
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
To draw the structure of the given compounds.
Concept introduction:
The structure of the organic compound and its name are closely related to each other. The structure of the compound can be drawn if the name is given and vice-versa. The name of an organic compounds tells about the number of carbons present in the compound which is necessary so as to draw the carbon skeleton in the structure. The suffix of the name of the compound provides information about the
(a)
Answer to Problem 55P
The structure of N,N-dimethylhexanamide is:
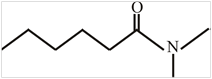
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the compound can be drawn if the name is given and vice-versa. The name of the compound is N,N-dimethylhexanamide. It indicates that six carbons are present in the compound. The suffix is ‘amide’ indicating the presence of an amide group
Thus, the structure is drawn as,

(b)
Interpretation:
To draw the structure of the given compounds.
Concept introduction:
The structure of the organic compound and its name are closely related to each other. The structure of the compound can be drawn if the name is given and vice-versa. The name of an organic compounds tells about the number of carbons present in the compound which is necessary so as to draw the carbon skeleton in the structure. The suffix of the name of the compound provides information about the functional group present in the compound.
(b)
Answer to Problem 55P
The structure of 3,3-dimethylhexanamide is:
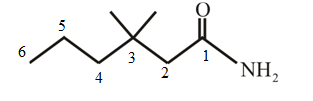
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the compound can be drawn if the name is given and vice-versa. The name of the compound is 3,3-dimethylhexanamide. It indicates that six carbons are present in the compound. The suffix is ‘amide’ indicating the presence of an amide functional group
Thus, the structure is drawn as,

(c)
Interpretation:
To draw the structure of the given compound.
Concept introduction:
The structure of the organic compound and its name are closely related to each other. The structure of the compound can be drawn if the name is given and vice-versa. The name of an organic compounds tells about the number of carbons present in the compound which is necessary so as to draw the carbon skeleton in the structure. The suffix of the name of the compound provides information about the functional group present in the compound.
(c)
Answer to Problem 55P
The structure of
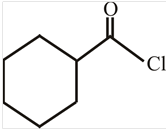
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the compound can be drawn if the name is given and vice-versa. The name of the compound is
Thus, the structure is drawn as,

(d)
Interpretation:
To draw the structure of the given compound.
Concept introduction:
The structure of the organic compound and its name are closely related to each other. The structure of the compound can be drawn if the name is given and vice-versa. The name of an organic compounds tells about the number of carbons present in the compound which is necessary so as to draw the carbon skeleton in the structure. The suffix of the name of the compound provides information about the functional group present in the compound.
(d)
Answer to Problem 55P
The structure of
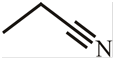
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the compound can be drawn if the name is given and vice-versa. The name of the compound is
Thus, the structure is drawn as,

(e)
Interpretation:
To draw the structure of the given compounds.
Concept introduction:
The structure of the organic compound and its name are closely related to each other. The structure of the compound can be drawn if the name is given and vice-versa. The name of an organic compounds tells about the number of carbons present in the compound which is necessary so as to draw the carbon skeleton in the structure. The suffix of the name of the compound provides information about the functional group present in the compound.
(e)
Answer to Problem 55P
The structure of
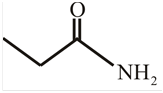
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the compound can be drawn if the name is given and vice-versa. The name of the compound is
Thus, the structure is drawn as,

(f)
Interpretation:
To draw the structure of the given compound.
Concept introduction:
The structure of the organic compound and its name are closely related to each other. The structure of the compound can be drawn if the name is given and vice-versa. The name of an organic compounds tells about the number of carbons present in the compound which is necessary so as to draw the carbon skeleton in the structure. The suffix of the name of the compound provides information about the functional group present in the compound.
(f)
Answer to Problem 55P
The structure of
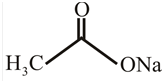
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the compound can be drawn if the name is given and vice-versa. The name of the compound is
Thus, the structure is drawn as,

(g)
Interpretation:
To draw the structure of the given compounds.
Concept introduction:
The structure of the organic compound and its name are closely related to each other. The structure of the compound can be drawn if the name is given and vice-versa. The name of an organic compounds tells about the number of carbons present in the compound which is necessary so as to draw the carbon skeleton in the structure. The suffix of the name of the compound provides information about the functional group present in the compound.
(g)
Answer to Problem 55P
The structure of
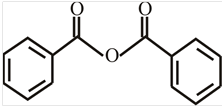
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the compound can be drawn if the name is given and vice-versa. The name of the compound is
The suffix is ‘anhydride’ indicating the presence of indicating the presence of an acid anhydride group in which the
Thus, the structure is drawn as,

(h)
Interpretation:
To draw the structure of the given compound.
Concept introduction: The structure of the organic compound and its name are closely related to each other. The structure of the compound can be drawn if the name is given and vice-versa. The name of an organic compounds tells about the number of carbons present in the compound which is necessary so as to draw the carbon skeleton in the structure. The suffix of the name of the compound provides information about the functional group present in the compound.
(h)
Answer to Problem 55P
The structure of
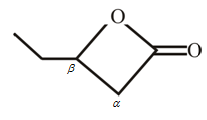
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the compound can be drawn if the name is given and vice-versa. The name of the compound is
Thus, the structure is drawn as,

(i)
Interpretation:
To draw the structure of the given compounds.
Concept introduction:
The structure of the organic compound and its name are closely related to each other. The structure of the compound can be drawn if the name is given and vice-versa. The name of an organic compounds tells about the number of carbons present in the compound which is necessary so as to draw the carbon skeleton in the structure. The suffix of the name of the compound provides information about the functional group present in the compound.
(i)
Answer to Problem 55P
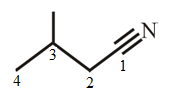
The structure of 3-methylbutanenitrile is:
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the compound can be drawn if the name is given and vice-versa. The name of the compound is 3-methylbutanenitrile. It indicates that four carbons are present in the carbon skeleton of the compound. The suffix is ‘nitrile’ indicating the presence of a nitrile functional group. There is a methyl group on the third carbon in the chain. The numbering of carbons starts from the functional group side.
Thus, the structure is drawn as,

(j)
Interpretation:
To draw the structure of the given compound.
Concept introduction: The structure of the organic compound and its name are closely related to each other. The structure of the compound can be drawn if the name is given and vice-versa. The name of an organic compounds tells about the number of carbons present in the compound which is necessary so as to draw the carbon skeleton in the structure. The suffix of the name of the compound provides information about the functional group present in the compound.
(j)
Answer to Problem 55P
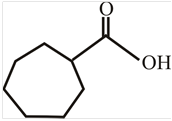
The structure of
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the compound can be drawn if the name is given and vice-versa. The name of the compound is
Thus, the structure is drawn as,

(k)
Interpretation:
To draw the structure of the given compound.
Concept introduction:
The structure of the organic compound and its name are closely related to each other. The structure of the compound can be drawn if the name is given and vice-versa. The name of an organic compounds tells about the number of carbons present in the compound which is necessary so as to draw the carbon skeleton in the structure. The suffix of the name of the compound provides information about the functional group present in the compound.
(k)
Answer to Problem 55P
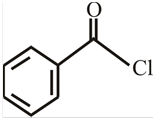
The structure of
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the compound can be drawn if the name is given and vice-versa. The name of the compound is
Thus, the structure is drawn as,

Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Organic Chemistry; Modified MasteringChemistry with Pearson eText -- ValuePack Access Card; Study Guide and Student Solutions Manual for Organic Chemistry, Books a la Carte Edition (7th Edition)
- help draw the moleculearrow_forwardHow to draw this claisen condensation reaction mechanisms/arrow_forwardWrite all of Me Possible Products For each Of the Following reactions. In each case identity all pains of enantiomers, all digsterzoners and all Meso compounds 9. 11-60 11-0-11 V-G Η Η H ~ C-11 +HB+ - 1 H b. पन्ना 171-0-11 H-C-H Н C-C=c-call +HBr Perendez ==arrow_forward
- How can i draw the mechanisms for this molecule?arrow_forwarda. Discuss and explain he difference IN Stability between the Chai and Boat Гольцу от судомехане b. For the Following Molecule draw both possible Clain conformations and explain which one is more stable and for what Reason. H. CH₂ CH₂ H "Harrow_forwarddraw out these molecules pleasearrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





