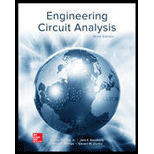
The two-port of Fig. 16.65 can be viewed as three separate cascaded two-ports A, B, and C. (a) Compute t for each network. (b) Obtain t for the cascaded network. (c) Verify your answer by naming the two middle nodes Vx and Vy, respectively, writing nodal equations, obtaining the admittance parameters from your nodal equations, and converting to t parameters using Table 16.1.
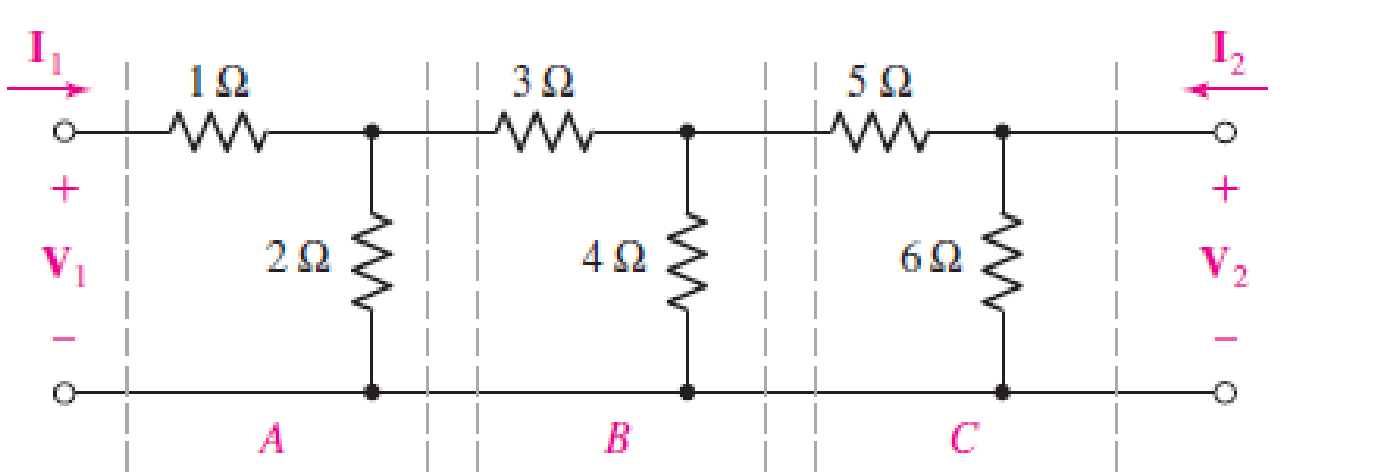
(a)
The
Answer to Problem 54E
The
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The required diagram is shown in Figure 1.
Here,
The mesh equation from the input side is given by,
The mesh equations at the output side is given by,
Substitute
The
Here,
Write equations (6) and (7) in matrix form.
Compare equation (3) with equation (4).
Compare equation (2) with equation (6).
The
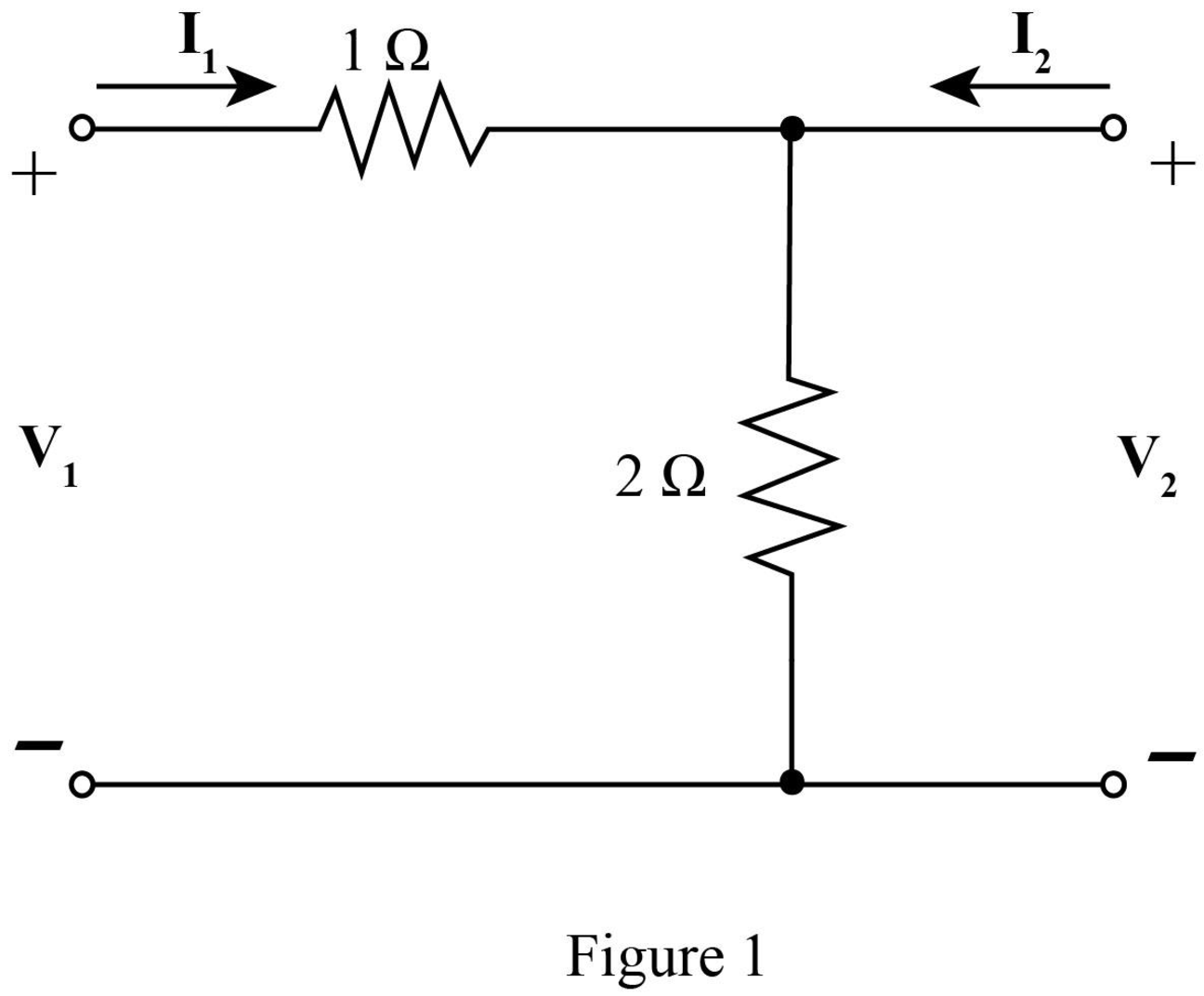
The required diagram is shown in Figure 2.
The mesh equation from the input side is given by,
The mesh equations at the output side is given by,
Substitute
Compare equation (8) with equation (4).
Compare equation (7) with equation (5).
The
The required diagram is shown in Figure 3.
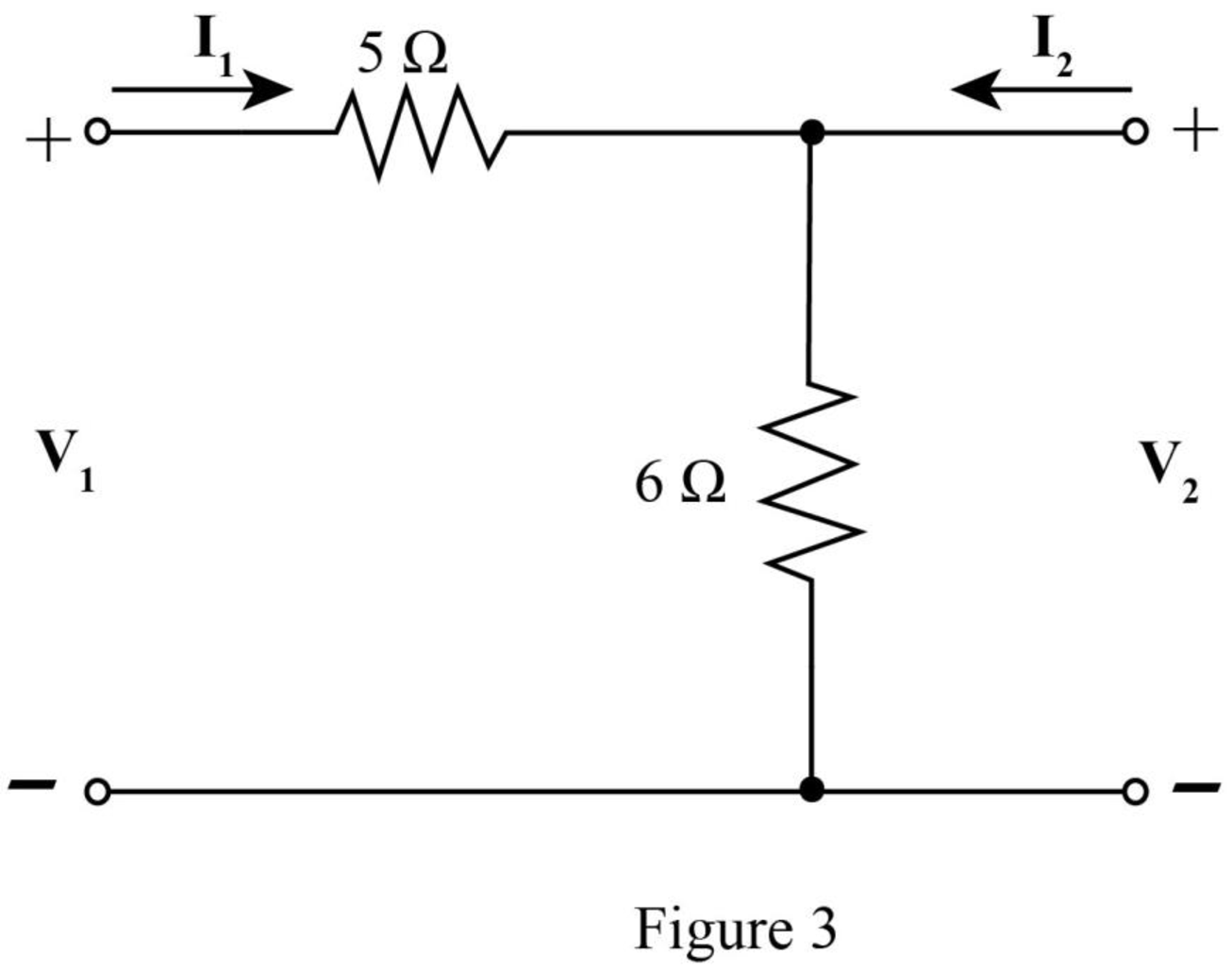
The mesh equation from the input side is given by,
The mesh equations at the output side is given by,
Substitute
Compare equation (11) with equation (4).
Compare equation (10) with equation (5).
The
Conclusion:
Therefore, the
(b)
The
Answer to Problem 54E
The
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the
(c)
To verify: The above answers by obtaining the admittance parameter and converting them to
Answer to Problem 54E
The values have been verified.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The required diagram is shown in Figure 4.
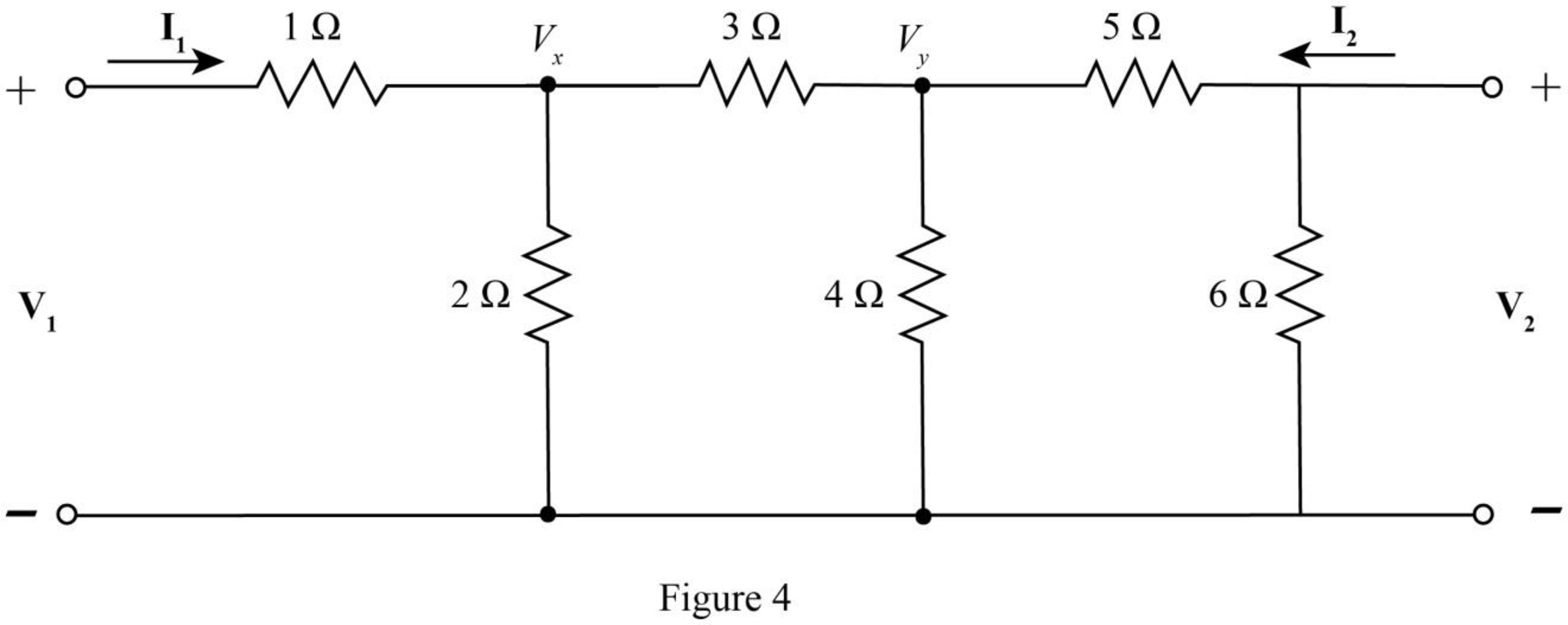
The nodal equation at node
The nodal equations at node
Substitute
Substitute
The current
Substitute
The current
Substitute
The
Here,
Compare equation (16) with equation (18).
Compare equation (17) with equation (19).
The determinant of the matrix
Substitute
The relation between
Substitute
Within the limits of error, the values have been verified.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the values have been verified.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Engineering Circuit Analysis
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
SURVEY OF OPERATING SYSTEMS
Modern Database Management
Starting Out with C++ from Control Structures to Objects (9th Edition)
- Q3. Answer the following questions T 1. Compared to the bipolar voltage-switching scheme, the unipolar scheme is "effectively" doubling the switching frequency. Explain the statement's meaning and how this effect can be generated. 2. What are the properties of a good power switch, and what are its basic ratings? 3. What are the objectives of any PWM strategy for three-phase inverters? 4. Why is the current control PWM rectifier in the dq rotating reference frame preferred over the abc reference frame? 5. Define the switch utilization factor. Show how this factor can be calculated for different single-phase inverters for square wave operation mode at the maximum rated output.arrow_forwardQ1.B. Explain output control by voltage cancellation in a single-phase inverter. What are the advantages over square wave operation?arrow_forwardQ3.B. What is the problem of three-phase HW rectifier and how can be resolved?arrow_forward
- Q3-consider the unity feedback system shown below: a.Evaluate general formula of ess? b.Calculate the steady state error of the closed loop system due to R(s) unit step input, D(s)=0]? c.Calculate the steady-state response when D(s) and ramp and R(s)=0?arrow_forward- = 400KHZ. Q1. In a Boost converter, L = 25 μH, Vin = 12 V, D = 0.4, P = 25 W, and fs (i) if the output load is changing. Calculate the critical value of the output load P,below which the converter will enter the discontinuous conduction mode of operation. Assume the total turn-on loss is equal to 2 W. (ii) Assuming the input voltage fluctuates from 10 V to 14 V and the output voltage is regulated to 20 V. Calculate the critical value of the inductance L below which this Boost converter will enter the discontinuous conduction mode of operation at P = 5 W. (iii) Draw the waveforms for inductor voltage, inductor current, and the capacitor current for this Boost converter at the output load that causes it to operate at the border of continuous and discontinuous modes. vd tow 77 N₂ AT 22 1-1arrow_forwardDon't use ai to answer I will report you answerarrow_forward
- Answer the following questions: 1- Write radiation resistance (R.) equation for infinitesimal dipole antenna. 2- Write the angle expression form of first null beam width (FNBW) for 2/2 dipole. 3- Define the Directivity of antenna. 4- Write radar cross section equation. 5- Write the input impedance (Z) expression of lossless transmission line.arrow_forwardThe input reactance of an infinitesimal linear dipole of length 1/60 and radius a = x/200 is given by [In(/2a) - 11 X-120- tan(kl/2) Assuming the wire of the dipole is copper with a conductivity of 5.7 × 10'S/m. determine at f = 1 GHz the (a) loss resistance (b) radiation resistance (c) radiation efficiency input impedancearrow_forwardQ4- a) For the block diagram of control system shown below with its unit step response. Determine (K, a,damping ration, Maximum overshoot, Wn, Wd,ẞ, ts, tp, td, tr, and overall transfer function? C(1) ↑ 1.4 1.2 1 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 R(s) E(s) K C(s) $(s + α) 0.05 0.1 0.15 0.2 +2% -2%arrow_forward
- Determine the power radiated for the antenna has the following specifications (48 ohm radiation resistance, 2 ohm loss resistance and 50 ohms reactance) connected to generator with 12 V open circuit and internal impedance 50 ohm via à long transmission line with 100 ohm characteristic impedance.arrow_forwardDon't use ai to answer I will report you answerarrow_forwardDon't use ai to answer I will report you answerarrow_forward
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





