
Concept explainers
The Geneva
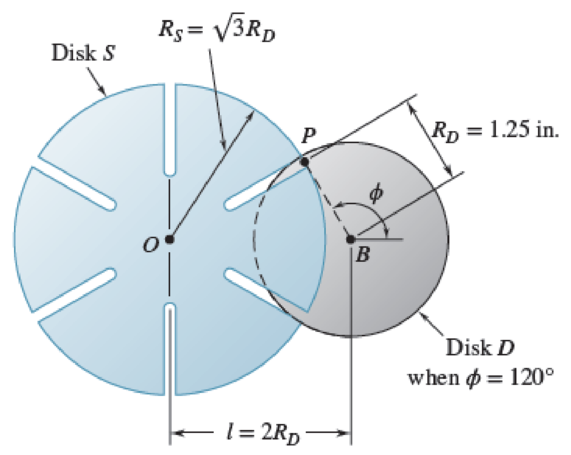
Fig. P16.164
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 16 Solutions
VECTOR MECH...,STAT.+DYNA.(LL)-W/ACCESS
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Starting Out with Programming Logic and Design (5th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Modern Database Management
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Automotive Technology: Principles, Diagnosis, And Service (6th Edition) (halderman Automotive Series)
- Carbon dioxide contained in a piston–cylinder device is compressed from 0.3 to 0.1 m3. During the process, the pressure and volume are related by P = aV–2, where a = 6 kPa·m6. Calculate the work done on carbon dioxide during this process. The work done on carbon dioxide during this process is kJ.arrow_forwardThe volume of 1 kg of helium in a piston–cylinder device is initially 5 m3. Now helium is compressed to 3 m3 while its pressure is maintained constant at 130 kPa. Determine the initial and final temperatures of helium as well as the work required to compress it, in kJ. The gas constant of helium is R = 2.0769 kJ/kg·K. The initial temperature of helium is K. The final temperature of helium is K. The work required to compress helium is kJ.arrow_forwardA piston-cylinder device initially contains 0.4 kg of nitrogen gas at 160 kPa and 140°C. Nitrogen is now expanded isothermally to a pressure of 80 kPa. Determine the boundary work done during this process. The properties of nitrogen are R= 0.2968 kJ/kg-K and k= 1.4. N₂ 160 kPa 140°C The boundary work done during this process is KJ.arrow_forward
- ! Required information An abrasive cutoff wheel has a diameter of 5 in, is 1/16 in thick, and has a 3/4-in bore. The wheel weighs 4.80 oz and runs at 11,700 rev/min. The wheel material is isotropic, with a Poisson's ratio of 0.20, and has an ultimate strength of 12 kpsi. Choose the correct equation from the following options: Multiple Choice о σmax= (314) (4r2 — r²) - о σmax = p² (3+) (4r² + r²) 16 σmax = (314) (4r² + r²) σmax = (314) (4² - r²)arrow_forwardI don't know how to solve thisarrow_forwardI am not able to solve this question. Each part doesn't make sense to me.arrow_forward
- Exercises Find the solution of the following Differential Equations 1) y" + y = 3x² 3) "+2y+3y=27x 5) y"+y=6sin(x) 7) y"+4y+4y = 18 cosh(x) 9) (4)-5y"+4y = 10 cos(x) 11) y"+y=x²+x 13) y"-2y+y=e* 15) y+2y"-y'-2y=1-4x³ 2) y"+2y' + y = x² 4) "+y=-30 sin(4x) 6) y"+4y+3y=sin(x)+2 cos(x) 8) y"-2y+2y= 2e* cos(x) 10) y+y-2y=3e* 12) y"-y=e* 14) y"+y+y=x+4x³ +12x² 16) y"-2y+2y=2e* cos(x)arrow_forwardQu. 15 What are the indices for the Plane 1 drawn in the following sketch? Qu. 16 What are the Miller indices for the Plane shown in the following cubic unit cell? this is material engineering please show all workarrow_forwardI do not understand how to approach this question. I tried to answer it but I kept getting it incorrect.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





