
Bundle: Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text, 5th + WebAssign Printed Access Card for Serway/Jewett's Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text, 5th Edition, Multi-Term
5th Edition
ISBN: 9781133422013
Author: Raymond A. Serway; John W. Jewett
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 15, Problem 62P
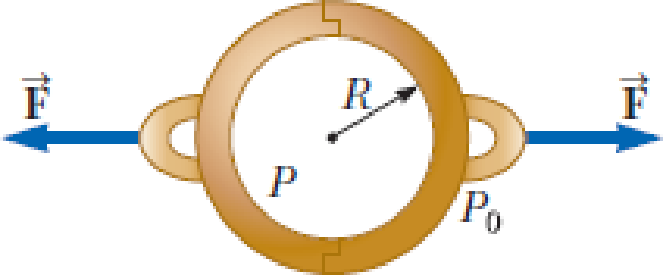
In about 1657, Otto von Guericke, inventor of the air pump, evacuated a sphere made of two brass hemispheres (Fig. P15.62). Two teams of eight horses each could pull the hemispheres apart only on some trials and then “with greatest difficulty,” with the resulting sound likened to a cannon firing. Find the force F required to pull the thin-walled evacuated hemispheres apart in terms of R, the radius of the hemispheres; P, the pressure inside the hemispheres; and atmospheric pressure P0.
Figure P15.62
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
4.) The diagram shows the electric field lines of a positively charged conducting sphere of
radius R and charge Q.
A
B
Points A and B are located on the same field line.
A proton is placed at A and released from rest. The magnitude of the work done by the electric field in
moving the proton from A to B is 1.7×10-16 J. Point A is at a distance of 5.0×10-2m from the centre of
the sphere. Point B is at a distance of 1.0×10-1 m from the centre of the sphere.
(a) Explain why the electric potential decreases from A to B. [2]
(b) Draw, on the axes, the variation of electric potential V with distance r from the centre of the
sphere.
R
[2]
(c(i)) Calculate the electric potential difference between points A and B. [1]
(c(ii)) Determine the charge Q of the sphere. [2]
(d) The concept of potential is also used in the context of gravitational fields. Suggest why scientists
developed a common terminology to describe different types of fields. [1]
3.) The graph shows how current I varies with potential difference V across a component X.
904
80-
70-
60-
50-
I/MA
40-
30-
20-
10-
0+
0
0.5
1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 4.5 5.0
VIV
Component X and a cell of negligible internal resistance are placed in a circuit.
A variable resistor R is connected in series with component X. The ammeter reads 20mA.
4.0V
4.0V
Component X and the cell are now placed in a potential divider circuit.
(a) Outline why component X is considered non-ohmic. [1]
(b(i)) Determine the resistance of the variable resistor. [3]
(b(ii)) Calculate the power dissipated in the circuit. [1]
(c(i)) State the range of current that the ammeter can measure as the slider S of the potential divider
is moved from Q to P. [1]
(c(ii)) Describe, by reference to your answer for (c)(i), the advantage of the potential divider
arrangement over the arrangement in (b).
1.) Two long parallel current-carrying wires P and Q are separated by 0.10 m. The current in wire P is 5.0 A.
The magnetic force on a length of 0.50 m of wire P due to the current in wire Q is 2.0 × 10-s N.
(a) State and explain the magnitude of the force on a length of 0.50 m of wire Q due to the current in P. [2]
(b) Calculate the current in wire Q. [2]
(c) Another current-carrying wire R is placed parallel to wires P and Q and halfway between them as shown.
wire P
wire R
wire Q
0.05 m
0.05 m
The net magnetic force on wire Q is now zero.
(c.i) State the direction of the current in R, relative to the current in P.[1]
(c.ii) Deduce the current in R. [2]
Chapter 15 Solutions
Bundle: Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text, 5th + WebAssign Printed Access Card for Serway/Jewett's Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text, 5th Edition, Multi-Term
Ch. 15.1 - Suppose you are standing directly behind someone...Ch. 15.2 - Prob. 15.2QQCh. 15.4 - An apple is held completely submerged just below...Ch. 15.4 - Prob. 15.4QQCh. 15.6 - Prob. 15.5QQCh. 15.7 - You observe two helium balloons floating next to...Ch. 15 - A wooden block floats in water, and a steel object...Ch. 15 - Prob. 2OQCh. 15 - Prob. 3OQCh. 15 - Prob. 4OQ
Ch. 15 - A solid iron sphere and a solid lead sphere of the...Ch. 15 - Prob. 6OQCh. 15 - Prob. 7OQCh. 15 - Prob. 8OQCh. 15 - An ideal fluid flows through a horizontal pipe...Ch. 15 - Prob. 10OQCh. 15 - Prob. 11OQCh. 15 - A small piece of steel is tied to a block of wood....Ch. 15 - A piece of unpainted porous wood barely floats in...Ch. 15 - Prob. 14OQCh. 15 - A water supply maintains a constant rate of flow...Ch. 15 - Prob. 1CQCh. 15 - Because atmospheric pressure is about 105 N/m2 and...Ch. 15 - Two thin-walled drinking glasses having equal base...Ch. 15 - Prob. 4CQCh. 15 - Prob. 5CQCh. 15 - Prob. 6CQCh. 15 - Prob. 7CQCh. 15 - Prob. 8CQCh. 15 - Prob. 9CQCh. 15 - Prob. 10CQCh. 15 - Prob. 11CQCh. 15 - Prob. 12CQCh. 15 - (a) Is the buoyant force a conservative force? (b)...Ch. 15 - An empty metal soap dish barely floats in water. A...Ch. 15 - Prob. 15CQCh. 15 - How would you determine the density of an...Ch. 15 - Prob. 17CQCh. 15 - Place two cans of soft drinks, one regular and one...Ch. 15 - Prob. 19CQCh. 15 - Prob. 1PCh. 15 - A 50.0-kg woman wearing high-heeled shoes is...Ch. 15 - Prob. 3PCh. 15 - Prob. 4PCh. 15 - Prob. 5PCh. 15 - The small piston of a hydraulic lift (Fig. P15.6)...Ch. 15 - A container is filled to a depth of 20.0 cm with...Ch. 15 - Prob. 8PCh. 15 - (a) Calculate the absolute pressure at an ocean...Ch. 15 - (a) A very powerful vacuum cleaner has a hose 2.86...Ch. 15 - What must be the contact area between a suction...Ch. 15 - Prob. 12PCh. 15 - Review. The tank in Figure P15.13 is filled with...Ch. 15 - Review. The tank in Figure P15.13 is filled with...Ch. 15 - Prob. 15PCh. 15 - Prob. 16PCh. 15 - Mercury is poured into a U-tube as shown in Figure...Ch. 15 - Prob. 18PCh. 15 - A backyard swimming pool with a circular base of...Ch. 15 - A tank with a flat bottom of area A and vertical...Ch. 15 - Prob. 21PCh. 15 - A Styrofoam slab has thickness h and density s....Ch. 15 - A table-tennis ball has a diameter of 3.80 cm and...Ch. 15 - The gravitational force exerted on a solid object...Ch. 15 - A 10.0-kg block of metal measuring 12.0 cm by 10.0...Ch. 15 - Prob. 26PCh. 15 - Prob. 27PCh. 15 - Prob. 28PCh. 15 - How many cubic meters of helium are required to...Ch. 15 - Prob. 30PCh. 15 - A plastic sphere floats in water with 50.0% of its...Ch. 15 - The weight of a rectangular block of low-density...Ch. 15 - Decades ago, it was thought that huge herbivorous...Ch. 15 - Prob. 34PCh. 15 - Prob. 35PCh. 15 - A light balloon is filled with 400 m3 of helium at...Ch. 15 - A horizontal pipe 10.0 cm in diameter has a smooth...Ch. 15 - Prob. 38PCh. 15 - A large storage tank with an open top is filled to...Ch. 15 - Review. Old Faithful Geyser in Yellowstone...Ch. 15 - (a) A water hose 2.00 cm in diameter is used to...Ch. 15 - Water flows through a fire hose of diameter 6.35...Ch. 15 - Prob. 43PCh. 15 - Prob. 44PCh. 15 - A village maintains a large tank with an open top,...Ch. 15 - Prob. 46PCh. 15 - Figure P15.47 shows a stream of water in steady...Ch. 15 - An airplane is cruising at altitude 10 km. The...Ch. 15 - The Bernoulli effect can have important...Ch. 15 - Prob. 50PCh. 15 - Prob. 51PCh. 15 - Prob. 52PCh. 15 - Prob. 53PCh. 15 - Prob. 54PCh. 15 - Prob. 55PCh. 15 - Prob. 56PCh. 15 - Prob. 57PCh. 15 - Prob. 58PCh. 15 - Review. A copper cylinder hangs at the bottom of a...Ch. 15 - Prob. 60PCh. 15 - An incompressible, nonviscous fluid is initially...Ch. 15 - In about 1657, Otto von Guericke, inventor of the...Ch. 15 - A 1.00-kg beaker containing 2.00 kg of oil...Ch. 15 - A beaker of mass mb containing oil of mass mo and...Ch. 15 - Prob. 65PCh. 15 - Prob. 66PCh. 15 - A U-tube open at both ends is partially filled...Ch. 15 - Prob. 68PCh. 15 - Prob. 69PCh. 15 - The spirit-in-glass thermometer, invented in...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 2.) A 50.0 resistor is connected to a cell of emf 3.00 V. The voltmeter and the ammeter in the circuit are ideal. V A 50.00 (a) The current in the ammeter is 59.0 mA. Calculate the internal resistance of the cell. The circuit is changed by connecting another resistor R in parallel to the 50.0 resistor. V A 50.00 R (b) Explain the effect of this change on R is made of a resistive wire of uniform cross-sectional area 3.1 × 10-8 m², resistivity 4.9 × 10-70m and length L. The resistance of R is given by the equation R = KL where k is a constant. (b.i) the reading of the ammeter. [2] (b.ii) the reading of the voltmeter. [2] (c) Calculate k. State an appropriate unit for your answer. [3] [2]arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- A rod 12.0 cm long is uniformly charged and has a total charge of -20.0 μc. Determine the magnitude and direction of the electric field along the axis of the rod at a point 32.0 cm from its center. 361000 ☑ magnitude What is the general expression for the electric field along the axis of a uniform rod? N/C direction toward the rodarrow_forwardA certain brand of freezer is advertised to use 730 kW h of energy per year. Part A Assuming the freezer operates for 5 hours each day, how much power does it require while operating? Express your answer in watts. ΜΕ ΑΣΦ ? P Submit Request Answer Part B W If the freezer keeps its interior at a temperature of -6.0° C in a 20.0° C room, what is its theoretical maximum performance coefficient? Enter your answer numerically. K = ΜΕ ΑΣΦ Submit Request Answer Part C What is the theoretical maximum amount of ice this freezer could make in an hour, starting with water at 20.0°C? Express your answer in kilograms. m = Ο ΑΣΦ kgarrow_forwardDescribe the development of rational choice theory in sociology. Please includearrow_forward
- A-E pleasearrow_forwardA 11.8 L gas tank containing 3.90 moles of ideal He gas at 26.0°C is placed inside a completely evacuated insulated bell jar of volume 39.0 L .A small hole in the tank allows the He to leak out into the jar until the gas reaches a final equilibrium state with no more leakage. Part A What is the change in entropy of this system due to the leaking of the gas? ■ ΜΕ ΑΣΦ AS = ? J/K Submit Request Answer Part B Is the process reversible or irreversible?arrow_forwardA-E pleasearrow_forward
- Three moles of an ideal gas undergo a reversible isothermal compression at 20.0° C. During this compression, 1900 J of work is done on the gas. For related problem-solving tips and strategies, you may want to view a Video Tutor Solution of Entropy change in a free expansion. Part A What is the change of entropy of the gas? ΤΕ ΑΣΦ AS = Submit Request Answer J/Karrow_forward5.97 Block A, with weight 3w, slides down an inclined plane S of slope angle 36.9° at a constant speed while plank B, with weight w, rests on top of A. The plank is attached by a cord to the wall (Fig. P5.97). (a) Draw a diagram of all the forces acting on block A. (b) If the coefficient of kinetic friction is the same between A and B and between S and A, determine its value. Figure P5.97 B A S 36.9°arrow_forwardPlease take your time and solve each part correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Fluids in Motion: Crash Course Physics #15; Author: Crash Course;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fJefjG3xhW0;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY