
Concept explainers
15.168 and 15.169 A chain is looped around two gears of radius 40 mm that can rotate freely with respect to the 320-mm arm AB. The chain moves about arm AB in a clockwise direction at the constant rate of 80 mm/s relative to the arm. Knowing that in the position shown arm AB rotates clockwise about A at the constant rate ω = 0.75 rad/s, determine the acceleration of each of the chain links indicated.
15.168 Links 1 and 2
15.169 Links 3 and 4
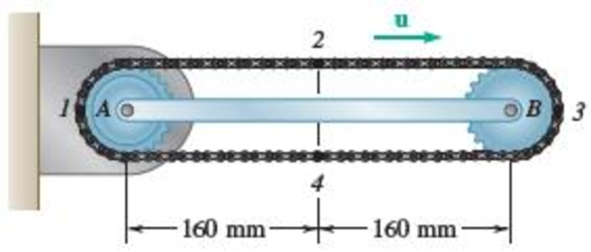
Fig. P15.168 and P15.169
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 15 Solutions
VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS W/CON >B
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Thinking Like an Engineer: An Active Learning Approach (4th Edition)
Starting Out With Visual Basic (8th Edition)
Automotive Technology: Principles, Diagnosis, And Service (6th Edition) (halderman Automotive Series)
SURVEY OF OPERATING SYSTEMS
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
- Procedure: 1- Cartesian system, 2(D)/(3)D, type of support 2- Free body diagram 3 - Find the support reactions 4- If you find a negative number then flip the force 5- Find the internal force 3D \sum Fx=0 \sum Fy=0 \sum Fz=0 \sum Mx=0 \sum My=0 \Sigma Mz=0 2D \Sigma Fx=0 \Sigma Fy=0 \Sigma Mz=0 5- Use method of section and cut the element where you want to find the internal force and keep either side of the sectionarrow_forwardFor each system below with transfer function G(s), plot the pole(s) on the s-plane. and indicate whether the system is: (a) "stable" (i.e., a bounded input will always result in a bounded output), (b) "marginally stable," or (c) "unstable" Sketch a rough graph of the time response to a step input. 8 a) G(s) = 5-5 8 b) G(s) = c) G(s) = = s+5 3s + 8 s² - 2s +2 3s +8 d) G(s): = s²+2s+2 3s+8 e) G(s): = s² +9 f) G(s): 8 00 == Sarrow_forwardPlease answer the following question. Include all work and plase explain. Graphs are provided below. "Consider the Mg (Magnesium) - Ni (Nickel) phase diagram shown below. This phase diagram contains two eutectic reactions and two intermediate phases (Mg2Ni and MgNi2). At a temperature of 505oC, determine what the composition of an alloy would need to be to contain a mass fraction of 0.20 Mg and 0.80 Mg2Ni."arrow_forward
- The triangular plate, having a 90∘∘ angle at AA, supports the load PP = 370 lblb as shown in (Figure 1).arrow_forwardDesign a 4-bar linkage to carry the body in Figure 1 through the two positions P1 and P2 at the angles shown in the figure. Use analytical synthesis with the free choice values z = 1.075, q= 210°, ß2 = −27° for left side and s = 1.24, y= 74°, ½ = − 40° for right side. φ 1.236 P2 147.5° 210° 2.138 P1 Figure 1 Xarrow_forwardDesign a 4-bar linkage to carry the body in Figure 1 through the two positions P1 and P2 at the angles shown in the figure. Use analytical synthesis with the free choice values z = 1.075, q= 210°, B₂ = −27° for left side and s = 1.24, y= 74°, ½ = − 40° for right side. 1.236 P2 147.5° 210° P1 Figure 1 2.138 Xarrow_forward
- can you explain how in a coordinate frame transformation: v = {v_n}^T {n-hat} and then it was found that {n-hat} = [C]^T {b-hat} so v_n = {v_n}^T [C]^T {b-hat}, how does that equation go from that to this --> v_n = [C]^T v_barrow_forward6) If (k = 0,7 cm) find Imax for figure below. 225mm 100mm ثلاثاء. 100mm 150mm 75mm Ans: Tmax=45:27 N/cm F-400 Narrow_forwardThe man has a weight W and stands halfway along the beam. The beam is not smooth, but the planes at A and B are smooth (and plane A is horizontal). Determine the magnitude of the tension in the cord in terms of W and θ.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





