
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Relationship between two given Fischer projections by means of stereoisomerism (identical or enantiomers) should be determined.
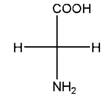 and,
and, 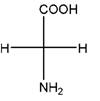
Concept Introduction:
Identical molecules are the ones with no isomers, neither constitutional isomers nor stereoisomers. Identical molecules have the same structural arrangement of atoms and the same three-dimensional arrangement.
Isomers are the molecules with the same formula but either with different structural connectivity (constitutional isomers) or different three-dimensional arrangement (stereoisomers).
A tetrahedral carbon atom bonded to four different groups is called a chiral center. A Molecule having at least one chiral center is a chiral molecule. When the mirror images of a chiral molecule are not superimposable, those mirror images become stereoisomers called enantiomers.
Fischer Projection is a method of drawing 3-D structures of organic molecules using cross formula. In this method, all non-terminal bonds are depicted as horizontal or vertical lines.
In the Fischer projection, horizontal bonds represent groups coming forward (drawn as wedges) and vertical bonds represent groups going backward (drawn as dashed wedges).
(b)
Interpretation:
Relationship between two given Fischer projections by means of stereoisomerism (identical or enantiomers) should be determined.
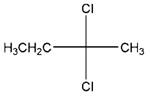 and,
and, 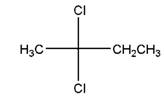
Concept Introduction:
Identical molecules are the ones with no isomers, neither constitutional isomers nor stereoisomers. Identical molecules have the same structural arrangement of atoms and the same three-dimensional arrangement.
Isomers are the molecules with the same formula but either with different structural connectivity (constitutional isomers) or different three-dimensional arrangement (stereoisomers).
A tetrahedral carbon atom bonded to four different groups is called a chiral center. A Molecule having at least one chiral center is a chiral molecule. When the mirror images of a chiral molecule are not superimposable, those mirror images become stereoisomers called enantiomers.
Fischer Projection is a method of drawing 3-D structures of organic molecules using cross formula. In this method, all non-terminal bonds are depicted as horizontal or vertical lines.
In the Fischer projection, horizontal bonds represent groups coming forward (drawn as wedges) and vertical bonds represent groups going backward (drawn as dashed wedges).
(c)
Interpretation:
Relationship between two given Fischer projections by means of stereoisomerism (identical or enantiomers) should be determined.
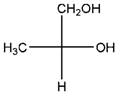 and,
and, 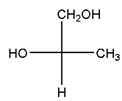
Concept Introduction:
Identical molecules are the ones with no isomers, neither constitutional isomers nor stereoisomers. Identical molecules have the same structural arrangement of atoms and the same three-dimensional arrangement.
Isomers are the molecules with the same formula but either with different structural connectivity (constitutional isomers) or different three-dimensional arrangement (stereoisomers).
A tetrahedral carbon atom bonded to four different groups is called a chiral center. A Molecule having at least one chiral center is a chiral molecule. When the mirror images of a chiral molecule are not superimposable, those mirror images become stereoisomers called enantiomers.
Fischer Projection is a method of drawing 3-D structures of organic molecules using cross formula. In this method, all non-terminal bonds are depicted as horizontal or vertical lines.
In the Fischer projection, horizontal bonds represent groups coming forward (drawn as wedges) and vertical bonds represent groups going backward (drawn as dashed wedges).
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 15 Solutions
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
- Write all of Me Possible Products For each Of the Following reactions. In each case identity all pains of enantiomers, all digsterzoners and all Meso compounds 9. 11-60 11-0-11 V-G Η Η H ~ C-11 +HB+ - 1 H b. पन्ना 171-0-11 H-C-H Н C-C=c-call +HBr Perendez ==arrow_forwardHow can i draw the mechanisms for this molecule?arrow_forwarda. Discuss and explain he difference IN Stability between the Chai and Boat Гольцу от судомехане b. For the Following Molecule draw both possible Clain conformations and explain which one is more stable and for what Reason. H. CH₂ CH₂ H "Harrow_forward
- Please provide the mechanism for this reacitonarrow_forwardQuestion 5: Name the following compound in two ways using side chain and using prefix amine (Common name and IUPAC name both) CH3NH2 CH3CH2NHCH3 CH₂CH₂N(CH3)2 Draw the structure of diethyl methyl amine Question 6. Write the balanced combustion reaction for: a. Hexane b. Propyne c. 2-pentene Question 7: Write the following electrophilic substitution reactions of benzene: Hint: Use notes if you get confused a. Halogenation reaction: b. Nitration reaction : c. Sulphonation reaction: d. Alkylation reaction: e. Aceylation reaction:arrow_forwardQuestion 4. Name the following structures ○ CH3-C-N-H H CH3CH2-C-N-H H CH3CH2-C-N-CH3 Harrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning



