
College Physics:
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305965515
Author: SERWAY, Raymond A.
Publisher: Brooks/Cole Pub Co
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
thumb_up100%
Chapter 15.4, Problem 15.6QQ
Rank the magnitudes of the electric field at points A, B, and C in Figure 15.15, with the largest magnitude first.
(a) A, B, C (b) A, C, B (c) C, A, B (d) The answer can’t be determined by visual inspection.
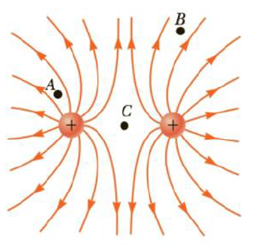
Figure 15.15 The electric field lines for two positive point charges. The points A, B, and C are discussed in Quick Quiz 15.6.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Please solve and answer this problem correctly please. Thank you!!
Please solve and answer this problem correctly please. Thank you!!
a) Use the node-voltage method to find v1, v2, and
v3 in the circuit in Fig. P4.14.
b) How much power does the 40 V voltage source
deliver to the circuit?
Figure P4.14
302
202
w
w
+
+
+
40 V
V1
80 Ω 02
ΣΑΩ
28 A
V3 +
w
w
102
202
Chapter 15 Solutions
College Physics:
Ch. 15.1 - A suspended object A is attracted to a neutral...Ch. 15.2 - Object A has a charge of +2 C, and object B has a...Ch. 15.3 - A test charge of + 3 C is at a point P where the...Ch. 15.3 - A circular ring of charge of radius b has a total...Ch. 15.3 - A free electron and a free proton are placed in an...Ch. 15.4 - Rank the magnitudes of the electric field at...Ch. 15.8 - Calculate the magnitude of the flux of a constant...Ch. 15.8 - Suppose the electric field of Quick Quiz 15.7 is...Ch. 15.8 - Find the electric flux through the surface in...Ch. 15.8 - For a closed surface through which the net flux is...
Ch. 15 - A glass object receives a positive charge of +3 nC...Ch. 15 - The fundamental charge is e = 1.60 1019 C....Ch. 15 - Each of the following statements is related to...Ch. 15 - Two uncharged, conducting spheres are separated by...Ch. 15 - Four concentric spheres S1, S2, S3, and S4 are...Ch. 15 - IF a suspended object A is attracted to a charged...Ch. 15 - Positive charge Q is located at the center of a...Ch. 15 - Consider point A in Figure CQ15.8 located an...Ch. 15 - A student stands on a thick piece of insulating...Ch. 15 - In fair weather, there is an electric field at the...Ch. 15 - A charged comb often attracts small bits of dry...Ch. 15 - Why should a ground wire be connected to the metal...Ch. 15 - There are great similarities between electric and...Ch. 15 - A spherical surface surrounds a point charge q....Ch. 15 - If more electric field lines leave a Gaussian...Ch. 15 - A student who grew up in a tropical country and is...Ch. 15 - What happens when a charged insulator is placed...Ch. 15 - A 7.50-nC charge is located 1.80 m from a 4.20-nC...Ch. 15 - A charged particle A exerts a force of 2.62 N to...Ch. 15 - Rocket observations show that dust particles in...Ch. 15 - A small sphere of mass m = 7.50 g and charge q1 =...Ch. 15 - The nucleus of 8Be, which consists of 4 protons...Ch. 15 - A molecule of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is 2.17...Ch. 15 - Two uncharged spheres are separated by 2.00 in. If...Ch. 15 - Four point charges are at the corners of a square...Ch. 15 - Two small identical conducting spheres are placed...Ch. 15 - Calculate the magnitude and direction of the...Ch. 15 - Three charges are arranged as shown in Figure...Ch. 15 - A positive charge q1 = 2.70 C on a frictionless...Ch. 15 - Three point charges are located at the corners of...Ch. 15 - Two identical metal blocks resting on a...Ch. 15 - Two small metallic spheres, each of mass m = 0.20...Ch. 15 - Panicle A of charge 3.00 104 C is at the origin,...Ch. 15 - A small object of mass 3.80 g and charge 18.0 C is...Ch. 15 - (a) Determine the electric field strength at a...Ch. 15 - An electric field of magnitude 5.25 105 N/C...Ch. 15 - An electron is accelerated by a constant electric...Ch. 15 - Charge q1 = 1.00 nC is at x1 = 0 and charge q2 =...Ch. 15 - A small sphere of charge q = +68 C and mass m =...Ch. 15 - A proton accelerates from rest in a uniform...Ch. 15 - (a) Find the magnitude and direction of the...Ch. 15 - Four point charges are located at the corners of a...Ch. 15 - A helium nucleus of mass m = 6.64 1027 kg and...Ch. 15 - A charged dust particle at rest in a vacuum is...Ch. 15 - A particle of mass 1.00 109 kg and charge 3.00 pC...Ch. 15 - Two equal positive charges are at opposite corners...Ch. 15 - Three point charges are located on a circular are...Ch. 15 - In Figure P15.31, determine the point (other than...Ch. 15 - Three charges are at the corners of an equilateral...Ch. 15 - Three identical charges (q = 5.0 C.) lie along a...Ch. 15 - Figure P15.31 shows the electric held lines for...Ch. 15 - (a) Sketch the electric field lines around an...Ch. 15 - (a) Sketch the electric field pattern around two...Ch. 15 - Two point charges are a small distance apart. (a)...Ch. 15 - Three equal positive charges are at the corners of...Ch. 15 - Refer 10 Figure 15.20. The charge lowered into the...Ch. 15 - The dome of a Van de Graaff generator receives a...Ch. 15 - If the electric field strength in air exceeds 3.0 ...Ch. 15 - In the Millikan oil-drop experiment illustrated in...Ch. 15 - A Van de Graaff generator is charged so that a...Ch. 15 - A uniform electric field of magnitude E = 435 N/C...Ch. 15 - An electric field of intensity 3.50 kN/C is...Ch. 15 - The electric field everywhere on the surface of a...Ch. 15 - Four closed surfaces, S1 through S4, together with...Ch. 15 - A charge q = +5.80 C is located at the center of a...Ch. 15 - Figure P15.49 shows a closed cylinder with...Ch. 15 - A charge of q = 2.00 109 G is spread evenly on a...Ch. 15 - A point charge q is located at the center of a...Ch. 15 - A charge of 1.70 102 C is at the center of a cube...Ch. 15 - Suppose the conducting spherical shell of Figure...Ch. 15 - A very large nonconducting plate lying in the...Ch. 15 - In deep spare, two spheres each of radius 5.00 m...Ch. 15 - A nonconducting, thin plane sheet of charge...Ch. 15 - Three point charges are aligned along the x-axis...Ch. 15 - A small plastic ball of mass m = 2.00 g is...Ch. 15 - A proton moving at v0 = 1.50 106 m/s enters the...Ch. 15 - The electrons in a particle beam each have a...Ch. 15 - A point charge +2Q is at the origin and a point...Ch. 15 - A 1.00-g cork ball having a positive charge of...Ch. 15 - Two 2.0-g spheres are suspended by 10.0-cm-long...Ch. 15 - a point charge of magnitude 5.00 C is at the...Ch. 15 - Two hard rubber spheres, each of mass m = 15.0 g,...Ch. 15 - Prob. 66APCh. 15 - A solid conducting sphere of radius 2.00 cm has a...Ch. 15 - Three identical point charges, each of mass m =...Ch. 15 - Each of the electrons in a particle beam has a...Ch. 15 - Protons are projected with an initial speed v0 = 9...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please solve and answer this problem correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forwardYou're on an interplanetary mission, in an orbit around the Sun. Suppose you make a maneuver that brings your perihelion in closer to the Sun but leaves your aphelion unchanged. Then you must have Question 2 options: sped up at perihelion sped up at aphelion slowed down at perihelion slowed down at aphelionarrow_forwardThe force of the quadriceps (Fq) and force of the patellar tendon (Fp) is identical (i.e., 1000 N each). In the figure below angle in blue is Θ and the in green is half Θ (i.e., Θ/2). A) Calculate the patellar reaction force (i.e., R resultant vector is the sum of the horizontal component of the quadriceps and patellar tendon force) at the following joint angles: you need to provide a diagram showing the vector and its components for each part. a1) Θ = 160 degrees, a2) Θ = 90 degrees. NOTE: USE ONLY TRIGNOMETRIC FUNCTIONS (SIN/TAN/COS, NO LAW OF COSINES, NO COMPLICATED ALGEBRAIC EQUATIONS OR ANYTHING ELSE, ETC. Question A has 2 parts!arrow_forward
- The force of the quadriceps (Fq) and force of the patellar tendon (Fp) is identical (i.e., 1000 N each). In the figure below angle in blue is Θ and the in green is half Θ (i.e., Θ/2). A) Calculate the patellar reaction force (i.e., R resultant vector is the sum of the horizontal component of the quadriceps and patellar tendon force) at the following joint angles: you need to provide a diagram showing the vector and its components for each part. a1) Θ = 160 degrees, a2) Θ = 90 degrees. NOTE: USE DO NOT USE LAW OF COSINES, NO COMPLICATED ALGEBRAIC EQUATIONS OR ANYTHING ELSE, ETC. Question A has 2 parts!arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardThe force of the quadriceps (Fq) and force of the patellar tendon (Fp) is identical (i.e., 1000 N each). In the figure below angle in blue is Θ and the in green is half Θ (i.e., Θ/2). A) Calculate the patellar reaction force (i.e., R resultant vector is the sum of the horizontal component of the quadriceps and patellar tendon force) at the following joint angles: you need to provide a diagram showing the vector and its components for each part. a1) Θ = 160 degrees, a2) Θ = 90 degrees. NOTE: USE ONLY TRIGNOMETRIC FUNCTIONS (SIN/TAN/COS, NO LAW OF COSINES, NO COMPLICATED ALGEBRAIC EQUATIONS OR ANYTHING ELSE, ETC. Question A has 2 parts!arrow_forward
- ་ The position of a particle is described by r = (300e 0.5t) mm and 0 = (0.3t²) rad, where t is in seconds. Part A Determine the magnitude of the particle's velocity at the instant t = 1.5 s. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. v = Value Submit Request Answer Part B ? Units Determine the magnitude of the particle's acceleration at the instant t = 1.5 s. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. a = Value A ? Unitsarrow_forwardSolve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forwardSolve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Electric Fields: Crash Course Physics #26; Author: CrashCourse;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mdulzEfQXDE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY