
Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics (14th Edition)
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780133915389
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 15.4, Problem 62P
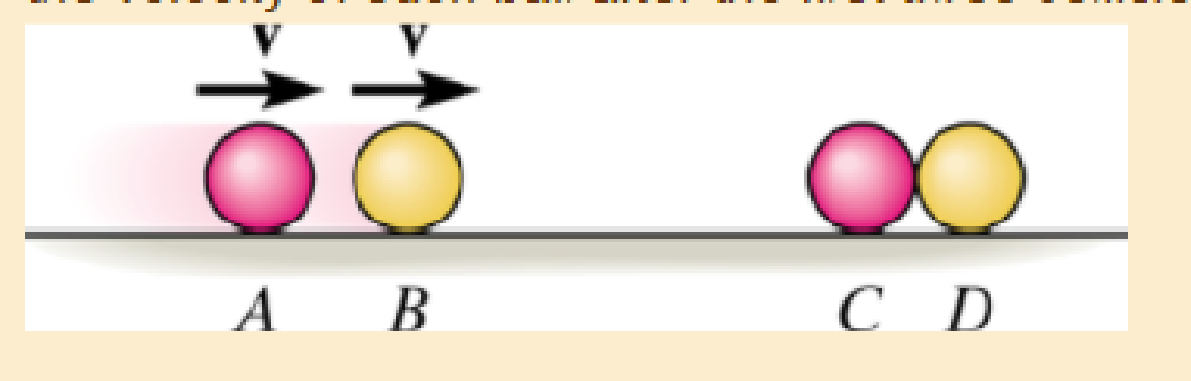
If A and B are rolling forward with velocity v and strike C, explain why after collision C and D each move off with velocity v. Why doesn't D move off with velocity 2v? The collision is elastic, e = 1. Neglect the size of each ball.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Please do not use any AI tools to solve this question.
I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor.
No AI-generated responses, please.
Please do not use any AI tools to solve this question.
I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor.
No AI-generated responses, please.
Please do not use any AI tools to solve this question.
I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor.
No AI-generated responses, please.
Chapter 15 Solutions
Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics (14th Edition)
Ch. 15.2 - Determine the impulse of the force for t = 2 s.Ch. 15.2 - Determine the magnitude of the impulse the ground...Ch. 15.2 - The crate starts from rest and is towed by the...Ch. 15.2 - Determine the speed of the 25-kg crate when t = 4...Ch. 15.2 - If the car starts from rest, determine its speed...Ch. 15.2 - The traction force developed at the wheels is FD =...Ch. 15.2 - Determine the impulse of his foot on the ball at...Ch. 15.2 - The crate starts from rest and is towed by the...Ch. 15.2 - Determine the average tension in each of the two...Ch. 15.2 - If the uniform beam has a weight of 5000 lb,...
Ch. 15.2 - Determine the magnitude of the net impulse exerted...Ch. 15.2 - If it takes 80 s for the train to increase its...Ch. 15.2 - If they start from rest, determine their speed...Ch. 15.2 - If the impact occurs in 0.06 s, determine the...Ch. 15.2 - The winch delivers a horizontal towing force T to...Ch. 15.2 - If the crate starts from rest and achieves a speed...Ch. 15.2 - To achieve this the 2-kg spike S is fired into the...Ch. 15.2 - If the van has a speed of 20 km/h when t = 0,...Ch. 15.2 - If the speed decreases to 40 km/h in 5 s,...Ch. 15.2 - If it strikes the barrier, determine the...Ch. 15.2 - If the 100 kg crate is originally at rest at t = 0...Ch. 15.2 - From the data shown in the graphs, determine the...Ch. 15.2 - Determine its speed, starting from rest, when t =...Ch. 15.2 - Determine the speed of the crate when t = 3 s and...Ch. 15.2 - If these loadings vary in the manner shown on the...Ch. 15.2 - If the cabinet is initially moving to the left...Ch. 15.2 - The propeller provides the propulsion force F...Ch. 15.2 - Determine the sleds maximum velocity and the...Ch. 15.2 - If the 34-lb crate is originally on the ground at...Ch. 15.2 - If the 34-lb crate is originally at rest on the...Ch. 15.2 - The balloon is rising at a constant velocity of 18...Ch. 15.2 - Prob. 26PCh. 15.2 - Determine the speed of the crate when t = 3 s,...Ch. 15.2 - Determine how high the crate has moved upward when...Ch. 15.2 - As a result of the explosion, the cylinder...Ch. 15.2 - If the carrier is traveling forward with a speed...Ch. 15.2 - If B is moving downward with a velocity (vB)1 = 3...Ch. 15.2 - Prob. 32PCh. 15.2 - The winch delivers a horizontal towing force T to...Ch. 15.2 - It then travels along the trajectory shown before...Ch. 15.2 - Determine the velocity of A after collision if the...Ch. 15.2 - If the cart has a smooth surface and it is...Ch. 15.3 - If the two blocks couple together after collision,...Ch. 15.3 - If the spring is compressed s = 200 mm and then...Ch. 15.3 - If A is stationary and B has a velocity of 15 m/s...Ch. 15.3 - If a 20-kg projectile is fired from the cannon...Ch. 15.3 - Meanwhile a 2-Mg car A is traveling at 15 m/s to...Ch. 15.3 - Determine the distance s the boy reaches up the...Ch. 15.3 - At the same time another car having a mass of 12...Ch. 15.3 - When a 2-g bullet strikes and becomes embedded in...Ch. 15.3 - If he lands on the second fiat car B, determine...Ch. 15.3 - Determine the speed of the block just after the...Ch. 15.3 - Determine the speed of the block just after the...Ch. 15.3 - Determine the distance the block will slide before...Ch. 15.3 - When the toboggan reaches the bottom of the slope...Ch. 15.3 - Determine its speed v2 and its direction 2 when it...Ch. 15.3 - A spring, having a stiffness of k = 60 N/m, is...Ch. 15.3 - Determine the maximum compression of the spring...Ch. 15.3 - They are placed on a smooth surface and the spring...Ch. 15.3 - If they exchange positions, A going to B and then...Ch. 15.3 - If A walks to B and stops, and both walk back...Ch. 15.3 - If someone drives the automobile to the other side...Ch. 15.3 - A 10-kg crate is released from rest at A and...Ch. 15.3 - Block A has a mass of 5 kg and is placed on the...Ch. 15.3 - if the coefficient of kinetic friction between A...Ch. 15.3 - When it reaches the bottom, a spring loaded gun...Ch. 15.3 - If the belt starts from rest and begins to run...Ch. 15.3 - If the 10-g bullet is traveling at 300 m/s when it...Ch. 15.3 - The velocities of A and B before and after the...Ch. 15.3 - If the coefficient of restitution between the...Ch. 15.4 - As it slides down the ramp, it strikes the 80-lb...Ch. 15.4 - If the coefficient of restitution between the ball...Ch. 15.4 - Disk B has a mass of 11 kg and is initially at...Ch. 15.4 - Two disks A and B each have a mass of 1 kg and the...Ch. 15.4 - Disk A has a mass of 250 g and is sliding on a...Ch. 15.4 - After the collision, the car moves with a velocity...Ch. 15.4 - If the coefficient of restitution between the...Ch. 15.4 - The block has a velocity v = 10 m/s when it is s =...Ch. 15.4 - If A and B are rolling forward with velocity v and...Ch. 15.4 - If A and B are rolling forward with velocity v and...Ch. 15.4 - If e = 0.7, determine the velocity of each ball...Ch. 15.4 - If the coefficient of restitution between A and B...Ch. 15.4 - If the coefficient of restitution between A and B...Ch. 15.4 - If ball A is released from rest and strikes ball B...Ch. 15.4 - Determine (a) the velocity at which it strikes the...Ch. 15.4 - If the coefficient of restitution between the ball...Ch. 15.4 - If A is given a velocity of 0, while sphere B is...Ch. 15.4 - Determine the initial velocity vA of the ball and...Ch. 15.4 - Determine the initial velocity vA, the final...Ch. 15.4 - If both disks are moving with the velocities shown...Ch. 15.4 - If both disks are moving with the velocities shown...Ch. 15.4 - If the coefficient of restitution between the ball...Ch. 15.4 - If it rebounds to a height of hl, determine the...Ch. 15.4 - If it makes a direct collision with ball B (e =...Ch. 15.4 - If the coefficient of restitution between the...Ch. 15.4 - If they collide with the initial velocities shown,...Ch. 15.4 - If the coefficient of restitution between the ball...Ch. 15.4 - Determine (a) the velocity at which it strikes the...Ch. 15.4 - The box has a velocity v = 15 ft/s when it is 2 ft...Ch. 15.4 - Prob. 83PCh. 15.4 - If it rebounds at an angle and the coefficient of...Ch. 15.4 - If it rebounds at the same angle = 45 , determine...Ch. 15.4 - lf A strikes B with a velocity (vA)1 = 1.5 m/s as...Ch. 15.4 - If each "stone" is smooth and has a weight of 47...Ch. 15.4 - If each "stone" is smooth and has a weight of 47...Ch. 15.4 - If they have masses mA = 4 kg and mB = 2 kg,...Ch. 15.4 - if cranberries having an e 0.8 are to be...Ch. 15.4 - Prob. 91PCh. 15.4 - Prob. 92PCh. 15.4 - If they are sliding on a smooth horizontal plane...Ch. 15.4 - Determine its angular momentum HO about point O.Ch. 15.4 - Determine its angular momentum Hp about point P.Ch. 15.7 - If a constant tangential force F = 5 N is applied...Ch. 15.7 - If the block starts from rest, determine its speed...Ch. 15.7 - If the system is subjected to a couple moment M =...Ch. 15.7 - If the spheres are subjected to tangential forces...Ch. 15.7 - Determine the angular momentum HO of the 6-lb...Ch. 15.7 - Determine the angular momentum HP of the 6-lb...Ch. 15.7 - Determine the angular momentum HO, of each of the...Ch. 15.7 - Determine the angular momentum Hp, of each of the...Ch. 15.7 - Determine the angular momentum HO of the 3-kg...Ch. 15.7 - Determine the angular momentum Hp of the 3-kg...Ch. 15.7 - If the rod is subjected to a torque M = (t2 + 2) N...Ch. 15.7 - If the helix descends 8 ft for every one...Ch. 15.7 - If the helix descends 8 ft for every one...Ch. 15.7 - If the attached cord is pulled down through the...Ch. 15.7 - If the attached cord is pulled down through the...Ch. 15.7 - The blocks are fixed to the horizontal rods, and...Ch. 15.7 - The particle is placed at the position shown and...Ch. 15.7 - The car starts from rest. The total mass of the...Ch. 15.7 - If the force F on the cord is increased, the bob...Ch. 15.7 - It is attached to a fixed point at A and a block...Ch. 15.7 - If at t = 0, the cable OA is pulled in toward O at...Ch. 15.7 - If the rope is pulled inward with a constant speed...Ch. 15.7 - If the track is flat and banked at an angle of 60,...Ch. 15.7 - If the launch angle at this position is A = 70,...Ch. 15.7 - Prob. 114PCh. 15.9 - If the water has a cross-sectional area of 0.05...Ch. 15.9 - If the fan ejects air with a speed of 14 m/s,...Ch. 15.9 - Prob. 117PCh. 15.9 - Prob. 118PCh. 15.9 - If one-fourth of the water flows downward while...Ch. 15.9 - Water flows through the pipe at A with a velocity...Ch. 15.9 - Prob. 121PCh. 15.9 - Prob. 122PCh. 15.9 - If the locomotive is traveling at a constant speed...Ch. 15.9 - Prob. 124PCh. 15.9 - Prob. 125PCh. 15.9 - The machine discharges the snow through a tube T...Ch. 15.9 - Prob. 127PCh. 15.9 - Prob. 128PCh. 15.9 - It is then divided equally between the two outlets...Ch. 15.9 - Prob. 130PCh. 15.9 - Prob. 131PCh. 15.9 - Prob. 132PCh. 15.9 - Prob. 133PCh. 15.9 - Prob. 134PCh. 15.9 - Prob. 135PCh. 15.9 - Prob. 136PCh. 15.9 - Prob. 137PCh. 15.9 - Prob. 138PCh. 15.9 - Prob. 139PCh. 15.9 - The jet is traveling at a speed of 720 km/h. If...Ch. 15.9 - Prob. 141PCh. 15.9 - Air enters the intake scoops S at the rate of 50...Ch. 15.9 - Prob. 143PCh. 15.9 - Prob. 144PCh. 15.9 - Prob. 145PCh. 15.9 - Prob. 146PCh. 15.9 - Prob. 147PCh. 15.9 - Prob. 148PCh. 15.9 - Prob. 149PCh. 15.9 - If the ball then moves horizontally to the right,...Ch. 15.9 - Prob. 2CPCh. 15.9 - If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the...Ch. 15.9 - The coefficient of kinetic friction between the...Ch. 15.9 - If a horizontal force F is applied such that it...Ch. 15.9 - They are traveling along the track with the...Ch. 15.9 - If the projectile penetrates and emerges from the...Ch. 15.9 - If the collision is perfectly elastic (e = 1),...Ch. 15.9 - If A strikes B with a velocity of (vA)1 = 2 m/s as...Ch. 15.9 - If the frame is subjected to a couple M = (8t2 +...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- [Q2]: The cost information supplied by the cost accountant is as follows:Sales 20,00 units, $ 10 per unitCalculate the (a/ newsale guantity and (b) new selling price to earn the sameVariable cost $ 6 per unit, Fixed Cost $ 30,000, Profit $ 50,000profit ifi) Variable cost increases by $ 2 per unitil) Fixed cost increase by $ 10,000Ili) Variable cost increase by $ 1 per unit and fixed cost reduces by $ 10,000arrow_forwardcan you please help me perform Visual Inspection and Fractography of the attatched image: Preliminary examination to identify the fracture origin, suspected fatigue striation, and corrosion evidences.arrow_forwardcan you please help[ me conduct Causal Analysis (FTA) on the scenario attatched: FTA diagram which is a fault tree analysis diagram will be used to gain an overview of the entire path of failure from root cause to the top event (i.e., the swing’s detachment) and to identify interactions between misuse, material decay and inspection errors.arrow_forward
- hi can you please help me in finding the stress intensity factor using a k-calcluator for the scenario attathced in the images.arrow_forwardHi, can you please help me .Identify and justify suitable analytical techniques of the scenario below, bearing in mind the kinds of information being handled to reach a conclusion (methodology). A child swing set was discovered to have failed at the fixing at the top of the chains connecting the seat to the top of the swing set. A 12 mm threaded steel bolt, connecting the shackle to the top beam, failed at the start of the threaded region on the linkage closest to the outside side of the swing set . The linkage and bolts were made of electro galvanised mild steel . The rigid bar chain alternatives and fixings were of the same material and appeared to be fitted in accordance with guidelines. The yield strength of the steel used is 260 MPa and the UTS is 380 MPa. The bolt that failed was threaded using a standard thread with a pitch (distance between threads) of 1.75 mm and a depth of approximately 1.1 mm. The swing set in question had been assigned to ‘toddlers’ with the application of…arrow_forwardHi, can you please define and calculate the failure mode of the linkage that failed on the swing (images added) : A child swing set was discovered to have failed at the fixing at the top of the chains connecting the seat to the top of the swing set. A 12 mm threaded steel bolt, connecting the shackle to the top beam, failed at the start of the threaded region on the linkage closest to the outside side of the swing set . The linkage and bolts were made of electro galvanised mild steel . The rigid bar chain alternatives and fixings were of the same material and appeared to be fitted in accordance with guidelines. The yield strength of the steel used is 260 MPa and the UTS is 380 MPa. The bolt that failed was threaded using a standard thread with a pitch (distance between threads) of 1.75 mm and a depth of approximately 1.1 mm. The swing set in question had been assigned to ‘toddlers’ with the application of a caged-type seat. However, the location was within the play area not…arrow_forward
- Page 11-68. The rectangular plate shown is subjected to a uniaxial stress of 2000 psi. Compute the shear stress and the tensile developed on a plane forming an angle of 30° with the longitud axis of the member. (Hint: Assume a cross-sectional area of unity) 2000 psi 2000 psi hparrow_forward11-70. A shear stress (pure shear) of 5000 psi exists on an element. (a) Determine the maximum tensile and compressive stresses caused in the element due to this shear. (b) Sketch the element showing the planes on which the maximum tensile and compressive stresses act.arrow_forward11-20. An aluminum specimen of circular cross section, 0.50 in. in diameter, ruptured under a tensile load of 12,000 lb. The plane of failure was found to be at 48° with a plane perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the specimen. (a) Compute the shear stress on the failure plane. (b) Compute the maximum tensile stress. (c) Compute the tensile stress on the failure plane. hparrow_forward
- A long flat steel bar 13 mm thick and 120 mm wide has semicircular grooves as shown and carries a tensile load of 50 kN Determine the maximum stress if plate r= 8mm r=21mm r=38mmarrow_forwardProblem 13: F₁ = A =250 N 30% Determine the moment of each of the three forces about point B. F₂ = 300 N 60° 2 m -3 m B 4 m F3=500 Narrow_forward3 kN 3 kN 1.8 kN/m 80 mm B 300 mm D an 1.5 m-1.5 m--1.5 m- PROBLEM 5.47 Using the method of Sec. 5.2, solve Prob. 5.16 PROBLEM 5.16 For the beam and loading shown, determine the maximum normal stress due to bending on a transverse section at C.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Dynamics - Lesson 1: Introduction and Constant Acceleration Equations; Author: Jeff Hanson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7aMiZ3b0Ieg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY