
(a)
Interpretation:
The molecular geometry, polarity and the strongest intermolecular force present in
Concept introduction:
Geometry of a molecule is the arrangement of atoms of a molecule in space. Geometry is dependent on the number of bond pairs, lone pairs and valence electrons of central atom. Polarity is defined as the tendency of atoms of a molecule to attract the electrons of the bond pairs towards itself.
Answer to Problem 15.3TC
The geometry, polarity and intermolecular force present in
Geometry is tetrahedral.
Polarity of methane is zero. It means
The strongest intermolecular force present is induced dipole.
Explanation of Solution
Methane,
Structure of methane is shown below.
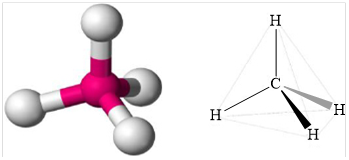
Figure 1
Therefore, methane is tetrahedral, non-polar and strongest intermolecular forces are induced dipole.
Geometry of methane is tetrahedral methane is non polar and the strongest intermolecular force present in methane is induced dipole.
(b)
Interpretation:
The geometry, polarity and the strongest intermolecular force present in
Concept introduction:
Geometry of a molecule of a molecule is the arrangements of atoms of a molecule in space. Geometry is depends on the number of bond pairs, lone pairs and valence electrons of central atom. Polarity is defined as the tendency of atoms of a molecule to attract the bond pairs towards itself.
Answer to Problem 15.3TC
The geometry, polarity and the strongest intermolecular force present in
Geometry is linear.
Polarity of carbon dioxide is zero. It means
Strongest intermolecular force present is induced dipole.
Explanation of Solution
Carbon dioxide
Structure of carbon dioxie is shown below.
![]()
Figure 2
Therefore, carbon dioxide is linear, non-polar and the strongest intermolecular force present is induced dipole.
Geometry of carbon dioxide is linear, polarity is zero means non polar molecule and the strongest intermolecular force present is induced dipole.
(c)
Interpretation:
The geometry, polarity and the strongest intermolecular force present in
Concept introduction:
Geometry of a molecule of a molecule is the arrangements of atoms of a molecule in space. Geometry is depends on the number of bond pairs, lone pairs and valence electrons of central atom. Polarity is defined as the tendency of atoms of a molecule to attract the bond pairs towards itself.
Answer to Problem 15.3TC
The geometry, polarity and intermolecular force present in
Geometry is bent.
Polarity of
Strongest intermolecular force present in
Explanation of Solution
Oxygen difluoride
Structure of oxygen difluoride is shown below.
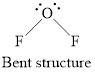
Figure 3
Therefore, oxygen difluoride is bent, polar, and the strongest intermolecular force present is dipole-dipole.
Geometry of oxygen difluoride is bent, polarity is non-zero means polar molecule and the strongest intermolecular force present is dipole dipole interaction.
(d)
Interpretation:
The geometry, polarity and the strongest intermolecular force present in
Concept introduction:
Geometry of a molecule of a molecule is the arrangements of atoms of a molecule in space. Geometry is depends on the number of bond pairs, lone pairs and valence electrons of central atom. Polarity is defined as the tendency of atoms of a molecule to attract the bond pairs towards itself.
Answer to Problem 15.3TC
The geometry, polarity and intermolecular force present in
Geometry is bent.
Polarity of
The strongest intermolecular force present is hydrogen bonding.
Explanation of Solution
Chloric acid
Structure of chloric acid is shown below.
![]()
Figure 4
Therefore, chloric acid is bent, polar and the strongest force present is hydrogen bonding.
Geometry of chloric acid is bent, polarity is non-zero means polar molecule and the strongest intermolecular force present is hydrogen bonding.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
EBK INTRODUCTORY CHEMISTRY: AN ACTIVE L
- For the condensation reaction between Alamine and histamine, please help me write the amididation reaction mechanism. Then write the three letter code for the product of the reaction, then write the one letter code for the product of the reaction. arrow_forwardHow to draw the reaction mechasnism belowarrow_forwardName the following molecules with IUpacarrow_forward
- What is the molecular orbital for cyclopropenyl anion and is it aromatic, antiaromatic or nonaromatic?arrow_forwardUsing the chart describe the change from cystine to tyrosine and its impact on the protein. Using the chart describe the change from histidine to aspartic acid and its impact on the protein.arrow_forwardHow to get the predicted product of this reaction belowarrow_forward
- Please help me fill out the chart then using the chart describe the change from cystine to tyrosine and its impact on the protein. Then using the chart describe the change from histidine to aspartic acid.arrow_forwardWrite the Esterification reaction mechanism for acetic acid, and one propanol to make propanol ethanoate (molecule that gives peas its odor in flavor)arrow_forwardProvide solutionsarrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning





