
Concept explainers
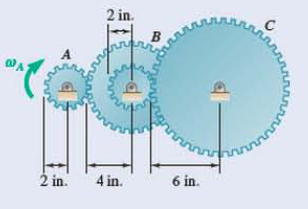
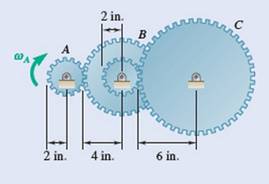
gear reduction system consists of three gears A, B, and C. Knowing that gear A rotates clockwise with a constant angular velocity 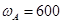 rpm, determine (a) the angular velocities of gears B and C, (b) the accelerations of the points on gears B and C which are in contact.
rpm, determine (a) the angular velocities of gears B and C, (b) the accelerations of the points on gears B and C which are in contact.
Fig. P15.24
(a)
The angular velocities of gears
Answer to Problem 15.24P
The angular velocity of gear
The angular velocity of gear
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Gear
Concept used:
The velocity
Calculation:

The velocity of the point
Since,
Thus,
The angular velocity of gear
The angular velocity of gear
Conclusion:
The angular velocity of gear
The angular velocity of gear
(b)
The accelerations of the points on gears
Answer to Problem 15.24P
The acceleration of the point on gear
The acceleration of the point on gear
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Gear

Concept used:
The velocity
The acceleration
Calculation:

The acceleration of the point
Consider point
Consider point
The acceleration of the point on gear
The acceleration of the point on gear
Conclusion:
The acceleration of the point on gear
The acceleration of the point on gear
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
- My ID# 016948724 please find the forces for Fx=0: fy=0: fz=0: please help me to solve this problem step by steparrow_forwardMy ID# 016948724 please solve the proble step by step find the forces fx=o: fy=0; fz=0; and find shear moment and the bending moment diagran please draw the diagram for the shear and bending momentarrow_forwardMy ID#016948724. Please help me to find the moment of inertia lx ly are a please show to solve step by stepsarrow_forward
- My ID# 016948724arrow_forwardPlease do not use any AI tools to solve this question. I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor. No AI-generated responses, please.arrow_forwardPlease do not use any AI tools to solve this question. I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor. No AI-generated responses, please.arrow_forward
- Please do not use any AI tools to solve this question. I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor. No AI-generated responses, please.arrow_forward[Q2]: The cost information supplied by the cost accountant is as follows:Sales 20,00 units, $ 10 per unitCalculate the (a/ newsale guantity and (b) new selling price to earn the sameVariable cost $ 6 per unit, Fixed Cost $ 30,000, Profit $ 50,000profit ifi) Variable cost increases by $ 2 per unitil) Fixed cost increase by $ 10,000Ili) Variable cost increase by $ 1 per unit and fixed cost reduces by $ 10,000arrow_forwardcan you please help me perform Visual Inspection and Fractography of the attatched image: Preliminary examination to identify the fracture origin, suspected fatigue striation, and corrosion evidences.arrow_forward
 Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L Precision Machining Technology (MindTap Course Li...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781285444543Author:Peter J. Hoffman, Eric S. Hopewell, Brian JanesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Precision Machining Technology (MindTap Course Li...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781285444543Author:Peter J. Hoffman, Eric S. Hopewell, Brian JanesPublisher:Cengage Learning Automotive Technology: A Systems Approach (MindTa...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781133612315Author:Jack Erjavec, Rob ThompsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Automotive Technology: A Systems Approach (MindTa...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781133612315Author:Jack Erjavec, Rob ThompsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Automotive TechnologyMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337794213Author:ERJAVEC, Jack.Publisher:Cengage,
Automotive TechnologyMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337794213Author:ERJAVEC, Jack.Publisher:Cengage, Understanding Motor ControlsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337798686Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Understanding Motor ControlsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337798686Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning





