Engineering Circuit Analysis
9th Edition
ISBN: 9780073545516
Author: Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, Kemmerly, Jack E. (jack Ellsworth), Durbin, Steven M.
Publisher: Mcgraw-hill Education,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 16, Problem 5E
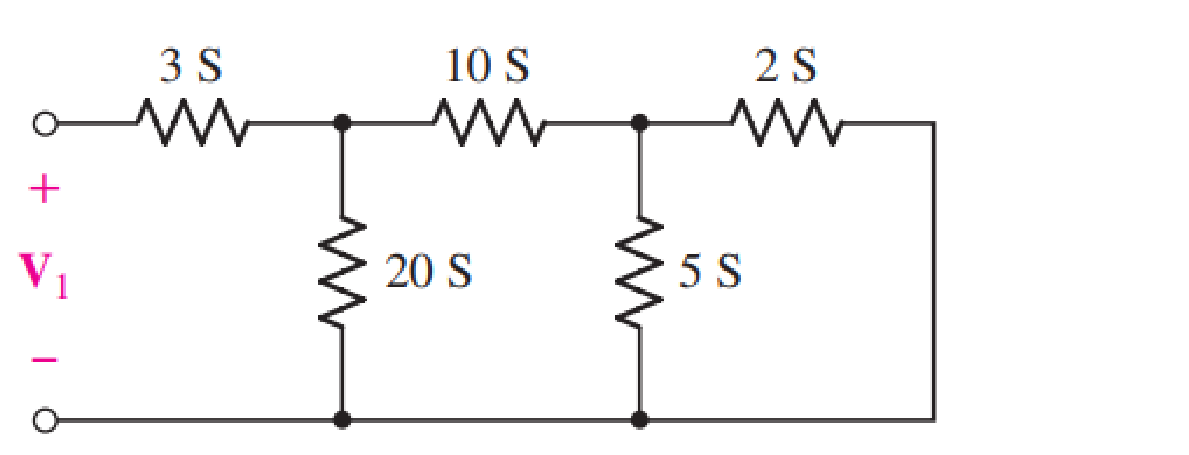
For the one-port network represented schematically in Fig. 16.35, choose the bottom node as the reference; name the junction between the 3, 10, and 20 S conductances V2 and the remaining node V3. (a) Write the three nodal equations. (b) Compute ∆Y. (c) Calculate the input admittance.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
I just want to know what is PPE and Give examples of it
Why is a starting resistor needed to bring a
motor up to speed?
Show one way to reverse the direction of ro-
tation of a compound motor.
8- is flip-flop which indicates some condition which arises after the execution of an
arithmetic or logic instruction.
a) Status flag
b) Instruction registers
c) Temporary register
d) None of these
9- El instruction is a_
a) Branching Instructions
b) Logical Instructions
c) Control Instructions
d) Data Transfer Instruction
e) Arithmetic Instructions
Chapter 16 Solutions
Engineering Circuit Analysis
Ch. 16.1 - Find the input impedance of the network shown in...Ch. 16.1 - Write a set of nodal equations for the circuit of...Ch. 16.2 - By applying the appropriate 1 V sources and short...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 4PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 5PCh. 16.3 - Prob. 6PCh. 16.3 - Use Y and Y transformations to determine Rin for...Ch. 16.4 - Find z for the two-port shown in (a) Fig. 16.23a;...Ch. 16.4 - Prob. 9PCh. 16.5 - Prob. 10P
Ch. 16.5 - Prob. 11PCh. 16.6 - Prob. 12PCh. 16 - For the following system of equations, (a) write...Ch. 16 - With regard to the passive network depicted in...Ch. 16 - Determine the input impedance of the network shown...Ch. 16 - For the one-port network represented schematically...Ch. 16 - Prob. 6ECh. 16 - Prob. 7ECh. 16 - Prob. 8ECh. 16 - Prob. 9ECh. 16 - (a) If both the op amps shown in the circuit of...Ch. 16 - Prob. 11ECh. 16 - Prob. 12ECh. 16 - Prob. 13ECh. 16 - Prob. 14ECh. 16 - Prob. 15ECh. 16 - Prob. 16ECh. 16 - Prob. 17ECh. 16 - Prob. 18ECh. 16 - Prob. 19ECh. 16 - Prob. 20ECh. 16 - For the two-port displayed in Fig. 16.49, (a)...Ch. 16 - Prob. 22ECh. 16 - Determine the input impedance Zin of the one-port...Ch. 16 - Determine the input impedance Zin of the one-port...Ch. 16 - Employ Y conversion techniques as appropriate to...Ch. 16 - Prob. 26ECh. 16 - Prob. 27ECh. 16 - Prob. 28ECh. 16 - Compute the three parameter values necessary to...Ch. 16 - It is possible to construct an alternative...Ch. 16 - Prob. 31ECh. 16 - Prob. 32ECh. 16 - Prob. 33ECh. 16 - Prob. 34ECh. 16 - The two-port networks of Fig. 16.50 are connected...Ch. 16 - Prob. 36ECh. 16 - Prob. 37ECh. 16 - Obtain both the impedance and admittance...Ch. 16 - Prob. 39ECh. 16 - Determine the h parameters which describe the...Ch. 16 - Prob. 41ECh. 16 - Prob. 42ECh. 16 - Prob. 43ECh. 16 - Prob. 44ECh. 16 - Prob. 45ECh. 16 - Prob. 46ECh. 16 - Prob. 47ECh. 16 - Prob. 48ECh. 16 - Prob. 49ECh. 16 - Prob. 50ECh. 16 - (a) Employ suitably written mesh equations to...Ch. 16 - Prob. 52ECh. 16 - Prob. 53ECh. 16 - The two-port of Fig. 16.65 can be viewed as three...Ch. 16 - Consider the two separate two-ports of Fig. 16.61....Ch. 16 - Prob. 56ECh. 16 - Prob. 57ECh. 16 - Prob. 58ECh. 16 - (a) Obtain y, z, h, and t parameters for the...Ch. 16 - Four networks, each identical to the one depicted...Ch. 16 - A cascaded 12-element network is formed using four...Ch. 16 - Prob. 62ECh. 16 - Continuing from Exercise 62, the behavior of a ray...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Consider the adage Never ask a question for which you do not want the answer. a. Is following that adage ethica...
Experiencing MIS
1.2 Explain the difference between geodetic and plane
surveys,
Elementary Surveying: An Introduction To Geomatics (15th Edition)
How does a computers main memory differ from its auxiliary memory?
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
The solid steel shaft AC has a diameter of 25 mm and is supported by smooth bearings at D and E. It is coupled ...
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Look at the following description of a problem domain:
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Data Structures (4th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
How is the hydrodynamic entry length defined for flow in a pipe? Is the entry length longer in laminar or turbu...
Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 1. Write a program to add 4 hex numbers located in the memory locations 2001h, 2002h, 2003h, 2004h and store the result at location 2005harrow_forwardnot use ai pleasearrow_forward17- In 8085 name the 16 bit registers. a) Program Counter b) Stack Pointer c) a and b d) Instruction Register 18- In response to RST 7.5 interrupt, the execution of control transfers to memory location. a) 0000H b) 003CH c) 002CH d) 0034H 19- Let contents of accumulator and B are 00000100 and 01000000 respectively. After execution of SUB B instruction, accumulator contents are a) 11000100 b) 01000000 c) 010001000 d) 00000100arrow_forward
- 1.) A single instruction to clear the lower 4 bits of accumulator in 8085 alp is, a) XRI FOH b) XRI OFH c) ANI OFH d) ANI FO 2.) The status of Z, AC, CY flags after execution of following instructions are, MVI A, A9H MVI B, 57H ADD B HLT a) 0,1,1 b) 1,0,0 c) 1,1,1 d) 1,0,1 3.) Consider the loop: LXI H 000A MVI C OB LOOP: DCX H DCR C JNZ LOOP HLT This loop will be executed by: a) infinite times b) 11 time c) 10 times d) 1 timearrow_forwardFundamentals Of Energy Systems HW 6 Q6arrow_forwardFundamentals Of Energy Systems HW 6 Q4arrow_forward
- 1. For the 2-dimensional lattice shown in the following figure, using the two sets of given primitive translation vectors to write the translation vectors that can translate lattice point A to point B. (10 pts) (1) (2) (1) T= (2) T T=arrow_forwardFundamentals Of Energy Systems HW 6 Q5arrow_forwardFundamentals Of Energy Systems HW 6 Q1arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Power System Analysis and Design (MindTap Course ...Electrical EngineeringISBN:9781305632134Author:J. Duncan Glover, Thomas Overbye, Mulukutla S. SarmaPublisher:Cengage Learning
Power System Analysis and Design (MindTap Course ...Electrical EngineeringISBN:9781305632134Author:J. Duncan Glover, Thomas Overbye, Mulukutla S. SarmaPublisher:Cengage Learning

Power System Analysis and Design (MindTap Course ...
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781305632134
Author:J. Duncan Glover, Thomas Overbye, Mulukutla S. Sarma
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Z Parameters - Impedance Parameters; Author: Electrical Engineering Authority;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qoD4AoNmySA;License: Standard Youtube License