
EE 98: Fundamentals of Electrical Circuits - With Connect Access
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781259981807
Author: Alexander
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 16, Problem 27P
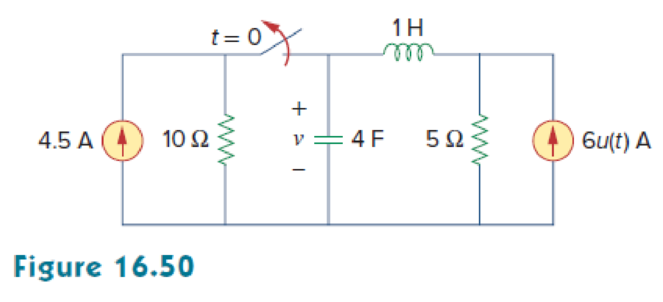
Find v (t) for t > 0 in the circuit in Fig. 16.50.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
1. Consider the following a unity feedback control system.
R(s) +
E(s)
500(s+2)(s+5)(s+6)
s(s+8)(s+10)(s+12)
-Y(s)
Find the followings:
a) Type of the system
b) Static position error constant Kp, Static velocity error constant Ry and Static
acceleration error constant Ka
c) Find the steady-state error of the system for (i) step input 1(t), (ii) ramp input t 1(t),
(iii) parabolic input t² 1(t).
2. Repeat the above problem for the following system.
R(s) + E(s)
500(s + 2)(s + 5)
(s+8)(s+ 10)(s+12)
Y(s)
3. Repeat the above problem for the following system.
R(s) +
E(s) 500(s+2)(s+4)(s+5)(s+6)(s+7)
s²(s+8)(s+10)(s+12)
Y(s)
4. Consider a unity (negative) feedback control system whose open-loop transfer
function is given by the following.
2
G(s) =
s³ (s + 2)
Find the steady-state error of the system for each of the following inputs.
=
a) u(t) (t²+8t+5) 1(t)
b) u(t) = 3t³ 1(t)
c) u(t) (t+5t² - 1) 1(t)
=
1
2. For the following closed-loop system, G(s) =
and H(s) = ½
(s+4)(s+6)
a. Please draw the root locus by hand and mark the root locus with arrows. Calculate the origin
and angle for asymptotes.
b. Use Matlab to draw the root locus to verify your sketch.
Input
R(s)
Output
C(s)
KG(s)
H(s)
Chapter 16 Solutions
EE 98: Fundamentals of Electrical Circuits - With Connect Access
Ch. 16.2 - Determine vo(t) in the circuit of Fig. 16.6,...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 2PPCh. 16.2 - Prob. 3PPCh. 16.3 - For the circuit shown in Fig. 16.12 with the same...Ch. 16.3 - Prob. 5PPCh. 16.3 - The initial energy in the circuit of Fig. 16.17 is...Ch. 16.4 - Prob. 7PPCh. 16.4 - Prob. 8PPCh. 16.4 - Prob. 9PPCh. 16.5 - Obtain the state variable model for the circuit...
Ch. 16.5 - Prob. 11PPCh. 16.5 - Prob. 12PPCh. 16.6 - For what value of is the circuit in Fig. 16.29...Ch. 16.6 - Prob. 14PPCh. 16.6 - Prob. 15PPCh. 16.6 - Synthesize the function Vo(s)Vin=2ss2+6s+10 using...Ch. 16 - Prob. 1RQCh. 16 - The current through an RL series circuit with...Ch. 16 - Prob. 3RQCh. 16 - Prob. 4RQCh. 16 - Prob. 5RQCh. 16 - Prob. 6RQCh. 16 - Prob. 7RQCh. 16 - Prob. 8RQCh. 16 - Prob. 9RQCh. 16 - Prob. 10RQCh. 16 - The current in an RLC circuit is described by...Ch. 16 - The differential equation that describes the...Ch. 16 - Prob. 3PCh. 16 - If R = 20 , L = 0.6 H, what value of C will make...Ch. 16 - The responses of a series RLC circuit are vc(t) =...Ch. 16 - Prob. 6PCh. 16 - Prob. 7PCh. 16 - Prob. 8PCh. 16 - Prob. 9PCh. 16 - The step responses of a series RLC circuit are Vc...Ch. 16 - The step response of a parallel RLC circuit is v =...Ch. 16 - Prob. 12PCh. 16 - Prob. 13PCh. 16 - Prob. 14PCh. 16 - For the circuit in Fig. 16.38. calculate the value...Ch. 16 - The capacitor in the circuit of Fig. 16.39 is...Ch. 16 - If is(t) = 7.5e2t u(t) A in the circuit shown in...Ch. 16 - Find v(t), t 0 in the circuit of Fig. 16.41. Let...Ch. 16 - The switch in Fig. 16.42 moves from position A to...Ch. 16 - Find i(t) for t 0 in the circuit of Fig. 16.43.Ch. 16 - In the circuit of Fig. 16.44, the switch moves...Ch. 16 - Find the voltage across the capacitor as a...Ch. 16 - Obtain v (t) for t 0 in the circuit of Fig....Ch. 16 - The switch in the circuit of Fig. 16.47 has been...Ch. 16 - Calculate v(t) for t 0 in the circuit of Fig....Ch. 16 - Prob. 26PCh. 16 - Find v (t) for t 0 in the circuit in Fig. 16.50.Ch. 16 - For the circuit in Fig. 16.51, find v(t) for t 0.Ch. 16 - Prob. 29PCh. 16 - Find vo(t), for all t 0, in the circuit of Fig....Ch. 16 - Prob. 31PCh. 16 - For the network in Fig. 16.55, solve for i(t) for...Ch. 16 - Using Fig. 16.56, design a problem to help other...Ch. 16 - Prob. 34PCh. 16 - Prob. 35PCh. 16 - Prob. 36PCh. 16 - Prob. 37PCh. 16 - The switch in the circuit of Fig. 16.61 is moved...Ch. 16 - Prob. 39PCh. 16 - Prob. 40PCh. 16 - Prob. 41PCh. 16 - Prob. 42PCh. 16 - Prob. 43PCh. 16 - Prob. 44PCh. 16 - Find v(t) for t 0 in the circuit in Fig. 16.68.Ch. 16 - Prob. 46PCh. 16 - Determine io(t) in the network shown in Fig....Ch. 16 - Prob. 48PCh. 16 - Find i0(t) for t 0 in the circuit in Fig. 16.72....Ch. 16 - Prob. 50PCh. 16 - In the circuit of Fig. 16.74, find i(t) for t 0.Ch. 16 - Prob. 52PCh. 16 - In the circuit of Fig. 16.76, the switch has been...Ch. 16 - Prob. 54PCh. 16 - Prob. 55PCh. 16 - Calculate io(t) for t 0 in the network of Fig....Ch. 16 - Prob. 57PCh. 16 - Prob. 58PCh. 16 - Find vo(t) in the circuit of Fig. 16.82 if vx(0) =...Ch. 16 - Prob. 60PCh. 16 - Prob. 61PCh. 16 - Using Fig. 16.85, design a problem to help other...Ch. 16 - Consider the parallel RLC circuit of Fig. 16.86....Ch. 16 - The switch in Fig. 16.87 moves from position 1 to...Ch. 16 - For the RLC circuit shown in Fig. 16.88, find the...Ch. 16 - For the op amp circuit in Fig. 16.89, find v0(t)...Ch. 16 - Given the op amp circuit in Fig. 16.90, if v1(0+)...Ch. 16 - Prob. 68PCh. 16 - Prob. 69PCh. 16 - Using Fig. 16.93, design a problem to help other...Ch. 16 - Prob. 71PCh. 16 - The transfer function of a system is H(s)=s23s+1...Ch. 16 - Prob. 73PCh. 16 - Design a problem to help other students better...Ch. 16 - Prob. 75PCh. 16 - For the circuit in Fig. 16.95, find H(s) =...Ch. 16 - Obtain the transfer function H(s) = VoVs for the...Ch. 16 - Prob. 78PCh. 16 - For the circuit in Fig. 16.97, find: (a) I1/Vs (b)...Ch. 16 - Refer to the network in Fig. 16.98. Find the...Ch. 16 - Prob. 81PCh. 16 - Prob. 82PCh. 16 - Refer to the RL circuit in Fig. 16.101. Find: (a)...Ch. 16 - A parallel RL circuit has R = 4 and L = 1 H. The...Ch. 16 - Prob. 85PCh. 16 - Prob. 86PCh. 16 - Prob. 87PCh. 16 - Prob. 88PCh. 16 - Develop the state equations for the circuit shown...Ch. 16 - Prob. 90PCh. 16 - Prob. 91PCh. 16 - Prob. 92PCh. 16 - Prob. 93PCh. 16 - Prob. 94PCh. 16 - Prob. 95PCh. 16 - Prob. 96PCh. 16 - A system is formed by cascading two systems as...Ch. 16 - Determine whether the op amp circuit in Fig....Ch. 16 - It is desired realize the transfer function...Ch. 16 - Prob. 100PCh. 16 - Prob. 101PCh. 16 - Synthesize the transfer function...Ch. 16 - Prob. 103CPCh. 16 - Prob. 104CPCh. 16 - Prob. 105CP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 5. Consider following feedback system. R(s) + 100 S+4 +1 Find the steady-state error for (i) step input and (ii) ramp input.arrow_forward6. Find (i) settling time (Ts), (ii) rise time (Tr), (iii) peak time (Tp), and (iv) percent overshoot (% OS) for each of the following systems whose transfer functions are given by: a) H(s) = 5 s²+12s+20 5 b) H(s) = s²+6s+25 c) H(s) = (s+2) (s²+12s+20) (s²+4s+13) Use dominant pole approximation if needed.arrow_forward7. Answer the following questions. Take help from ChatGPT to answer these questions (if you need). But write the answers briefly using your own words with no more than two sentences and make sure you check whether ChatGPT is giving you the appropriate answers in the context of class. a) Why do we need transient performance metrics? Name a few of such metrics. b) Define (i) settling time, (ii) rise time, (iii) peak time and (iv) percent overshoot. c) What is damping ratio? How does overshoot change with the change of damping ratio? When do we have zero overshoot? d) What is the criterion for selecting dominant pole in higher order systems? When dominant pole approximation is not valid? How will you calculate the transient performance metrics for the case when dominant pole approximation does not hold?arrow_forward
- The transformer rating is 1200:2400 V @ 120 kVA. What is the apparent power provided by the source? What does this mean for the operation of the transformer? Draw the power triangle at the source and calculate the power factor. The magnitude of the voltage source is given in VRMS.arrow_forwardDon't use ai to answer i will report your answerarrow_forwarda) Find the Real and Imaginary Voltage across the inductor to 3 decimal points. b) Find the current and phase angle (phasor) magnitude from the Vs source to 3 decimal points. c) Find the magnitude and phase angle of the complex power(phasor) delivered by the Vs source to 3 decimal points.arrow_forward
- Consider the circuit diagram below. If four identical capacitors, each with a capacitance of 0.07 F, are used to smooth the output, what will the ripple voltage VR be? The diode forward bias voltage, VF, is found to be 0.5 V. Note that the amplitude of v(t) is given in VRMS.arrow_forwarda) Find the complex power absorbed by the -j3 ohm capacitor to 3 decimal points.b) Find the complex power absorbed by the 4 ohm resistor to 3 decimal pointsc) Find the complex power absorbed by the j5 ohm inductor to 3 decimal points.arrow_forwardI am looking for schematic ideas or recommendations for designing the required step-down system. Since the input is a 600V DC supply, a DC-DC converter may be necessary, as transformers are typically used for AC voltage. Key considerations would include: Voltage regulation: Ensuring a stable and consistent 120V DC output.Component selection: Choosing appropriate DC-DC converter modules, capacitors for filtering, and protective components such as fuses or circuit breakers.Lighting system: Recommendations on energy-efficient lighting options like LEDs, which work well with DC power and offer durability for railway applications.Thermal management: Addressing heat dissipation within the converter and lighting circuit.Safety and standards: Complying with safety regulations for electrical systems in railways. I would greatly appreciate detailed insights into the design process, including key circuit components and configurations, as well as any schematic diagrams or references.arrow_forward
- 1 2. For the following closed-loop system, G(s) = and H(s) = ½ (s+4)(s+6) a. Please draw the root locus by hand and mark the root locus with arrows. Calculate the origin and angle for asymptotes. b. Use Matlab to draw the root locus to verify your sketch. Input R(s) Output C(s) KG(s) H(s)arrow_forward1. In the following unity feedback system, we have G(s) = R(s) + K(s + 1) s(s + 2)(s +5) G(s) C(s) use Routh-Hurwitz stability criterion to find the range of K for the stability of the system.arrow_forwardWhat is the current flowing through the load resistor, RL (in ARMS)? How much power does the voltage source, V1, provide to the circuit? The magnitude of V1 is given in VRMS.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Systems and Simulation - Lecture 3: Modelling of Mechanical systems; Author: bioMechatronics Lab;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fMcDdyoC9mA;License: Standard Youtube License