
A U-tube open at both ends is partially filled with water (Fig. P15.67a). Oil having a density 750 kg/m3 is then poured into the right arm and forms a column L = 5.00 cm high (Fig. P15.67b). (a) Determine the difference h in the heights of the two liquid surfaces. (b) The right arm is then shielded from any air motion while air is blown across the top of the left arm until the surfaces of the two liquids are at the same height (Fig. P15.67c). Determine the speed of the air being blown across the left arm. Take the density of air as constant at 1.20 kg/m3.
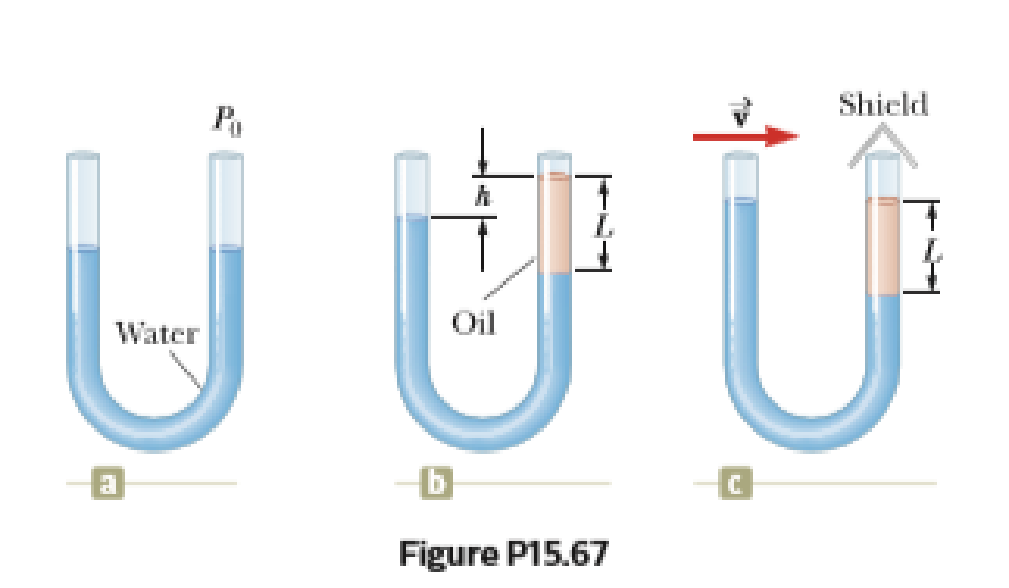
(a)
The difference
Answer to Problem 67P
The difference
Explanation of Solution
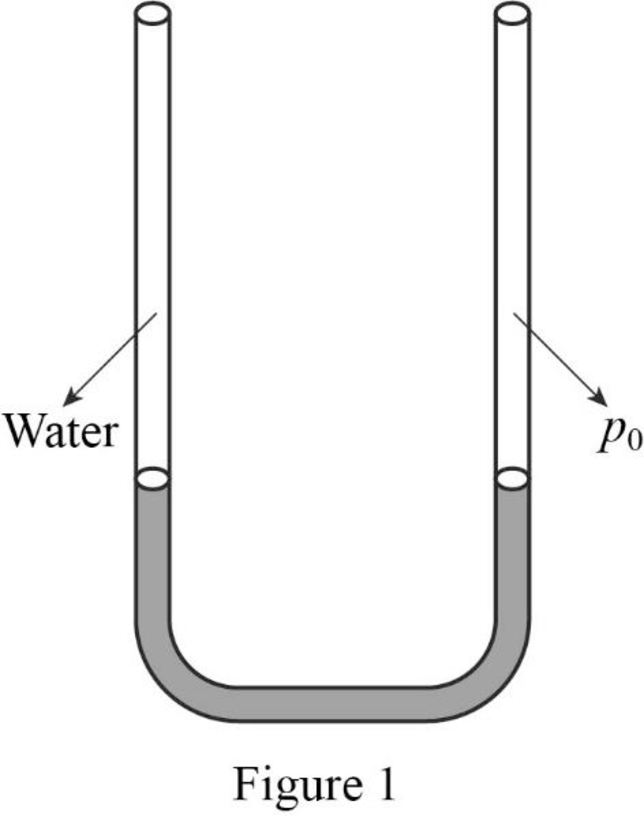
The initial condition of the U-tube is shown in figure 1.
The representation of the tube after the oil is poured is shown in figure 2.
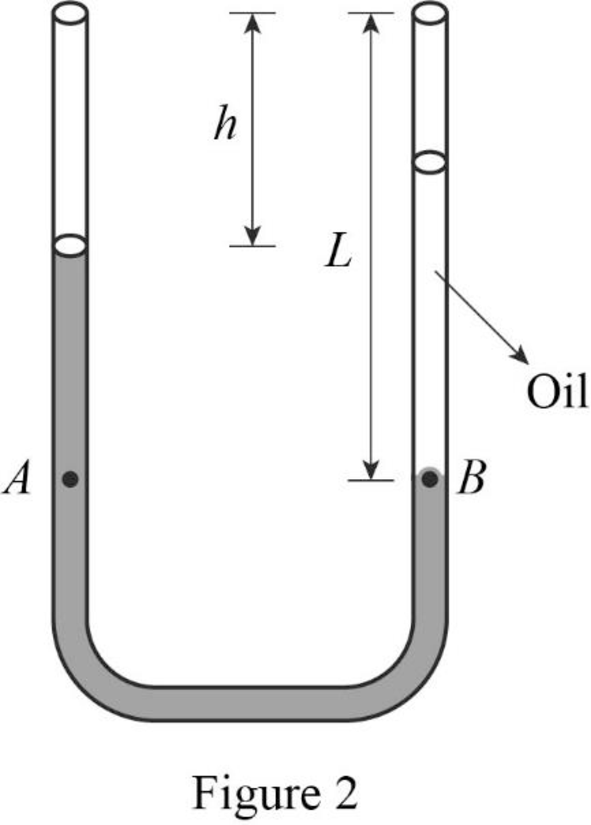
Consider two points A and B in figure 2.
According to the Pascal’s principle, the pressure at points A and B must be equal.
Write the relationship between the pressure at points A and B.
Here,
Write the equation for
Here,
Write the equation for
Here,
Put equations (II) and (III) in equation (I) and rewrite for
Conclusion:
The density of water is
Substitute
Therefore, the difference
(b)
The speed of the air being blown across the left arm.
Answer to Problem 67P
The speed of the air being blown across the left arm is
Explanation of Solution
The situation when the air flow over the left tube stabilizes the fluid levels in the two tubes is shown in figure 3.
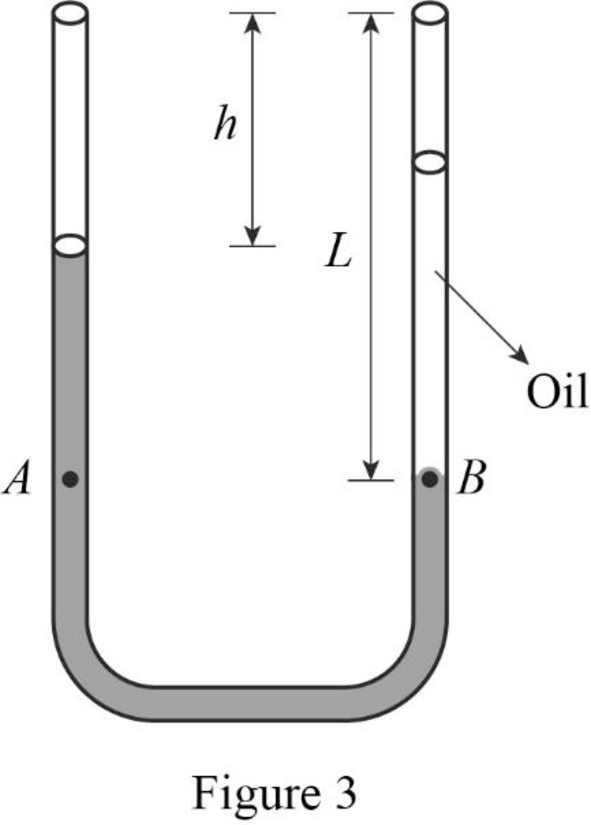
Write the Bernoulli’s equation for the two points A and B.
Here,
The value of
Replace
Consider two points C and D which are at the level of oil-water interface in the right tube.
According to the Pascal’s principle, the pressure at points C and D must be equal.
Write the relationship between the pressure at points C and D.
Here,
Write the equation for
Here,
Write the equation for
Put equations (VIII) and (IX) in equation (VII).
Put equation (VI) in the above equation.
Conclusion:
The value of
Substitute
Therefore, the speed of the air being blown across the left arm is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text, Hybrid (with Enhanced WebAssign Printed Access Card)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Genetics: From Genes to Genomes
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
Chemistry
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College





