
Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics (14th Edition)
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780133915389
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 15.7, Problem 94P
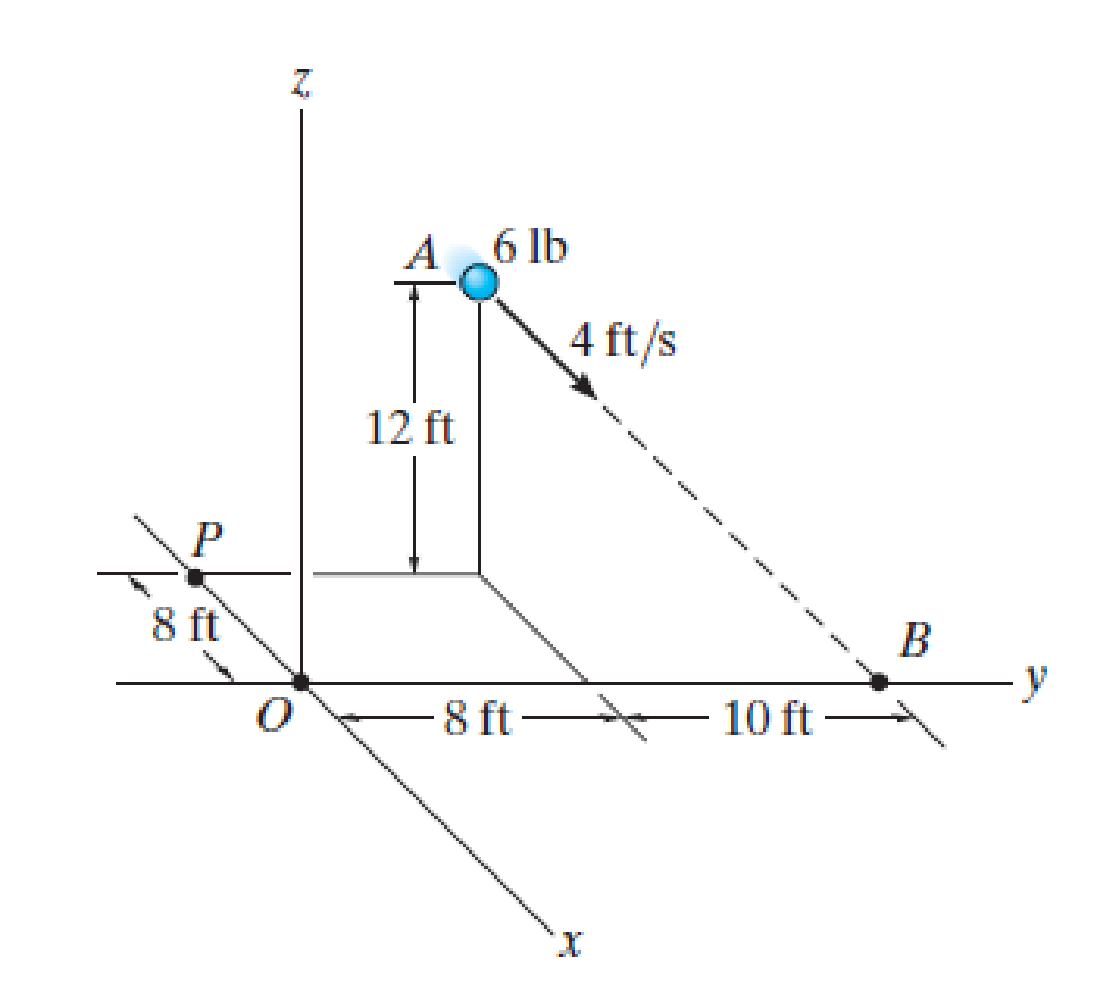
Determine the angular momentum HO of the 6-lb particle about point O.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Q.1: (15 Marks)
Find the first three natural frequencies and mode shapes of the axial and torsional
vibration for a steel shaft free at both ends, having a length of 3 m. Find the subsequent
axil motion if the shaft is subjected to the following initial conditions, given that E = 210
GPa, G=80 GPa, p = 7800 kg/m³:
f(x)=0
v(x) = {1
2.8
Q.4: (15 Marks)
A uniform rotor of mass 500 kg and diametral moment of inertia of 20 kg.m², is supported
by identical short bearings of stiffness 1 MN/m in the horizontal and vertical directions. If
the distance between the bearings is 0.6 m:
(a) What is the corresponding polar moment of inertia if the backward whirling speed is
80% of the static structure tilting natural frequency?
(b) Determine the forward whirling speed.
45.27
University of Babylon
Collage of Engineering/
Al-Musayab
Department of Automobiles
Mid Examination/ Stage: 3rd
Subject: Theory of Vehicles
Date: 14 \ 4 \2025
Time: 1.5 Hours
2025-2024
Q1: The arms of a Porter governor are 250 mm long. The upper arms are pivoted on
the axis of revolution, but the lower arms are attached to a sleeve at a distance of 50
mm from the axis of rotation. The weight on the sleeve is 600 N and the weight of
each ball is 80 N. Determine the equilibrium speed when the radius of rotation of the
balls is 150 mm. If the friction is equivalent to a load of 25 N at the sleeve, determine
the range of speed for this position.
Q2: In a loaded Proell governor shown in Figure below each ball weighs 3 kg and
the central sleeve weighs 25 kg. The arms are of 200 mm length and pivoted about
axis displaced from the central axis of rotation by 38.5 mm, y=238 mm, x=303.5
mm, CE 85 mm, MD 142.5 mm. Determine the equilibrium speed.
Fe
mg
E
M
2
Q3: In a spring loaded Hartnell type…
Chapter 15 Solutions
Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics (14th Edition)
Ch. 15.2 - Determine the impulse of the force for t = 2 s.Ch. 15.2 - Determine the magnitude of the impulse the ground...Ch. 15.2 - The crate starts from rest and is towed by the...Ch. 15.2 - Determine the speed of the 25-kg crate when t = 4...Ch. 15.2 - If the car starts from rest, determine its speed...Ch. 15.2 - The traction force developed at the wheels is FD =...Ch. 15.2 - Determine the impulse of his foot on the ball at...Ch. 15.2 - The crate starts from rest and is towed by the...Ch. 15.2 - Determine the average tension in each of the two...Ch. 15.2 - If the uniform beam has a weight of 5000 lb,...
Ch. 15.2 - Determine the magnitude of the net impulse exerted...Ch. 15.2 - If it takes 80 s for the train to increase its...Ch. 15.2 - If they start from rest, determine their speed...Ch. 15.2 - If the impact occurs in 0.06 s, determine the...Ch. 15.2 - The winch delivers a horizontal towing force T to...Ch. 15.2 - If the crate starts from rest and achieves a speed...Ch. 15.2 - To achieve this the 2-kg spike S is fired into the...Ch. 15.2 - If the van has a speed of 20 km/h when t = 0,...Ch. 15.2 - If the speed decreases to 40 km/h in 5 s,...Ch. 15.2 - If it strikes the barrier, determine the...Ch. 15.2 - If the 100 kg crate is originally at rest at t = 0...Ch. 15.2 - From the data shown in the graphs, determine the...Ch. 15.2 - Determine its speed, starting from rest, when t =...Ch. 15.2 - Determine the speed of the crate when t = 3 s and...Ch. 15.2 - If these loadings vary in the manner shown on the...Ch. 15.2 - If the cabinet is initially moving to the left...Ch. 15.2 - The propeller provides the propulsion force F...Ch. 15.2 - Determine the sleds maximum velocity and the...Ch. 15.2 - If the 34-lb crate is originally on the ground at...Ch. 15.2 - If the 34-lb crate is originally at rest on the...Ch. 15.2 - The balloon is rising at a constant velocity of 18...Ch. 15.2 - Prob. 26PCh. 15.2 - Determine the speed of the crate when t = 3 s,...Ch. 15.2 - Determine how high the crate has moved upward when...Ch. 15.2 - As a result of the explosion, the cylinder...Ch. 15.2 - If the carrier is traveling forward with a speed...Ch. 15.2 - If B is moving downward with a velocity (vB)1 = 3...Ch. 15.2 - Prob. 32PCh. 15.2 - The winch delivers a horizontal towing force T to...Ch. 15.2 - It then travels along the trajectory shown before...Ch. 15.2 - Determine the velocity of A after collision if the...Ch. 15.2 - If the cart has a smooth surface and it is...Ch. 15.3 - If the two blocks couple together after collision,...Ch. 15.3 - If the spring is compressed s = 200 mm and then...Ch. 15.3 - If A is stationary and B has a velocity of 15 m/s...Ch. 15.3 - If a 20-kg projectile is fired from the cannon...Ch. 15.3 - Meanwhile a 2-Mg car A is traveling at 15 m/s to...Ch. 15.3 - Determine the distance s the boy reaches up the...Ch. 15.3 - At the same time another car having a mass of 12...Ch. 15.3 - When a 2-g bullet strikes and becomes embedded in...Ch. 15.3 - If he lands on the second fiat car B, determine...Ch. 15.3 - Determine the speed of the block just after the...Ch. 15.3 - Determine the speed of the block just after the...Ch. 15.3 - Determine the distance the block will slide before...Ch. 15.3 - When the toboggan reaches the bottom of the slope...Ch. 15.3 - Determine its speed v2 and its direction 2 when it...Ch. 15.3 - A spring, having a stiffness of k = 60 N/m, is...Ch. 15.3 - Determine the maximum compression of the spring...Ch. 15.3 - They are placed on a smooth surface and the spring...Ch. 15.3 - If they exchange positions, A going to B and then...Ch. 15.3 - If A walks to B and stops, and both walk back...Ch. 15.3 - If someone drives the automobile to the other side...Ch. 15.3 - A 10-kg crate is released from rest at A and...Ch. 15.3 - Block A has a mass of 5 kg and is placed on the...Ch. 15.3 - if the coefficient of kinetic friction between A...Ch. 15.3 - When it reaches the bottom, a spring loaded gun...Ch. 15.3 - If the belt starts from rest and begins to run...Ch. 15.3 - If the 10-g bullet is traveling at 300 m/s when it...Ch. 15.3 - The velocities of A and B before and after the...Ch. 15.3 - If the coefficient of restitution between the...Ch. 15.4 - As it slides down the ramp, it strikes the 80-lb...Ch. 15.4 - If the coefficient of restitution between the ball...Ch. 15.4 - Disk B has a mass of 11 kg and is initially at...Ch. 15.4 - Two disks A and B each have a mass of 1 kg and the...Ch. 15.4 - Disk A has a mass of 250 g and is sliding on a...Ch. 15.4 - After the collision, the car moves with a velocity...Ch. 15.4 - If the coefficient of restitution between the...Ch. 15.4 - The block has a velocity v = 10 m/s when it is s =...Ch. 15.4 - If A and B are rolling forward with velocity v and...Ch. 15.4 - If A and B are rolling forward with velocity v and...Ch. 15.4 - If e = 0.7, determine the velocity of each ball...Ch. 15.4 - If the coefficient of restitution between A and B...Ch. 15.4 - If the coefficient of restitution between A and B...Ch. 15.4 - If ball A is released from rest and strikes ball B...Ch. 15.4 - Determine (a) the velocity at which it strikes the...Ch. 15.4 - If the coefficient of restitution between the ball...Ch. 15.4 - If A is given a velocity of 0, while sphere B is...Ch. 15.4 - Determine the initial velocity vA of the ball and...Ch. 15.4 - Determine the initial velocity vA, the final...Ch. 15.4 - If both disks are moving with the velocities shown...Ch. 15.4 - If both disks are moving with the velocities shown...Ch. 15.4 - If the coefficient of restitution between the ball...Ch. 15.4 - If it rebounds to a height of hl, determine the...Ch. 15.4 - If it makes a direct collision with ball B (e =...Ch. 15.4 - If the coefficient of restitution between the...Ch. 15.4 - If they collide with the initial velocities shown,...Ch. 15.4 - If the coefficient of restitution between the ball...Ch. 15.4 - Determine (a) the velocity at which it strikes the...Ch. 15.4 - The box has a velocity v = 15 ft/s when it is 2 ft...Ch. 15.4 - Prob. 83PCh. 15.4 - If it rebounds at an angle and the coefficient of...Ch. 15.4 - If it rebounds at the same angle = 45 , determine...Ch. 15.4 - lf A strikes B with a velocity (vA)1 = 1.5 m/s as...Ch. 15.4 - If each "stone" is smooth and has a weight of 47...Ch. 15.4 - If each "stone" is smooth and has a weight of 47...Ch. 15.4 - If they have masses mA = 4 kg and mB = 2 kg,...Ch. 15.4 - if cranberries having an e 0.8 are to be...Ch. 15.4 - Prob. 91PCh. 15.4 - Prob. 92PCh. 15.4 - If they are sliding on a smooth horizontal plane...Ch. 15.4 - Determine its angular momentum HO about point O.Ch. 15.4 - Determine its angular momentum Hp about point P.Ch. 15.7 - If a constant tangential force F = 5 N is applied...Ch. 15.7 - If the block starts from rest, determine its speed...Ch. 15.7 - If the system is subjected to a couple moment M =...Ch. 15.7 - If the spheres are subjected to tangential forces...Ch. 15.7 - Determine the angular momentum HO of the 6-lb...Ch. 15.7 - Determine the angular momentum HP of the 6-lb...Ch. 15.7 - Determine the angular momentum HO, of each of the...Ch. 15.7 - Determine the angular momentum Hp, of each of the...Ch. 15.7 - Determine the angular momentum HO of the 3-kg...Ch. 15.7 - Determine the angular momentum Hp of the 3-kg...Ch. 15.7 - If the rod is subjected to a torque M = (t2 + 2) N...Ch. 15.7 - If the helix descends 8 ft for every one...Ch. 15.7 - If the helix descends 8 ft for every one...Ch. 15.7 - If the attached cord is pulled down through the...Ch. 15.7 - If the attached cord is pulled down through the...Ch. 15.7 - The blocks are fixed to the horizontal rods, and...Ch. 15.7 - The particle is placed at the position shown and...Ch. 15.7 - The car starts from rest. The total mass of the...Ch. 15.7 - If the force F on the cord is increased, the bob...Ch. 15.7 - It is attached to a fixed point at A and a block...Ch. 15.7 - If at t = 0, the cable OA is pulled in toward O at...Ch. 15.7 - If the rope is pulled inward with a constant speed...Ch. 15.7 - If the track is flat and banked at an angle of 60,...Ch. 15.7 - If the launch angle at this position is A = 70,...Ch. 15.7 - Prob. 114PCh. 15.9 - If the water has a cross-sectional area of 0.05...Ch. 15.9 - If the fan ejects air with a speed of 14 m/s,...Ch. 15.9 - Prob. 117PCh. 15.9 - Prob. 118PCh. 15.9 - If one-fourth of the water flows downward while...Ch. 15.9 - Water flows through the pipe at A with a velocity...Ch. 15.9 - Prob. 121PCh. 15.9 - Prob. 122PCh. 15.9 - If the locomotive is traveling at a constant speed...Ch. 15.9 - Prob. 124PCh. 15.9 - Prob. 125PCh. 15.9 - The machine discharges the snow through a tube T...Ch. 15.9 - Prob. 127PCh. 15.9 - Prob. 128PCh. 15.9 - It is then divided equally between the two outlets...Ch. 15.9 - Prob. 130PCh. 15.9 - Prob. 131PCh. 15.9 - Prob. 132PCh. 15.9 - Prob. 133PCh. 15.9 - Prob. 134PCh. 15.9 - Prob. 135PCh. 15.9 - Prob. 136PCh. 15.9 - Prob. 137PCh. 15.9 - Prob. 138PCh. 15.9 - Prob. 139PCh. 15.9 - The jet is traveling at a speed of 720 km/h. If...Ch. 15.9 - Prob. 141PCh. 15.9 - Air enters the intake scoops S at the rate of 50...Ch. 15.9 - Prob. 143PCh. 15.9 - Prob. 144PCh. 15.9 - Prob. 145PCh. 15.9 - Prob. 146PCh. 15.9 - Prob. 147PCh. 15.9 - Prob. 148PCh. 15.9 - Prob. 149PCh. 15.9 - If the ball then moves horizontally to the right,...Ch. 15.9 - Prob. 2CPCh. 15.9 - If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the...Ch. 15.9 - The coefficient of kinetic friction between the...Ch. 15.9 - If a horizontal force F is applied such that it...Ch. 15.9 - They are traveling along the track with the...Ch. 15.9 - If the projectile penetrates and emerges from the...Ch. 15.9 - If the collision is perfectly elastic (e = 1),...Ch. 15.9 - If A strikes B with a velocity of (vA)1 = 2 m/s as...Ch. 15.9 - If the frame is subjected to a couple M = (8t2 +...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Q.2: (15 Marks) = 1400 For the following system, determine the first natural frequency using Dunkerley's equation, Given that the disk has moment of inertia J = 2 kg.m², the shaft has G = 20 GPa, p kg/m³, polar moment of cross-sectional area of the shaft Ip = 8×108 m². 500 mm 220 mm k=200 N/m FOF m=1 kg 14.14 56.56. W слarrow_forwardQ.2: (15 Marks) = 1400 For the following system, determine the first natural frequency using Dunkerley's equation, Given that the disk has moment of inertia J = 2 kg.m², the shaft has G = 20 GPa, p kg/m³, polar moment of cross-sectional area of the shaft Ip = 8×108 m². 500 mm 220 mm k=200 N/m FOF m=1 kg 14.14 56.56. W слarrow_forwardQ1: In Figure below, pinion A having 15 teeth is fixed to motor shaft. Za-20, Z-15, where B and C are a compound gear wheel. Wheel E is keyed to the machine shaft. Arm F rotates about the same shaft on which A is fixed and carries the compound wheel B, C. If the motor runs at 1200 rpm counter-clockwise, find (a) the speed of the machine shaft and (b) ratio of the reduction gear. C B D Q1: A compound epicyclic gear is shown diagrammatically in Figure below. The gears A, D and E are free to rotate on the axis P. The compound gear B and C rotate together on the axis Q at the end of arm F. All the gears have equal pitch. The number of external teeth on the gears A, B and C are 18, 45 and 21 respectively. The gears D and E are annular gears. The gear A rotates at 100 r.p.m. in the anticlockwise direction and the gear D rotates at 450 r.p.m. clockwise. Find the speed and direction of the arm and the gear E. D E A P F LL B Carrow_forward
- Calculate the force in cable AB and the angle θ for the support system shown. Round your final answers to two decimal places.arrow_forward1.53 In the steel structure shown, a 6-mm-diameter pin is used at C and 10-mm-diameter pins are used at B and D. The ultimate shearing stress is 150 MPa at all connections, and the ultimate normal stress is 400 MPa in link BD. Knowing that a factor of safety of 3.0 is desired, determine the largest load P that can be applied at A. Note that link BD is not reinforced around the pin holes. Front view D D 6 mm 18 mm B A B Side view 160 mm 120 mm A B Top viewarrow_forwardCORRECT AND DETAILED HANDWRITTEN SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE THANK YOU. CORRECT ANSWER IS ALREADY PROVIDED. 16: Determine (a) the maximum bending stress, (b)the maximum shearing stress, (c) compressive bending stress atthe roller support, and (d) the shearing stress 1 in below the topsurface of the beam at the location 1 ft to the right of the rollersupport in the simply supported beam shown in Fig. 8-70.ANS: (a) 21,945.313 lb/in2; (b) 1656.25 lb/in2; (c) 10,000 lb/in2; (d) 190.972 lb/in2arrow_forward
- CORRECT AND DETAILED HANDWRITTEN SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE THANK YOU. CORRECT ANSWER IS ALREADY PROVIDED. 20: A 2022 Porsche 911 (992) GT3 is crossing a 20 ft bridge. The specification of the car is shown below.Determine the maximum shear (in lb) and moment (in lb-ft) on the bridge. ANS: Vmax = 2,680.850 lb ; Mmax = 11,233.13 lb-ftarrow_forwardCORRECT AND DETAILED HANDWRITTEN SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE THANK YOU. CORRECT ANSWER IS ALREADY PROVIDED. Answers: P1 = 208.625 KN/M P2 = 281.310 KN/M P = 15.491 KN/M FB = 463.402 MPA FV = 55.034 MPAarrow_forwardCORRECT AND DETAILED HANDWRITTEN SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE THANK YOU. CORRECT ANSWER IS ALREADY PROVIDED. 18: Determine the maximum shear and moment that would be experienced by a 10 m beam if a three-wheelmoving load of 10 kN, 30 kN, and 5 kN respectively will pass it by. The distance between the 1st and 2nd load is 1 m and the distance between the 2nd and 3rd load is 3 m.ANS: Vmax = 40 kN ; Mmax = 100.014 kN-marrow_forward
- CORRECT AND DETAILED HANDWRITTEN SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE THANK YOU. CORRECT ANSWER IS ALREADY PROVIDED. 5: A 12-m simply supported bridge is constructed with 100-mm concrete slab deck supported by precastconcrete stringers spaced 800 mm on center. Analyze the stringers when subjected to a moving load consisting of 3 evenly spaced axle loads at 3 m and equivalent to 20 kN, 30 kN and 40 kN respectively. The self-weight of the stringers is 8.5 kN/m and the concrete deck has a unit weight of 24 kN/m3 . Neglect all other superimposed loads. Calculate: (a) the maximum shear force in the stringers; (b) the maximum bending moment in the stringers. Answer: Vmax = 135.020 KN, Mmax = 477.388 KN-Marrow_forwardCORRECT AND DETAILED HANDWRITTEN SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE THANK YOU. CORRECT ANSWER IS ALREADY PROVIDED. 19: A 22-wheeler truck is crossing over 25 m bridge. The dimensions between the axles of the truck are shownin the figure below. Axles 1 to 3 carry a 90 kN load each, axles 4 and 5 carry a 65 kN load each, and the axle directly below the cab of the truck has a load of 100 kN. Determine the maximum shear and moment on the bridge.ANS: Vmax = 374.92 kN ; Mmax = 1,702.229 kN-marrow_forwardCORRECT AND DETAILED HANDWRITTEN SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE THANK YOU. CORRECT ANSWER IS ALREADY PROVIDED. 1. A H = 6 m cantilever retaining wall is subjected to a soil pressurelinearly varying from zero at the top to 90 kPa at the bottom. As an additionalsupport, it is anchored at depth y = 2 m. with maximum tension equal to 25kN. Assume that the stem provides fully retrained support. Draw the shearand moment diagram of the wall to calculate the following: (a) Maximumpositive bending moment per linear meter; (b) maximum negative bendingmoment per linear meter; (c) maximum shear force per linear meter. answer: +MMax = 440 kn-m, -Mmax = 0kn-M, Vmax = 245 KNarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Dynamics - Lesson 1: Introduction and Constant Acceleration Equations; Author: Jeff Hanson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7aMiZ3b0Ieg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY