
(a)
Interpretation:
The intermolecular interactions that operate in
Concept introduction:
There are three types of interactions through which the molecules are stabilized. They are hydrogen-bonding interactions, the dipole-dipole interactions and the induced dipole interactions. These interactions influence the properties of the compounds like boiling point, melting point and so on.
Answer to Problem 40E
The intermolecular interactions that operate in
Explanation of Solution
In all molecular substances, the intermolecular interactions exist. These interactions are induced dipole interactions, dipole-dipole interactions and hydrogen bonding.
The structure of
![]()
Figure 1
There is electronegativity difference in the molecule. This gives polarity to the molecule. Therefore, the dominant intermolecular interaction in this molecule is dipole-dipole interaction along with the induced dipole interaction.
The intermolecular interactions that operate in
(b)
Interpretation:
The intermolecular interactions that operate in
Concept introduction:
There are three types of interactions through which the molecules are stabilized. They are hydrogen-bonding interactions, the dipole-dipole interactions and the induced dipole interactions. These interactions influence the properties of the compounds like boiling point, melting point and so on.
Answer to Problem 40E
The intermolecular interactions that operate in
Explanation of Solution
In all molecular substances, the intermolecular interactions exist. These interactions are induced dipole interactions, dipole-dipole interactions and hydrogen bonding.
The structure of
![]()
Figure 2
The electronegative atom oxygen
The intermolecular interactions that operate in
(c)
Interpretation:
The intermolecular interactions that operate in
Concept introduction:
There are three types of interactions through which the molecules are stabilized. They are hydrogen-bonding interactions, the dipole-dipole interactions and the induced dipole interactions. These interactions influence the properties of the compounds like boiling point, melting point and so on.
Answer to Problem 40E
The intermolecular interactions that operate in
Explanation of Solution
In all molecular substances, the intermolecular interactions exist. These interactions are induced dipole interactions, dipole-dipole interactions and hydrogen bonding.
The structure of
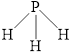
Figure 3
There is electronegativity difference in the molecule. This gives polarity to the molecule. Therefore, the dominant intermolecular interaction in this molecule is dipole-dipole interaction along with the induced dipole interaction.
The intermolecular interactions that operate in
(d)
Interpretation:
The intermolecular interactions that operate in
Concept introduction:
There are three types of interactions through which the molecules are stabilized. They are hydrogen-bonding interactions, the dipole-dipole interactions and the induced dipole interactions. These interactions influence the properties of the compounds like boiling point, melting point and so on.
Answer to Problem 40E
The intermolecular interactions that operate in
Explanation of Solution
In all molecular substances, the intermolecular interactions exist. These interactions are induced dipole interactions, dipole-dipole interactions and hydrogen bonding.
The structure of
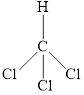
Figure 4
The molecule has electronegative atoms
The intermolecular interactions that operate in
(e)
Interpretation:
The intermolecular interactions that operate in
Concept introduction:
There are three types of interactions through which the molecules are stabilized. They are hydrogen-bonding interactions, the dipole-dipole interactions and the induced dipole interactions. These interactions influence the properties of the compounds like boiling point, melting point and so on.
Answer to Problem 40E
The intermolecular interactions that operate in
Explanation of Solution
In all molecular substances, the intermolecular interactions exist. These interactions are induced dipole interactions, dipole-dipole interactions and hydrogen bonding.
The structure of
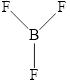
Figure 5
The molecule has electronegative atom
The intermolecular interactions that operate in
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
EBK INTRODUCTORY CHEMISTRY: AN ACTIVE L
- Draw the products of a reaction of the following alkyle chloride, shown below in the 3D ball and stick model with NaSCH3. Ignore inorganic byproducts. In the figure, a gray ball indicates a carbon atom a white ball indicates a hydrogen atom anda agreen ball indicated a chlorine atomarrow_forwardDraw the most stable cations formed in the mass spectrometer by a deavage of the following compound Draw the most stable cations formed in the mass spectrometer by a cleavage of the following compound онarrow_forwardCurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting anand product sytucutrs, draw the curved electron-pusing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic steps. Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bind-making stepsarrow_forward
- Draw the major elimination and substitution products formed in this reavtion. Use a dash or wedge bond to indicatr the stereochemistry of substituents on assymetric centers, wheere applicable. Ignore any inorganic byproducts.arrow_forwardDraw the two possible products produced in this E2 elimination. Ignore any inorganic byproductsarrow_forwardDraw the major products of this SN1 reaction. Ignore any inorganic byproducts.arrow_forward
- Draw the major elimination and substitution products formed in this reaction. Use a dash or wedge bond to indicate the stereochemistry of substituents on asymmetric centers, wehre applicable. Ignore and inorganic byproducts.arrow_forwardCurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s). Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. Drawing Arrows THE Problem 33 of 35 N. C:0 Na + Submit Drag To Pan +arrow_forwardDraw the product of the E2 reaction shown below. Include the correct stereochemistry. Ignore and inorganic byproducts.arrow_forward
- Draw the major producrs of this SN1 reaction. Ignore any inorganic byproducts. Use a dash or wedge bond to indicate the sereochemistry of substituents on asymmetric centers where appllicable.arrow_forward5) Oxaloacetic Acid is an important intermediate in the biosynthesis of citric acid. Synthesize oxaloacetic acid using a mixed Claisen Condensation reaction with two different esters and a sodium ethoxide base. Give your answer as a scheme Hint 1: Your final acid product is producing using a decarboxylation reaction. Hint 2: Look up the structure of oxalic acid. HO all OH oxaloacetic acidarrow_forward20. The Brusselator. This hypothetical system was first proposed by a group work- ing in Brussels [see Prigogine and Lefever (1968)] in connection with spatially nonuniform chemical patterns. Because certain steps involve trimolecular reac tions, it is not a model of any real chemical system but rather a prototype that has been studied extensively. The reaction steps are A-X. B+X-Y+D. 2X+ Y-3X, X-E. 305 It is assumed that concentrations of A, B, D, and E are kept artificially con stant so that only X and Y vary with time. (a) Show that if all rate constants are chosen appropriately, the equations de scribing a Brusselator are: dt A-(B+ 1)x + x²y, dy =Bx-x²y. diarrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning World of ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780618562763Author:Steven S. ZumdahlPublisher:Houghton Mifflin College Div
World of ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780618562763Author:Steven S. ZumdahlPublisher:Houghton Mifflin College Div Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning





