
a)
Interpretation:
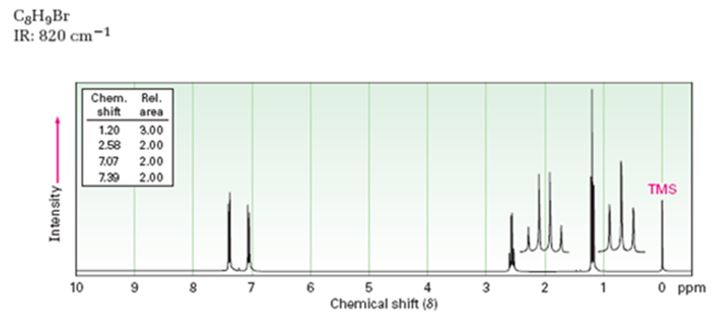
A structure for the compound whose 1HNMR spectrum given is to be proposed. Given: M.F = C8H9Br I.R: 820 cm-1.
1HNMR spectrum: 7.07δ (2H, doublet); 7.39δ (2H, doublet); 2.58δ (2H, quartet); 1.20δ (3H, triplet).
Concept introduction:
In 1HNMR spectrum
In I.R, the o-disubstituted benzenes absorb around 735-770 cm-1, m-disubstituted benzenes absorb around 690-710 cm-1 and p-disubstituted benzenes absorb around 810-840 cm-1.
To propose:
A structure for the compound whose 1HNMR spectrum given is to be proposed. Given: M.F = C8H9Br I.R: 820 cm-1.
1HNMR spectrum: 7.07δ (2H, doublet); 7.39δ (2H, doublet); 2.58δ (2H, quartet); 1.20δ (3H, triplet).
Answer to Problem 47AP
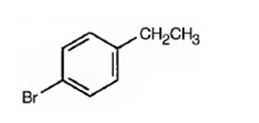
A structure for the compound with M.F = C8H9Br with spectral characteristics: I.R: 820 cm-1, 1HNMR spectrum: 7.07δ (2H, doublet); 7.39δ (2H, doublet); 2.58δ (2H, quartet); 1.20δ (3H, triplet) is
Explanation of Solution
The molecular formula of the compound is C8H9Br.
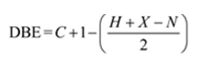
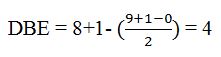
Thus the compound has four unsaturation units like double bonds and/or rings. The two doublets at 7.07δ and 7.39δ each corresponding to two protons indicate the compound is aromatic and each proton responsible for the doublet has a proton on the adjacent carbon. The two proton quartet at 2.58δ (benzylic) and three proton triplet at 1.20δ (primary) could be accounted for only if an ethyl substituent is present on the ring along with bromine. The I.R absorption at 820 cm-1 indicates that the ethyl group and bromine are arranged in para positions. Hence the compound is p-bromoethyl benzene.
A structure for the compound with M.F=C8H9Br with spectral characteristics: I.R: 820 cm-1, 1HNMR spectrum: 7.07δ (2H, doublet); 7.39δ (2H, doublet); 2.58δ (2H, quartet); 1.20δ (3H, triplet) is

b)
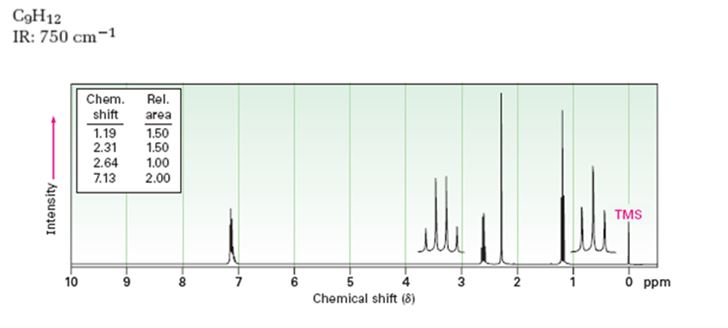
Interpretation:
A structure for the compound whose 1HNMR spectrum given is to be proposed.
Given: M.F = C9H12 I.R: 750 cm-1
1HNMR spectrum: 7.13δ (4H, broad); 2.64δ (2H, quartet); 2.31δ (3H, singlet); 1.19δ (3H, triplet).
Concept introduction:
In 1HNMR spectrum aromatic protons give a broad peak in the range 6.5δ-8.0δ, the primary alkyl protons around 0.7δ-1.3δ, the secondary alkyl protons around 1.2δ-1.6δ, and a tertiary alkyl protons in between 1.4δ-1.8δ. The multiplicity of a signal gives an idea about the protons present in the adjacent carbons.
In I.R, the o-disubstituted benzenes absorb around 735-770 cm-1, m-disubstituted benzenes absorb around 690-710 cm-1and p-disubstituted benzenes absorb around 810-840 cm-1.
To propose:
A structure for the compound whose 1HNMR spectrum given is to be proposed. Given: M.F = C9H12 I.R: 750 cm-1.
1HNMR spectrum: 7.13δ (4H, broad); 2.64δ (2H, quartet); 2.31δ (3H, singlet); 1.19δ (3H, triplet).
Answer to Problem 47AP
A structure for the compound whose 1HNMR spectrum given is to be proposed. Given: M.F = C9H12, I.R: 750 cm-1, 1HNMR spectrum: 7.13δ (4H, broad); 2.64δ (2H, quartet); 2.31δ (3H, singlet); 1.19δ (3H, triplet) is
Explanation of Solution
The molecular formula of the compound is C9H12.
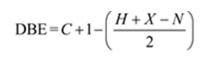
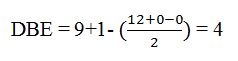
Thus the compound has four unsaturation units like double bonds and/or rings. The four proton broad band at 7.13δ indicates that the compound is aromatic with two substituent groups attached to the benzene ring. The two proton quartet at 2.64δ (benzylic) and three proton triplet at 1.19δ (primary alkyl) could be accounted for only if an ethyl group is present on the ring. The three proton singlet at 2.31δ (benzylic) can be attributed to a methyl group attached to the ring. Thus the two substituent groups attached to the benzene ring are ethyl and methyl. The I.R absorption at 750 cm-1 requires that the ethyl and methyl groups to be arranged in ortho positions. Hence the compound is o-ethyltoluene.
A structure for the compound whose 1HNMR spectrum given is to be proposed. Given: M.F = C9H12, I.R: 750 cm-1, 1HNMR spectrum: 7.13δ (4H, broad); 2.64δ (2H, quartet); 2.31δ (3H, singlet); 1.19δ (3H, triplet) is

c)
Interpretation:
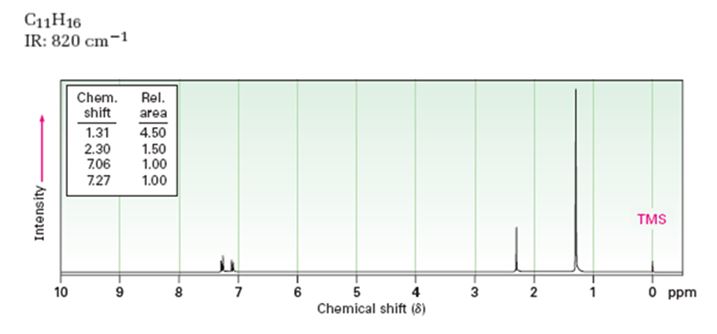
A structure for the compound whose 1HNMR spectrum given is to be proposed. Given: M.F = C11H16 I.R: 820 cm-1.
1HNMR spectrum: 7.27δ (2H, doublet); 7.06δ (2H, doublet); 2.30δ (3H, singlet); 1.31δ (9H, singlet).
Concept introduction:
In 1HNMR spectrum aromatic protons give a broad peak in the range 6.5δ-8.0δ, the primary alkyl protons around 0.7δ-1.3 δ, the secondary alkyl protons around 1.2δ-1.6δ, and a tertiary alkyl protons in between 1.4δ-1.8δ. The multiplicity of a signal gives an idea about the protons present in the adjacent carbons.
In I.R, the o-disubstituted benzenes absorb around 735-770 cm-1, m-disubstituted benzenes absorb around 690-710 cm-1 and p-disubstituted benzenes absorb around 810-840 cm-1.
To propose:
A structure for the compound whose 1HNMR spectrum given is to be proposed. Given: M.F = C11H16 I.R: 820 cm-1.
1HNMR spectrum: 7.27δ (2H, doublet); 7.06δ (2H, doublet); 2.30δ (3H, singlet); 1.31δ (9H, singlet).
Answer to Problem 47AP
A structure for the compound whose 1HNMR spectrum given is to be proposed. Given: M.F = C11H16; I.R: 820 cm-1; 1HNMR spectrum: 7.27δ (2H, doublet); 7.06δ (2H, doublet); 2.30δ (3H, singlet); 1.31δ (9H, singlet).
Explanation of Solution
The molecular formula of the compound is C11H16.
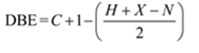
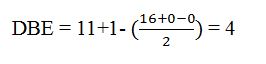
Thus the compound has four unsaturation units like double bonds and/or rings. The two doublets at 7.27δ and 7.06δ each corresponding to two protons indicate the compound is aromatic and each proton responsible for the doublet has a proton on the adjacent carbon. The three proton singlet at 2.58δ (benzylic) could be accounted for a methyl group attached to the benzene ring. The remaining four carbons and nine hydrogens indicate the presence of a tert-butyl group attached to the benzene ring which is confirmed by the nine proton singlet at 1.31δ (primary alkyl). Thus methyl and tert-butyl are the two substituent groups on the benzene ring. The I.R absorption at 820 cm-1 indicates that the two substituent groups are arranged in para positions. Hence the compound is p-t-butyltoluene.
A structure for the compound whose 1HNMR spectrum given is to be proposed. Given: M.F = C11H16; I.R: 820 cm-1; 1HNMR spectrum: 7.27δ (2H, doublet); 7.06δ (2H, doublet); 2.30δ (3H, singlet); 1.31δ (9H, singlet).

Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
EP ORGANIC CHEMISTRY,24 MONTH-OWLV2
- K Draw the starting structure that would lead to the major product shown under the provided conditions. Drawing 1. NaNH2 2. PhCH2Br 4 57°F Sunny Q Searcharrow_forward7 Draw the starting alkyl bromide that would produce this alkyne under these conditions. F Drawing 1. NaNH2, A 2. H3O+ £ 4 Temps to rise Tomorrow Q Search H2arrow_forward7 Comment on the general features of the predicted (extremely simplified) ¹H- NMR spectrum of lycopene that is provided below. 00 6 57 PPM 3 2 1 0arrow_forward
