i -0.0864 -0.1397 j) m/s² i+ i+ iarrow_forward
- 3. The hydraulic cylinder C extends and causes the collar A to move and accelerate to the left. 3) If the length /= 1.5 ft, the angle = 33°, the linear velocity of collar A, VÀ is 5.5 ft/s, and the linear acceleration of collar A, a is 3.1 ft/s², determine the magnitude of the angular velocity, WAB, of rod AB. Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 2 places after the decimal point, and proper unit. X Your Answer: Answer k Ө units VA as ←arrow_forwardThe slider P can be moved inward by means of the string S, while the slotted arm rotates about point O. The angular position of the arm is given by 0 = 0.74t -0.046t², where is in radians and t is in seconds. The slider is at r = 1.39 m when t = 0 and thereafter is drawn inward at the constant rate of 0.14 m/s. Determine the velocity v and acceleration a of the slider when t = 2.9 s. Express your answers in the x-y coordinate system. Answers: At t = 2.9 s, v = ( i a=i -0.3018 -0.08977 i+ i -1.8605 i+ i -0.9043 j) m/s j) m/s²arrow_forwardThe slider P can be moved inward by means of the string S, while the slotted arm rotates about point O. The angular position of the arm is given by 0 = 0.84t - 0.056t2, where is in radians and t is in seconds. The slider is at r = 1.42 m when t = 0 and thereafter is drawn inward at the constant rate of 0.15 m/s. Determine the velocity v and acceleration a of the slider when t = 2.5 s. Express your answers in the x-y coordinate system. Answers: At t = 2.5 s, v = (i a = ( IN p x i+ i+ i j) m/s j) m/s²arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Dynamics - Lesson 1: Introduction and Constant Acceleration Equations; Author: Jeff Hanson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7aMiZ3b0Ieg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY