
(a)
Suitable design speed for the rural collector highway.
Answer to Problem 1P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
In mountains terrain is designed to carry volume of
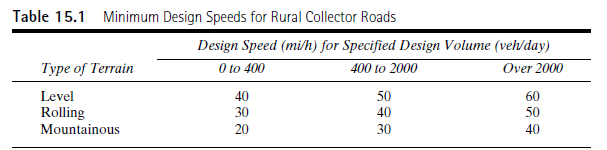
For a rural collector highway located in mountains terrain is designed to carry a design volume
From the table the design speed for
(b)
Lane and usable shoulder lengths for the rural collector highway.
Answer to Problem 1P
Lane=
Shoulder =
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
In mountains terrain is designed to carry volume of
For a rural collector highway located in mountains terrain is designed to carry a design volume
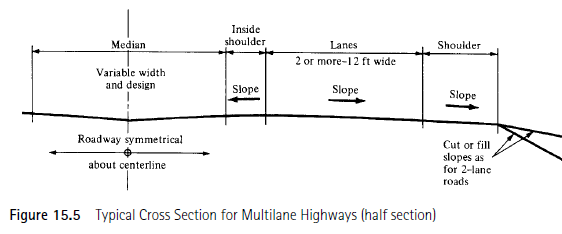
From the figure
Width of shoulder is total
(c)
Maximum desirable grade for the rural collector highway.
Answer to Problem 1P
Maximum desirable grade=
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
In mountains terrain is designed to carry volume of
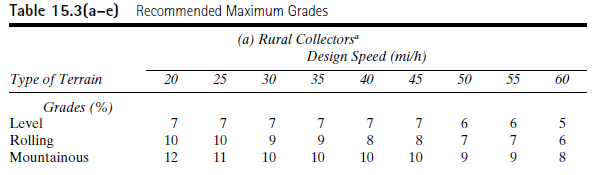
From the Table
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Traffic And Highway Engineering
- H.W: An activated sludge process operates under the following data: Q=0.21 m³/s, S.- 250 mg/l, S-6.2 mg/l, MLVSS (X) = 3500 mg/1, 0= 10 days Return sludge concentration (X)= 10000 mg/l, Y=0.5, K₁ =0.06 d', volatile super solid represent 80% of SS, Find: 1- Treatment efficiency 2- Reactor volume 3- Qwa (sludge wasted from areation tank) 4- Qur (sludge wasted from recirculation tank) 5- Quantity of sludge wasted/day 6- Recirculated ratio V.X VX Qwa Qwr= Qwr-Xr 0Xarrow_forwardFor the beam shown, where should a uniformly distributed downward live load, wl, be placed to cause the maximum upward reaction at support A? (D, E, and F are the supports, from left to right, to the right of C.) B C a. From A to B and D to E b. From A to D and E to F c. From B to D and E to F ☑ d. From B to C and D to E L Larrow_forwardQuestion 1 1. A solid shaft of 1.55 m is used as a tractor propeller (prop) shaft. The shaft twists through 1.8 while rotating at 900 rpm. The diameter of the shaft is 60 mm and the modulus of rigidity is 85 GPa. Calculate 1.1 The maximum shear stress in the shaft 1.2 The power transmitted by the shaft. 2. The tractor has undergone minor modifications to increase the transmitted power by 20%. The solid shaft is replaced by a lighter hollow shaft of the same material, with a dimeter ratio of 2:1. Calculate the suitable dimeters of the hollow shaft.arrow_forward
- Use Area Moment Method of Beam Deflectionsarrow_forwardDetermine rotations at all the nodes of the beam and reactions at the supports. Assume support 1 and 3 are roller and support 2 is pinned, L1=1.25m, L2=3.75m and w=60kN/m. Please show all working and FBD's where relevant.arrow_forwardspecific gravity of the soil is 1.41 percentage of water content by weight at field capacity and wilting point are 15% and 7% respectively calculate the equivalent moisture content as equivalent depth for 1.2m root zone: A. At permanent wilting point B. At field capacity C. For ready available water Ex 4-3: If the crop consumptive use in Ex(4-2) is 18 m³/donum/day,calculate: A. Irrigation interval in days B. Field water duty assuming 40% losses during irrigation C. Amount of added water to irrigate one donum. n: CFc- IWC) * As *D Lg dn - Q.te A date. A d9 Q IWC- 20% FC-271 Qg-40e D=100cm sec area of the field. Ed=65% 1 hectare As 1.3arrow_forward
- ۰۹:۲۵ ZV9 HW2-C.pdf Dept: Civil Eng. Kerbala HW2 3rd Year (C) Ex 4-1: The field capacity and wilting point as depth equivalent of soil are 178mm and 102 mm respectively. PAD-60% Calculate the irrigation interval if the water consumptive use is 4.5 mm/day. Ex 4-2: The specific gravity of the soil is 1.41 percentage of water content by weight at field capacity and wilting point are 15% and 7% respectively. a) calculate the equivalent depth of moisture content for 1.2m root zone and PAD 70% at permanent wilting point, at field capacity and for readily available water b) If the crop consumptive use is 18 m/donum/day, calculate: Irrigation interval in days, field water duty assuming 40% losses during irrigation and amount of added water to irrigate one hectare. Ex4-3: Using Blaney-Criddle formula, calculate the irrigation interval through specific interval of plant growth according to the following data: . Mean air temperature 25 C percentage of day light hour through the month 8.4% Crop…arrow_forwardDetermine the global stiffness matrix of the beam shown in Fig. 3. Assume supports at 1 and 3 are rollers and the support at 2 is a pinned support. Indicate the degrees of freedom in all the stiffness matrices. EI is constant, w=60kN/m, L1=1.25m and L2=3.75m please explain how the code numbers for global matrix are determined in detailarrow_forwardFor the truss shown in Fig 2, determine the nodal displacement and member forces for all elements of the truss. Assume for each member A = 0.0015 m2 and E = 200 GPa please show all working, relevant FBD's and use ID's indicated in the diagram, if using an alpha numerical in equations please indicate where it is being applied to in the truss.arrow_forward
- Determine the global stiffness matrix of the beam shown in Fig. 3. Assume supports at 1 and 3 are rollers and the support at 2 is a pinned support. Indicate the degrees of freedom in all the stiffness matrices. EI is constant, w=60kN/m, L1=1.25m and L2=3.45m please explain how the code numbers for global matrix are determined in detailarrow_forward= 20 kips = 20 kips B w₁ = 2 kips/ft 20" 12'- 7760 12" 6"arrow_forward= 20 kips = 20 kips B w₁ = 2 kips/ft 20" 12'- 7760 12" 6"arrow_forward
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
