
a.
To determine:
The position of the codon in the mRNA that must be altered by which Leucine is converted to glutamine. (
Introduction:
The basic unit of genetic code is called a codon. The genetic code is a triplet code, in which three nucleotides encode each amino acid in a protein. The genetic code has sixty-one codons that specify the twenty amino acids. The degeneracy of genetic code means that the code is redundant and the amino acids may be specified by more than one codon.
Tryptophan and methionine are the only amino acids that are encoded by a single codon.
a.
Explanation of Solution
The codon table represents the codons and coded amino acids:
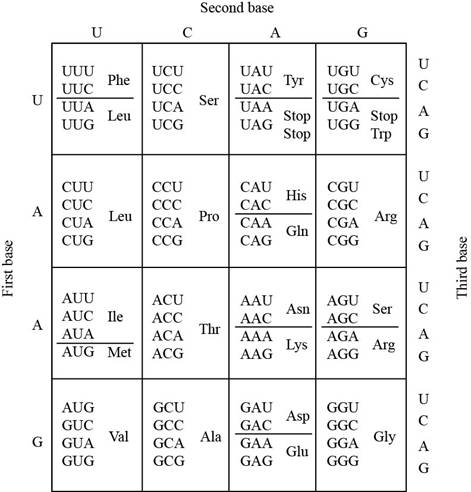
The codon table shows that the amino acid Leucine (Leu) is specified by six codons CUU, CUC, CUA, CUG, UAA, and UUG. The amino acid glutamine is specified by only two codons CAA and CAG.
The codons of glutamine could be developed by mutation of two codons of Leucine that includes CUA and CUG. The mutation occurs at a single base position in the codon.
b.
To determine:
The position of the codon in the mRNA that must be altered by which phenylalanineis converted to serine
Introduction:
The basic unit of genetic code is called a codon. The genetic code is a triplet code, in which three nucleotides encode each amino acid in a protein. The genetic code has sixty-one codons that specify the twenty amino acids. The degeneracy of genetic code means that the code is redundant and the amino acids may be specified by more than one codon.
Tryptophan and methionine are the only amino acids that are encoded by a single codon.
b.
Explanation of Solution
The codon table represents the codons and coded amino acids:
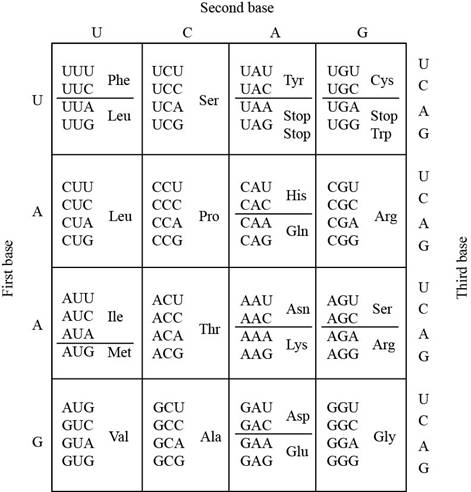
The codon table shows that the amino acid phenylalanine (Phe) is specified by onlytwo codons UUU and UUC. The amino acid serine (Ser) is specified by four codons UCA, UCC, UCA,andUCG.
The codons of serine could be developed by mutation of both codons of phenylalaninethat includes UUU and UUC. The mutation occurs at a single base position in the codon.
c.
To determine:
The position of the codon in the mRNA that must be altered by which phenylalanine is converted to isoleucine
Introduction:
The basic unit of genetic code is called a codon. The genetic code is a triplet code, in which three nucleotides encode each amino acid in a protein. The genetic code has sixty-one codons that specify the twenty amino acids. The degeneracy of genetic code means that the code is redundant and the amino acids may be specified by more than one codon.
Tryptophan and methionine are the only amino acids that are encoded by a single codon.
c.
Explanation of Solution
The codon table represents the codons and coded amino acids:
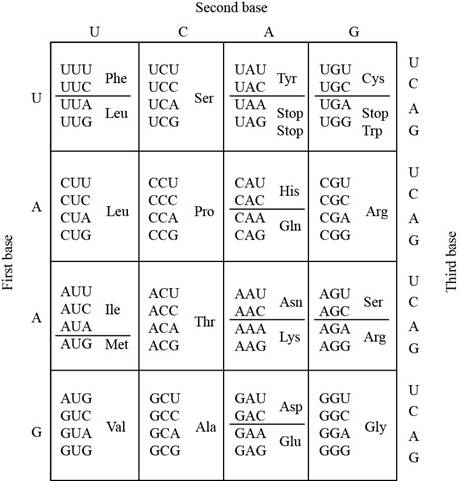
The codon table shows that the amino acid phenylalanine (Phe) is specified by only two codons UUU and UUC. The amino acid isoleucine (Ile) is specified by three codons AUU, AUC, and AUA.
The codons of isoleucine could be developed by mutation of both codons of phenylalanine that includes UUU and UUC. The mutation occurs at a single base position in the codon.
d.
To determine:
The position of the codon in the mRNA that must be altered by which proline is converted to alanine
Introduction:
The basic unit of genetic code is called a codon. The genetic code is a triplet code, in which three nucleotides encode each amino acid in a protein. The genetic code has sixty-one codons that specify the twenty amino acids. The degeneracy of genetic code means that the code is redundant and the amino acids may be specified by more than one codon.
Tryptophan and methionine are the only amino acids that are encoded by a single codon.
d.
Explanation of Solution
The codon table represents the codons and coded amino acids:
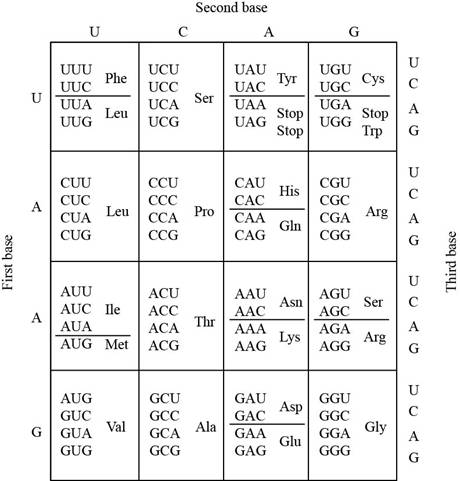
The codon table shows that the amino acid proline (Pro) is specified byfour codons CCU, CCA, CCC, and CCG. The amino acid alanine (Ala) is specified by GCU, GCG, GCC, and GCA.
The codons of alanine could be developed by mutation of all codons of proline that includes CCU, CCA, CCC, and CCG. The mutation occurs at a single base position in the codon.
e.
To determine:
The position of the codon in the mRNA that must be altered by which asparagine is converted to lysine
Introduction:
The basic unit of genetic code is called a codon. The genetic code is a triplet code, in which three nucleotides encode each amino acid in a protein. The genetic code has sixty-one codons that specify the twenty amino acids. The degeneracy of genetic code means that the code is redundant and the amino acids may be specified by more than one codon.
Tryptophan and methionine are the only amino acids that are encoded by a single codon.
e.
Explanation of Solution
The codon table represents the codons and coded amino acids:

The codon table shows that the amino acid asparagine (Asn) is specified by two codons AAU and AAC. The amino acid lysine is specified by the codons AAA and AAG.
The codons of lysine could be developed by mutation of bothcodons of asparagine that includes AAU and AAC. The mutation occurs at a single base position in the codon.
f.
To determine:
The position of the codon in the mRNA that must be altered by which isoleucine is converted to asparagine
Introduction:
The basic unit of genetic code is called a codon. The genetic code is a triplet code, in which three nucleotides encode each amino acid in a protein. The genetic code has sixty-one codons that specify the twenty amino acids. The degeneracy of genetic code means that the code is redundant and the amino acids may be specified by more than one codon.
Tryptophan and methionine are the only amino acids that are encoded by a single codon.
f.
Explanation of Solution
The codon table represents the codons and coded amino acids:

The codon table shows that the amino acid isoleucine (Ile) is specified by three codons AUU, AUC, and AUA. The amino acid asparagine is specified by the codons AAU and AAC
The codons of asparagine could be developed by mutation of only two codons of isoleucine that includes AUU and AUC. The mutation occurs at a single base position in the codon.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Genetics
- ✓ Details Draw a protein that is embedded in a membrane (a transmembrane protein), label the lipid bilayer and the protein. Identify the areas of the lipid bilayer that are hydrophobic and hydrophilic. Draw a membrane with two transporters: a proton pump transporter that uses ATP to generate a proton gradient, and a second transporter that moves glucose by secondary active transport (cartoon-like is ok). It will be important to show protons moving in the correct direction, and that the transporter that is powered by secondary active transport is logically related to the proton pump.arrow_forwarddrawing chemical structure of ATP. please draw in and label whats asked. Thank you.arrow_forwardOutline the negative feedback loop that allows us to maintain a healthy water concentration in our blood. You may use diagram if you wisharrow_forward
- Give examples of fat soluble and non-fat soluble hormonesarrow_forwardJust click view full document and register so you can see the whole document. how do i access this. following from the previous question; https://www.bartleby.com/questions-and-answers/hi-hi-with-this-unit-assessment-psy4406-tp4-report-assessment-material-case-stydu-ms-alecia-moore.-o/5e09906a-5101-4297-a8f7-49449b0bb5a7. on Google this image comes up and i have signed/ payed for the service and unable to access the full document. are you able to copy and past to this response. please see the screenshot from google page. unfortunality its not allowing me attch the image can you please show me the mathmetic calculation/ workout for the reult sectionarrow_forwardIn tabular form, differentiate between reversible and irreversible cell injury.arrow_forward
- 1.)What cross will result in half homozygous dominant offspring and half heterozygous offspring? 2.) What cross will result in all heterozygous offspring?arrow_forward1.Steroids like testosterone and estrogen are nonpolar and large (~18 carbons). Steroids diffuse through membranes without transporters. Compare and contrast the remaining substances and circle the three substances that can diffuse through a membrane the fastest, without a transporter. Put a square around the other substance that can also diffuse through a membrane (1000x slower but also without a transporter). Molecule Steroid H+ CO₂ Glucose (C6H12O6) H₂O Na+ N₂ Size (Small/Big) Big Nonpolar/Polar/ Nonpolar lonizedarrow_forwardwhat are the answer from the bookarrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





