
Concept explainers
(a)
To write: A balanced equation of the reactions catalyzed by each enzyme of citric acid cycle.
Concept introduction: Citric acid cycle is also known as the TCA cycle (Tricarboxylic acid cycle) or Krebs’s cycle. Pyruvate obtained from glycolysis is first converted into acetyl groups, these groups enter into citric acid cycle. In citric acid cycle the sugars, amino acids, and fatty acids are oxidized into CO2 and H2O.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Explanation:
Enzymes used in TCA are citrate synthase, aconitase, isocitrate dehydrogenase, α- ketoglutarate dehydrogenase, succinyl CoA synthetase, succinate dehydrogenase, fumarase, and malate dehydrogenase.
Before citric acid cycle starts, pyruvates give acetyl-CoA which enters the citric acid cycle. Acetyl CoA reacts with oxaloacetate to produce citrate with the help of citrate synthase as shown in Fig.1.
Aconitase is responsible for conversion of citrate into isocitrate as shown in Fig.2.
Isocitrate dehydrogenase converts isocitrate into α- ketoglutarate as shown in Fig.3.
α- ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex converts α- ketoglutarate into succinyl- CoA as shown in Fig.4.
Succinyl co A is converted into succinate, the succinyl CoA synthetase catalyses the reaction. Succinate is an intermediate and quickly gets converted into fumarate with the action of succinate dehydrogenase as shown in Fig.5.
In the next step of reaction hydrolysis of fumarate takes place and it gets convert into malate as shown in Fig.6.
Malate dehydrogenase catalyzes malate to get it convert into oxaloacetate as shown in Fig.7.
Pictorial representation: The reactions catalyzed by the enzymes in citric acid cycle is represented in the following figures.
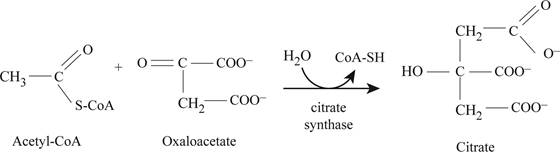
Fig1: Enzyme citrate synthase activity.
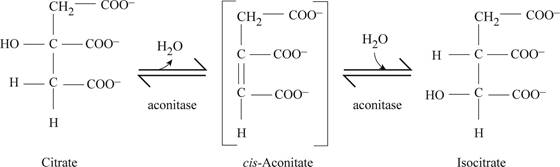
Fig2: Enzyme aconitase activity.
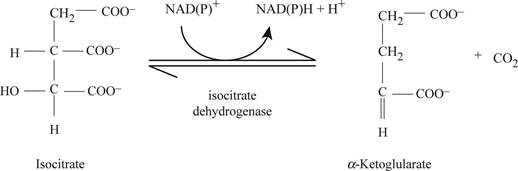
Fig3: Enzyme isocitrate dehydrogenase activity.
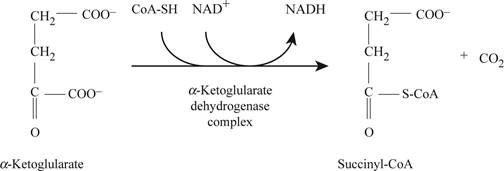
Fig4: Enzyme α- ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex activity.
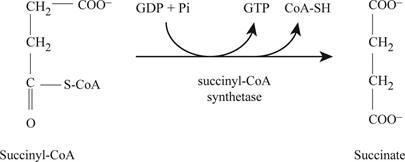
Fig5: Enzyme succinyl CoA synthetase activity.
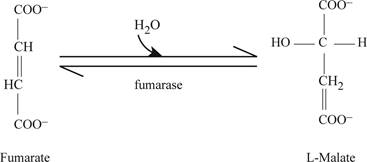
Fig6: Enzyme fumarase activity.
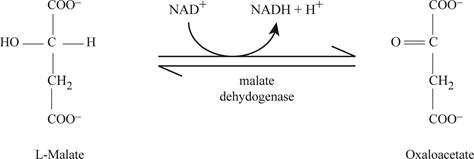
Fig7: Enzyme malate dehydrogenase activity.
(b)
To name: The cofactors which are required for each enzymatic reactions.
Concept introduction:
Citric acid cycle is also known as the TCA cycle (Tricarboxylic acid cycle) or Krebs’s cycle. Pyruvate obtained from glycolysis is first converted into acetyl groups, these groups enter into citric acid cycle. In citric acid cycle the sugars, amino acids, and fatty acids are oxidized into CO2 and H2O.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Explanation:
Presence of cofactors in the reactions is mandatory for the functioning of enzymes. Enzymes can catalyze the reaction only in the presence of cofactors.
When isocitrate converts into α- ketoglutarate then isocitrate dehydrogenase enzyme gets involve. The cofactor which is required at this step is NADH.
In the next step when α- ketoglutarate gets convert into succinyl CoA α- ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex enzyme takes part and NADH is found present to facilitate the enzyme functioning.
GTP is the required cofactor when succinyl CoA synthetase catalyzes the conversion of succinyl CoA into succinate.
Fumarase enzyme uses FADH2 as its cofactor when fumarate is converted into malate.
NADH is present for the functioning of malate dehydrogenase when malate gets convert into oxaloacetate.
(c)
To determine: The types of reactions catalyzed, condensation, dehydration, hydration, decarboxylation, oxidation-reduction, substrate level phosphorylation and isomerization.
Concept introduction:
Citric acid cycle is also known as the TCA cycle (Tricarboxylic acid cycle) or Krebs’s cycle. Pyruvate obtained from glycolysis is first converted into acetyl groups, these groups enter into citric acid cycle. In citric acid cycle the sugars, amino acids, and fatty acids are oxidized into CO2 and H2O.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Explanation:
Fig1 is showing the formation of citrate from acetyl coA, this process is Claisen condensation process because methyl group found on acetyl coA gets converted into methylene of citrate.
The conversion of citrate to isocitrate is isomerization reaction. Fig2 is showing the processof conversion of citrate into isocitrate with the formation of one intermediate cis- aconitate, in this process first dehydration and then rehydration takes place. Citrate undergoes dehydration and cis aconitate is obtained, then rehydration of cis aconitate takes place which produces isocitrate.
Fig 3 is showing the production of α- ketoglutarate from isocitrate via oxidative decarboxylation, hydroxyl group of isocitrate is oxidized into carbonyl.
Fig 4 is the reaction of conversion of α- ketoglutarate into succinyl coA which is a oxidative decarboxylation process.
Fig 5 is the step of conversion of succinyl coA into succinate via substrate level phosphorylation process.
The succinate is converted into fumarate via oxidation reaction. Fumarate is converted into L-Malate by hydration reaction. Finally by oxidation reaction L-Malate is converted into oxaloacetate.
Fig 7 is the dehydrogenation of malate to get convert into oxaloacetate.
(d)
To write: Net balanced equation of the catabolic reaction of acetyl CoA to CO2.
Concept introduction:
Citric acid cycle is also known as the TCA cycle (Tricarboxylic acid cycle) or Krebs’s cycle. Pyruvate obtained from glycolysis is first converted into acetyl groups, these groups enter into citric acid cycle. In citric acid cycle the sugars, amino acids, and fatty acids are oxidized into CO2 and H2O.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
Explanation:
Acetyl CoA is converted into CO2 along with amount of energy. Net equation of reaction of acetyl CoA to CO2 is:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
EBK LEHNINGER PRINCIPLES OF BIOCHEMISTR
- What is the formation of glycosylated hemoglobin (the basis for the HbA1c test)? Can you describe it?arrow_forwardPlease analze the gel electrophoresis column of the VRK1 kinase (MW: 39.71 kDa). Also use a ruler to measure the length of the column in centimeters and calculate the MW of each band observed. Lane 1: buffer Lane 2 : Ladder Lane 3: Lysate Lane 4: Flowthrough Lane 5: Wash Lanes 6-8: E1, E2, E3 Lane 9: Dialyzed VRK1 Lane 10: LDHarrow_forwardDo sensory neurons express ACE2 or only neurolipin-1 receptors for COVID19 virus particle binding?arrow_forward
- Explain the process of CNS infiltration of COVID19 through sensory neurons from beginning to end, including processes like endocytosis, the different receptors/proteins that are involved, how they are transported and released, etc.,arrow_forwardH2C CH2 HC-COOO CH2 ܘHO-C-13c-O isocitrate C-S-COA H213c CH2 C-OO 13C-S-COA CH2 C-00 the label will not be present in succinyl CoA C-S-COA succinyl-CoAarrow_forwardA culture of kidneys cells contains all intermediates of the citric acid cycle. It is treated with an irreversible inhibitor of malate dehydrogenase, and then infused withglucose. Fill in the following list to account for the number of energy molecules that are formed from that one molecule of glucose in this situation. (NTP = nucleotidetriphosphate, e.g., ATP or GTP)Net number of NTP:Net number of NADH:Net number of FADH2:arrow_forward
- 16. Which one of the compounds below is the final product of the reaction sequence shown here? OH A B NaOH Zn/Hg aldol condensation heat aq. HCI acetone C 0 D Earrow_forward2. Which one of the following alkenes undergoes the least exothermic hydrogenation upon treatment with H₂/Pd? A B C D Earrow_forward6. What is the IUPAC name of the following compound? A) (Z)-3,5,6-trimethyl-3,5-heptadiene B) (E)-2,3,5-trimethyl-1,4-heptadiene C) (E)-5-ethyl-2,3-dimethyl-1,5-hexadiene D) (Z)-5-ethyl-2,3-dimethyl-1,5-hexadiene E) (Z)-2,3,5-trimethyl-1,4-heptadienearrow_forward
- Consider the reaction shown. CH2OH Ex. CH2 -OH CH2- Dihydroxyacetone phosphate glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate The standard free-energy change (AG) for this reaction is 7.53 kJ mol-¹. Calculate the free-energy change (AG) for this reaction at 298 K when [dihydroxyacetone phosphate] = 0.100 M and [glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate] = 0.00300 M. AG= kJ mol-1arrow_forwardIf the pH of gastric juice is 1.6, what is the amount of energy (AG) required for the transport of hydrogen ions from a cell (internal pH of 7.4) into the stomach lumen? Assume that the membrane potential across this membrane is -70.0 mV and the temperature is 37 °C. AG= kJ mol-1arrow_forwardConsider the fatty acid structure shown. Which of the designations are accurate for this fatty acid? 17:2 (48.11) 18:2(A9.12) cis, cis-A8, A¹¹-octadecadienoate w-6 fatty acid 18:2(A6,9)arrow_forward
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON





