
(a)
Interpretation:
The number of expected
Concept introduction:
Answer to Problem 16.62P
The number of expected
Explanation of Solution
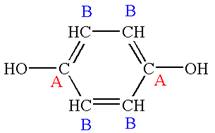
The structure of the given molecule is
The molecule has a plane of symmetry, which divides the molecule in two equal halves, and thus it has two distinct carbons indicated as
Every chemically distinct carbon atom in a molecule produces one
(b)
Interpretation:
The number of expected
Concept introduction:
Answer to Problem 16.62P
The number of expected
Explanation of Solution
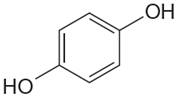
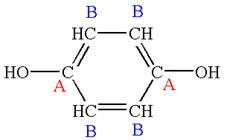
The structure of the given molecule is
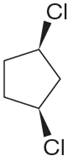
The molecule has a plane of symmetry, which divides the molecule in two equal halves, and thus it has three distinct carbons indicated as
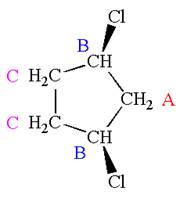
Every chemically distinct carbon atom in a molecule produces one
(c)
Interpretation:
The number of expected
Concept introduction:
Answer to Problem 16.62P
The number of expected
Explanation of Solution
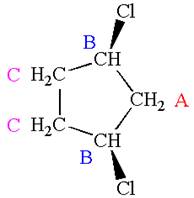
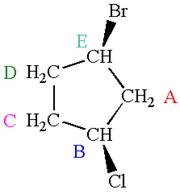
The structure of the given molecule is
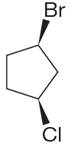
The molecule has ring with two different substituents, and thus all five carbons are distinctly indicated as
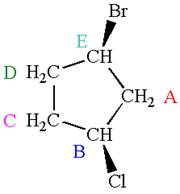
Every chemically distinct carbon atom in a molecule produces one
(d)
Interpretation:
The number of expected
Concept introduction:
Answer to Problem 16.62P
The number of expected
Explanation of Solution
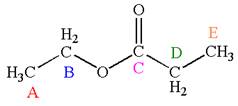
The structure of the given molecule is
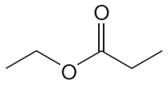
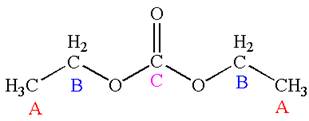
The molecule has one carbonyl carbon, two methylene carbons, and two methyl carbons. The two methylene carbons are in different chemical environment as one is bonded to oxygen and another to carbonyl carbon; thus they are distinct carbons. Therefore, the methyl carbons bonded to these methylene carbons are also distinct. Hence the molecule has total five distinct carbons indicated as
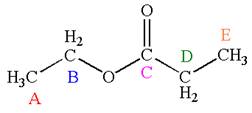
Every chemically distinct carbon atom in a molecule produces one
(e)
Interpretation:
The number of expected
Concept introduction:
Answer to Problem 16.62P
The number of expected
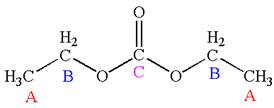
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the given molecule is
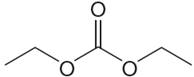
It has a plane of symmetry passing through
Every chemically distinct carbon atom in a molecule produces one
(f)
Interpretation:
The number of expected
Concept introduction:
Answer to Problem 16.62P
The number of expected
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the given molecule is
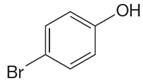
As the molecule is para disubstituted, it has a plane of symmetry passing through
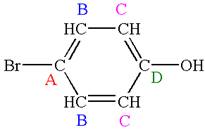
Every chemically distinct carbon atom in a molecule produces one
(g)
Interpretation:
The number of expected
Concept introduction:
Answer to Problem 16.62P
The number of expected
Explanation of Solution
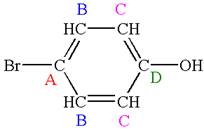
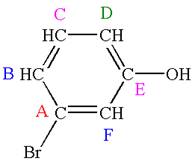
The structure of the given molecule is
The molecule is meta disubstituted with different substituents and has no plane of symmetry; thus all carbons are chemically non-equivalent. Hence it has six chemically distinct carbons indicated as

Every chemically distinct carbon atom in a molecule produces one
(h)
Interpretation:
The number of expected
Concept introduction:
Answer to Problem 16.62P
The number of expected
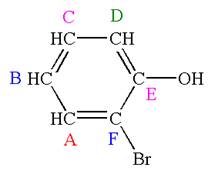
Explanation of Solution
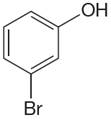
The structure of the given molecule is
The molecule is ortho disubstituted with different substituents and has no plane of symmetry; thus all carbons are chemically non-equivalent. Hence it has six chemically distinct carbons indicated as
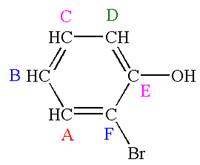
Every chemically distinct carbon atom in a molecule produces one
(i)
Interpretation:
The number of expected
Concept introduction:
Answer to Problem 16.62P
The number of expected
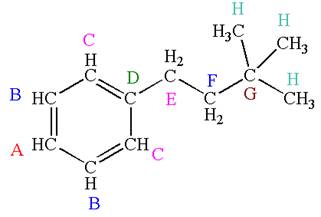
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the given molecule is:\
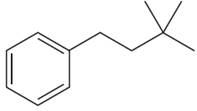
The molecule is monosubstituted benzene; thus there are four types of

Every chemically distinct carbon atom in a molecule produces one
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY: PRINCIPLES AND M
- Provide the reagents for the following reactions.arrow_forwardIf I have 1-bromopropene, to obtain compound Z, I have to add two compounds A1 and A2. Indicate which compounds are needed. P(C6H5)3arrow_forwardDraw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Assume that the water side product is continuously removed to drive the reaction toward products. O CH3CH2NH2, TSOH Select to Draw >arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained by reacting fluorobenzene with a sulfonitric mixture.arrow_forwardIf I have 1-bromopropene, to obtain compound A, I have to add NaOH and another compound. Indicate which compound that would be. C6H5 CH3arrow_forwardIf I have 1-bromopropene and I want to obtain (1,1-dipropoxyethyl)benzene, indicate the compound that I should add in addition to NaOH.arrow_forward
- Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Ο HSCH2CH2CH2SH, BF3 Select to Draw I Submitarrow_forwardFeedback (7/10) Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Assume that the water side product is continuously removed to drive the reaction toward products. Incorrect, 3 attempts remaining Ο (CH3CH2)2NH, TSOH Select to Draw V N. 87% Retryarrow_forwardIf I want to obtain (1,1-dipropoxyethyl)benzene from 1-bromopropene, indicate the product that I have to add in addition to NaOH.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





