
Concept explainers
a)
Interpretation:
The structure of phenyl acetate has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Nomenclature of carboxylate (ester): Carboxylate (deprotonated form of

b)
Interpretation:
The structure of
Concept Introduction:
Nomenclature of Lactam: Cyclic amides are called lactam. In systematic name, ‘2-azacycloalkanones’ (‘aza’- indicates the nitrogen atom). For, common name, the length of the carbon chain is indicated by the common name of the carboxylic acid, and a Greek letter specifies the carbon to which the nitrogen is attached. 6-membered ring lactams are
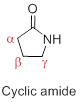
c)
Interpretation:
The structure of N-benzylethanamide has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Nomenclature of Amides: Amides are named by replacing ‘oic acid’, ‘ic’ acid, or ‘ylic’ acid of the acid name with ‘amide’. If a substituent is bonded to the nitrogen, the name of the substituent is stated first (if more, stated in alphabetical order) followed by the name of the amide. The name of each substituent is preceded by N to indicate that the substituent is bonded to a nitrogen.
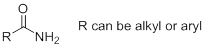
d)
Interpretation:
The structure of
Concept Introduction:
Nomenclature of carboxylic acid: Carboxylic acid is named by replacing the terminal ‘e’ of the
Carboxylic acids in which a carboxyl group is attached to a ring are named by adding ‘carboxylic acid’ to the name of the cyclic compound.
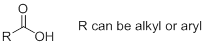
e)
Interpretation:
The structure of ethyl 2-chloropentanoate has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Nomenclature of carboxylate (ester): Carboxylate (deprotonated form of carboxylic acid) is named by replacing the terminal ‘oic acid’ of the name with ‘oate’. In common nomenclature, the position of a substituent is designated by a lowercase Greek letter, and the carbonyl carbon is not given a designation. Thus, the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl carbon is the alpha-carbon, the carbon adjacent to the alpha-carbon is the beta-carbon, and so on.

f)
Interpretation:
The structure of
Concept Introduction:
Nomenclature of Amides: Amides are named by replacing ‘oic acid’, ‘ic’ acid, or ‘ylic’ acid of the acid name with ‘amide’. If a substituent is bonded to the nitrogen, the name of the substituent is stated first (if more, stated in alphabetical order) followed by the name of the amide. The name of each substituent is preceded by a N to indicate that the substituent is bonded to a nitrogen.
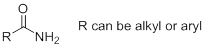
g)
Interpretation:
The structure of cyclohexanecarbonyl chloride has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Nomenclature of Acyl chlorides: Acyl chlorides are named by replacing ‘ic acid’ of the acid name with ‘yl chloride’. For cyclic acids, that end with ‘carboxylic acid’ is replaced with ‘carbonyl chloride’.
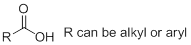
h)
Interpretation:
The structure of
Concept Introduction:
Nomenclature of carboxylic acid: Carboxylic acid is named by replacing the terminal ‘e’ of the alkane or alkene name with ‘oic acid’. In common nomenclature, the position of a substituent is designated by a lowercase Greek letter, and the carbonyl carbon is not given a designation. Thus, the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl carbon is the alpha-carbon, the carbon adjacent to the alpha-carbon is the beta-carbon, and so on.
Carboxylic acids in which a carboxyl group is attached to a ring are named by adding ‘carboxylic acid’ to the name of the cyclic compound.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 16 Solutions
Organic Chemistry; Modified MasteringChemistry with Pearson eText -- ValuePack Access Card; Study Guide and Student Solutions Manual for Organic Chemistry, Books a la Carte Edition (7th Edition)
- Given the following data, determine the order of the reaction with respect to H2. H2(g) + 21Cl(g) → I2(g) + 2HCl(g) Experiment [H2] (torr) [ICI] (torr) Rate (M/s) 1 250 325 0.266 2 250 81 0.0665 3 50 325 0.266arrow_forwardWhich one of the following molecules is chiral? H- NH₂ H3C དང་།་ OH H HO H₂N HO- -H CHO -OH H HO- OH H- -H CH₂OH OHarrow_forwardThe structure of an unsaturated phospholipid is shown below. Which region of the molecule is most hydrophilic ? H₂N-CH₂ H₂C IV CH3 CH3 hydro-water philic-likes = Hydrophilic likes water ○ IV All regions are equally hydrophilic. IIIarrow_forward
- Which of the following compounds would you most appropriately call hydrophobic? ○ CH4 H2CO CO HCI ○ NaClarrow_forwardWhich of the following triglycerides would you most expect to be a liquid at room temperature? saturated fat trans monounsaturated fat trans polyunsaturated fat cis monounsaturated fat ○ cis polyunsaturated fatarrow_forwardWhich best describes the intermolecular forces present in NH3? dispersion forces only hydrogen bonding and dispersion forces dipole-dipole, hydrogen bonding, and dispersion forces dipole-dipole forces only ion-dipole and dispersion forcesarrow_forward
- List three structural features and corresponding absorption ranges that can be used to identify cyclohexene by IR spectroarrow_forwardThe following chemical structure represents a molecule of what molecular formula? N.arrow_forwardPredict the product(s) of the following reactions. If no reaction, write "NR". a) b) HNO3 H2SO4 SO3 H2SO4 c) Bra FeBr3 Br2, FeBrз OCH3 d) تمنی e) HO f) SO3 H2SO4 CH3Cl NO2 AICI3arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





