
Concept explainers
A 10.0-kg block of metal measuring 12.0 cm by 10.0 cm by 10.0 cm is suspended from a scale and immersed in water as shown in Figure P15.24b. The 12.0-cm dimension is vertical, and the top of the block is 5.00 cm below the surface of the water. (a) What are the magnitudes of the forces acting on the top and on the bottom of the block due to the surrounding water? (b) What is the reading of the spring scale? (c) Show that the buoyant force equals the difference between the forces at the top and bottom of the block.
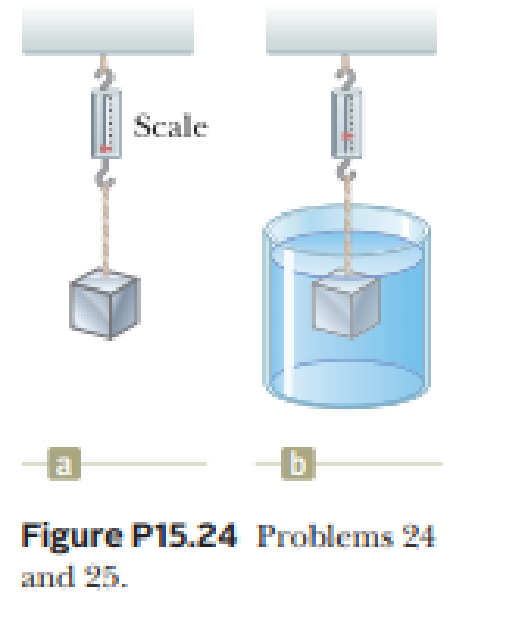
(a)
The magnitudes of the forces acting on the top and on the bottom of the block due to the surrounding water.
Answer to Problem 25P
The magnitude of the force acting on the top of the block due to the surrounding water is
Explanation of Solution
Write the equation for the pressure at a depth.
Here,
Write the equation for pressure.
Here,
Rewrite the above equation for
Use equation (II) to write the expression for the force at the top of the block.
Here,
Use equation (II) to write the expression for the force on the bottom of the block.
Here,
Conclusion:
The value of
Substitute
Since the vertical dimension of the block is
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Therefore, the magnitude of the force acting on the top of the block due to the surrounding water is
(b)
The reading of the spring scale.
Answer to Problem 25P
The reading of the spring scale is
Explanation of Solution
The free-body diagram of the system is shown below.
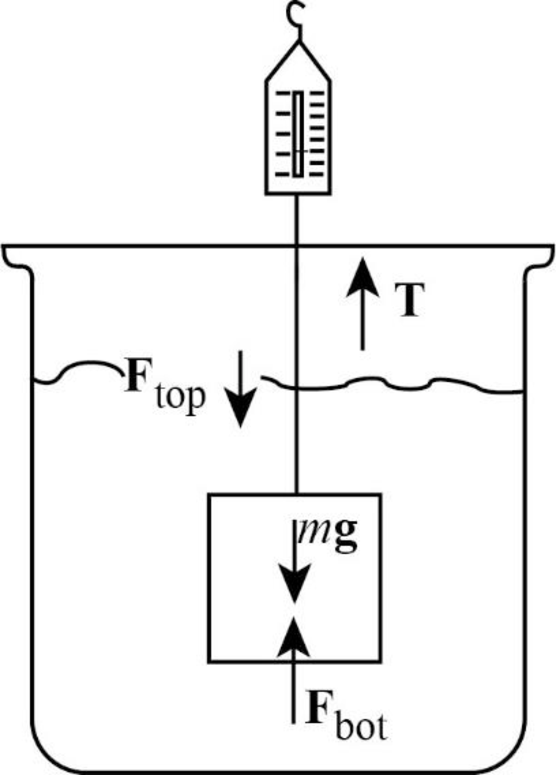
The tension in the string is the spring scale reading.
The tension in the string is balanced by the vector sum of the weight of the block and the buoyant force.
Write the equation for the tension in the string.
Here,
Write the equation for the weight of the block.
Here,
Write the equation for the buoyant force.
Here,
Put equations (VI) and (VII) in equation (V).
Conclusion:
Substitute
Therefore, the reading of the spring scale is
(c)
To show that the buoyant force equals the difference between the forces at the top and bottom of the block.
Answer to Problem 25P
It is showed that the buoyant force equals the difference between the forces at the top and bottom of the block.
Explanation of Solution
Write the equation for the difference between the forces at the top and bottom of the block.
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
The value of the difference between the forces at the top and bottom of the block and the magnitude of the buoyant force are equal.
Thus, it is showed that the buoyant force equals the difference between the forces at the top and bottom of the block.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text, Hybrid (with Enhanced WebAssign Printed Access Card)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
Genetics: Analysis and Principles
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Brock Biology of Microorganisms (15th Edition)
Chemistry: The Central Science (14th Edition)
- Is work function of a metals surface related to surface energy and surface tension? What is the need to the work function component in the math of tension of metal surfaces that cannot be provided by existing equations of surface energy and surface tension? What are the key differences in each parameter and variables that allow for a differentiation of each function? What has a more significant meaning work function, surface tension or surface energy? Are there real differences and meaning? Please clarify and if possible provide examples . Does surface tension dependant on thickness of a metal or type of metal surface all having the same thickness? Clearly temperature has a profound change on surface tension what other variables besides temperature are key to surface tension. What if any is there a connection between crystal structure of the element and surface energy and tension? This is NOT a Assignment Question!!!arrow_forwardThe cylindrical beam of a 12.7-mW laser is 0.920 cm in diameter. What is the rms value of the electric field? V/marrow_forwardConsider a rubber rod that has been rubbed with fur to give the rod a net negative charge, and a glass rod that has been rubbed with silk to give it a net positive charge. After being charged by contact by the fur and silk...? a. Both rods have less mass b. the rubber rod has more mass and the glass rod has less mass c. both rods have more mass d. the masses of both rods are unchanged e. the rubber rod has less mass and the glass rod has mroe massarrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College





