
Concept explainers
A cylinder that has a 40.0-cm radius and is 50.0 cm deep is filled with air at 20.0°C and 1.00 atm (Fig. P10.74a). A 20.0-kg piston is now lowered into the cylinder, compressing the air trapped inside as it takes equilibrium height hi (Fig. P16.74b). Finally, a 25.0-kg dog stands on the piston, further compressing the air, which remains at 20°C (Fig. P16.74c). (a) How far down (Δh) does the piston move when the dog steps onto it? (b) To what temperature should the gas be warmed to raise the piston and dog back to hi?
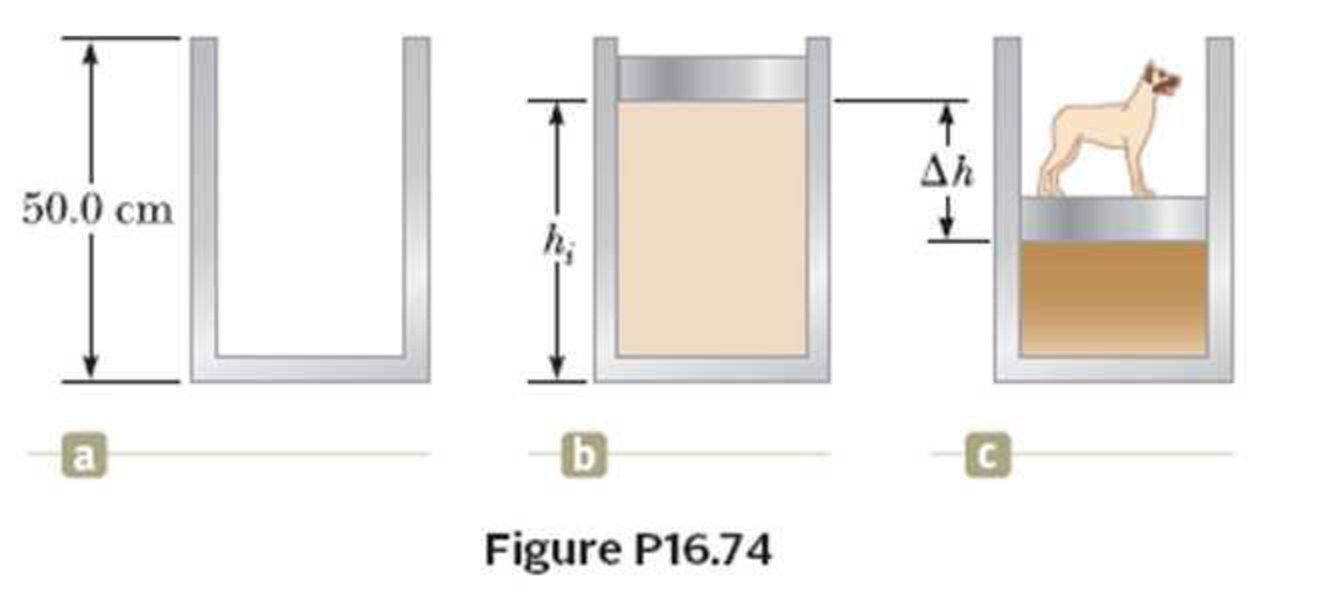
(a)
The height which the piston moves down when the dog steps onto the piston.
Answer to Problem 74P
The height at which the piston move down when the dog steps onto the piston is
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for Boyle’s law, for the initial and final state since the temperature is constant.
Here,
Use
Here,
When the piston moves down, then the external pressure on the piston is
Equate the equation (II) with the equation
Replace the mass
Here,
The piston moves downward when the dog steps on the piston. It can be expressed as,
Use equation (III) and (IV) in (V).
Conclusion:
Substitute,
Therefore, the height at which the piston move down when the dog steps onto the piston is
(b)
The temperature at which the gas should be warmed to raise the piston and dog back to
Answer to Problem 74P
The temperature at which the gas should be warmed to raise the piston and dog back to
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for Charles’s law, for the initial and final state since the pressure is constant.
Here,
Use
Use equation (III) and (IV) in the equation (VIII).
Conclusion:
Substitute,
Therefore, The temperature at which the gas should be warmed to raise the piston and dog back to
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
- Suppose a toy boat moves in a pool at at a speed given by v=1.0 meter per second at t=0, and that the boat is subject to viscous damping. The damping on the boat causes the rate of speed loss to be given by the expression dv/dt=-2v. How fast will the boat be traveling after 1 second? 3 seconds? 10 seconds? Use separation of variables to solve this.arrow_forwardWhat functional form do you expect to describe the motion of a vibrating membrane without damping and why?arrow_forwardIf speed is tripled, how much larger will air drag become for an object? Show the math.arrow_forward
- What does it tell us about factors on which air drag depends if it is proportional to speed squared?arrow_forwardWhat is the net charge on a sphere that has the following? x (a) 5.75 × 106 electrons and 8.49 × 106 protons 4.39e-13 What is the charge of an electron? What is the charge of a proton? C (b) 200 electrons and 109 protons 1.60e-10 What is the charge of an electron? What is the charge of a proton? Carrow_forwardA spider begins to spin a web by first hanging from a ceiling by his fine, silk fiber. He has a mass of 0.025 kg and a charge of 3.5 μC. A second spider with a charge of 4.2 μC rests in her own web exactly 2.1 m vertically below the first spider. (a) What is the magnitude of the electric field due to the charge on the second spider at the position of the first spider? 8.57e3 N/C (b) What is the tension in the silk fiber above the first spider? 0.125 How does the electric field relate to the force? How do you calculate the net force? Narrow_forward
- Point charges of 6.50 μC and -2.50 μC are placed 0.300 m apart. (Assume the negative charge is located to the right of the positive charge. Include the sign of the value in your answers.) (a) Where can a third charge be placed so that the net force on it is zero? 0.49 m to the right of the -2.50 μC charge (b) What if both charges are positive? 0.185 xm to the right of the 2.50 μC chargearrow_forwardc = ad Find the electric field at the location of q, in the figure below, given that q₁ = 9₁ = 9₁ = +4.60 nC, q=-1.00 nC, and the square is 20.0 cm on a side. (The +x axis is directed to the right.) magnitude direction N/C ° counterclockwise from the +x-axis 9a % 9 9barrow_forwardPlastic beads can often carry a small charge and therefore can generate electric fields. Three beads are oriented such that 92 is between q₁ and 93. The sum of the charge on 9₁ and 92 is 9₁ + 92 = −2.9 µС, and the net charge of the system of all three beads is zero. E field lines 93 92 What charge does each bead carry? 91 92 -1.45 What is the net charge of the system? What charges have to be equal? μC 2.9 ✓ What is the net charge of the system? What charges have to be equal? μC 93 2.9 μεarrow_forward
- A spider begins to spin a web by first hanging from a ceiling by his fine, silk fiber. He has a mass of 0.025 kg and a charge of 3.5 μC. A second spider with a charge of 4.2 μC rests in her own web exactly 2.1 m vertically below the first spider. (a) What is the magnitude of the electric field due to the charge on the second spider at the position of the first spider? 8.57e3 N/C (b) What is the tension in the silk fiber above the first spider? 0.275 How does the electric field relate to the force? How do you calculate the net force? Narrow_forwardPlastic beads can often carry a small charge and therefore can generate electric fields. Three beads are oriented such that 92 is between 91 system of all three beads is zero. E field lines 91 92 93 X What charge does each bead carry? 91 = 92 = ?2.9 0 μC × What is the net charge of the system? What charges have to be equal? μC 93 2.9 με and 93. The sum of the charge on 91 and 92 is 91 +92 = -2.9 μC, and the net charge of thearrow_forwardAn electron has an initial speed of 5.26 x 100 m/s in a uniform 5.73 x 105 N/C strength electric field. The field accelerates the electron in the direction opposite to its initial velocity. (a) What is the direction of the electric field? opposite direction to the electron's initial velocity same direction as the electron's initial velocity not enough information to decide × What is the direction of the force on the electron? How does it compare to the direction of the electric field, considering the sign of the electron's charge? (b) How far does the electron travel before coming to rest? 0.0781 × What kinematic equation is relevant here? How do you calculate the force due to the electric field? m (c) How long does it take the electron to come to rest? 5.27e8 What is the final velocity of the electron? s (d) What is the electron's speed when it returns to its starting point? 5.26e6 m/sarrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





