
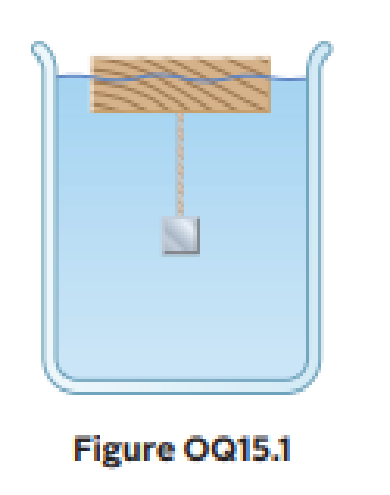
A wooden block floats in water, and a steel object is attached to the bottom of the block by a string as in Figure OQ15.1. If the block remains floating, which of the following statements are valid? (Choose all correct statements.) (a) The buoyant force on the steel object is equal to its weight. (b) The buoyant force on the block is equal to its weight. (c) The tension in the string is equal to the weight of the steel object. (d) The tension in the string is less than the weight of the steel object. (e) The buoyant force on the block is equal to the volume of water it displaces.
The statements which are valid.
Answer to Problem 1OQ
Option (d).
Explanation of Solution
Buoyant force is the upward force exerted by a fluid on any immersed object. The magnitude of the buoyant force on an object always equals the weight of the fluid displaced by the object. Since the buoyant force is exerted by the fluid, it is not determined by the properties of the object except the amount of fluid displaced by it.
The buoyant force on the steel object is not equal to its weight since there are other forces acting on it. Similarly, the buoyant force on the block is either not equal to its weight. The weight of the steel object is not balanced by the tension in the string so that the tension is less than the weight of the steel object.
Conclusion:
Since the tension in the string is less than the weight of the steel object, option (d) is correct.
Since the buoyant force on the steel object is not equal to its weight, option (a) is incorrect.
Since the buoyant force on the block is not equal to its weight, option (b) is incorrect.
Since the tension in the string is not equal to the weight of the steel object, option (c) is incorrect.
Since the buoyant force on the block is not equal to the volume of the water it displaces but the weight of the water it displaces, option (e) is incorrect.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text, Hybrid (with Enhanced WebAssign Printed Access Card)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Organic Chemistry
Fundamentals Of Thermodynamics
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
- pls help on thesearrow_forward20. Two small conducting spheres are placed on top of insulating pads. The 3.7 × 10-10 C sphere is fixed whie the 3.0 × 107 C sphere, initially at rest, is free to move. The mass of each sphere is 0.09 kg. If the spheres are initially 0.10 m apart, how fast will the sphere be moving when they are 1.5 m apart?arrow_forwardpls help on allarrow_forward
- 19. Mount Everest, Earth's highest mountain above sea level, has a peak of 8849 m above sea level. Assume that sea level defines the height of Earth's surface. (re = 6.38 × 106 m, ME = 5.98 × 1024 kg, G = 6.67 × 10 -11 Nm²/kg²) a. Calculate the strength of Earth's gravitational field at a point at the peak of Mount Everest. b. What is the ratio of the strength of Earth's gravitational field at a point 644416m below the surface of the Earth to a point at the top of Mount Everest? C. A tourist watching the sunrise on top of Mount Everest observes a satellite orbiting Earth at an altitude 3580 km above his position. Determine the speed of the satellite.arrow_forwardpls help on allarrow_forwardpls help on allarrow_forward
- 6. As the distance between two charges decreases, the magnitude of the electric potential energy of the two-charge system: a) Always increases b) Always decreases c) Increases if the charges have the same sign, decreases if they have the opposite signs d) Increases if the charges have the opposite sign, decreases if they have the same sign 7. To analyze the motion of an elastic collision between two charged particles we use conservation of & a) Energy, Velocity b) Momentum, Force c) Mass, Momentum d) Energy, Momentum e) Kinetic Energy, Potential Energyarrow_forwardpls help on all asked questions kindlyarrow_forwardpls help on all asked questions kindlyarrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





