
(a)
Interpretation: For the given set of compounds the location of the partial charges that results due to inductive effect should be identified.
Concept Introduction: The nature of the bond depends on the electronegativity values of the shared electron pair of the involved atoms.
Electronegativity is the important chemical property of the elements in the periodic table. It is the tendency of the atoms to attract electrons towards it.
If the difference in electronegativity is between 0.5 and 1.7, a bond between two different electronegative atoms becomes polar. Most electronegative atoms get partial negative charge because they attract electrons from least electronegative atom towards it. The least electronegative atoms get partial positive charge because it loses electrons towards most electronegative atoms.
The process of the attraction of electrons from electron-donating atoms (less electronegative atoms) towards electron-withdrawing atoms (most electronegative atoms) is called induction. It can be represented by the following arrow:
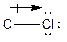
Here, chlorine atom has more electronegative than carbon atom. Chlorine attracts electrons towards it. This difference in electron density is called inductive effect. It can be shown by Greek symbol delta (
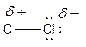
To find: Categorize all polar covalent bonds in the given compound (a)
(b)
Interpretation: For the given set of compounds the location of the partial charges that results due to inductive effect should be identified.
Concept Introduction: The nature of the bond depends on the electronegativity values of the shared electron pair of the involved atoms.
Electronegativity is the important chemical property of the elements in the periodic table. It is the tendency of the atoms to attract electrons towards it.
If the difference in electronegativity is between 0.5 and 1.7, a bond between two different electronegative atoms becomes polar. Most electronegative atoms get partial negative charge because they attract electrons from least electronegative atom towards it. The least electronegative atoms get partial positive charge because it loses electrons towards most electronegative atoms.
The process of the attraction of electrons from electron-donating atoms (less electronegative atoms) towards electron-withdrawing atoms (most electronegative atoms) is called induction. It can be represented by the following arrow:
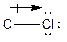
Here, chlorine atom has more electronegative than carbon atom. Chlorine attracts electrons towards it. This difference in electron density is called inductive effect. It can be shown by Greek symbol delta (
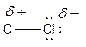
To find: Categorize all polar covalent bonds in the given compound (b)
(c)
Interpretation: For the given set of compounds the location of the partial charges that results due to inductive effect should be identified.
Concept Introduction: The nature of the bond depends on the electronegativity values of the shared electron pair of the involved atoms.
Electronegativity is the important chemical property of the elements in the periodic table. It is the tendency of the atoms to attract electrons towards it.
If the difference in electronegativity is between 0.5 and 1.7, a bond between two different electronegative atoms becomes polar. Most electronegative atoms get partial negative charge because they attract electrons from least electronegative atom towards it. The least electronegative atoms get partial positive charge because it loses electrons towards most electronegative atoms.
The process of the attraction of electrons from electron-donating atoms (less electronegative atoms) towards electron-withdrawing atoms (most electronegative atoms) is called induction. It can be represented by the following arrow:
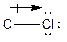
Here, chlorine atom has more electronegative than carbon atom. Chlorine attracts electrons towards it. This difference in electron density is called inductive effect. It can be shown by Greek symbol delta (
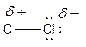
To find: Categorize all polar covalent bonds in the given compound (c)
(d)
Interpretation: For the given set of compounds the location of the partial charges that results due to inductive effect should be identified.
Concept Introduction: The nature of the bond depends on the electronegativity values of the shared electron pair of the involved atoms.
Electronegativity is the important chemical property of the elements in the periodic table. It is the tendency of the atoms to attract electrons towards it.
If the difference in electronegativity is between 0.5 and 1.7, a bond between two different electronegative atoms becomes polar. Most electronegative atoms get partial negative charge because they attract electrons from least electronegative atom towards it. The least electronegative atoms get partial positive charge because it loses electrons towards most electronegative atoms.
The process of the attraction of electrons from electron-donating atoms (less electronegative atoms) towards electron-withdrawing atoms (most electronegative atoms) is called induction. It can be represented by the following arrow:
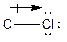
Here, chlorine atom has more electronegative than carbon atom. Chlorine attracts electrons towards it. This difference in electron density is called inductive effect. It can be shown by Greek symbol delta (
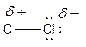
To find: Categorize all polar covalent bonds in the given compound (d)
(e)
Interpretation: For the given set of compounds the location of the partial charges that results due to inductive effect should be identified.
Concept Introduction: The nature of the bond depends on the electronegativity values of the shared electron pair of the involved atoms.
Electronegativity is the important chemical property of the elements in the periodic table. It is the tendency of the atoms to attract electrons towards it.
If the difference in electronegativity is between 0.5 and 1.7, a bond between two different electronegative atoms becomes polar. Most electronegative atoms get partial negative charge because they attract electrons from least electronegative atom towards it. The least electronegative atoms get partial positive charge because it loses electrons towards most electronegative atoms.
The process of the attraction of electrons from electron-donating atoms (less electronegative atoms) towards electron-withdrawing atoms (most electronegative atoms) is called induction. It can be represented by the following arrow:
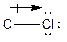
Here, chlorine atom has more electronegative than carbon atom. Chlorine attracts electrons towards it. This difference in electron density is called inductive effect. It can be shown by Greek symbol delta (
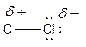
To find: Categorize all polar covalent bonds in the given compound (e)
(f)
Interpretation: For the given set of compounds the location of the partial charges that results due to inductive effect should be identified.
Concept Introduction: The nature of the bond depends on the electronegativity values of the shared electron pair of the involved atoms.
Electronegativity is the important chemical property of the elements in the periodic table. It is the tendency of the atoms to attract electrons towards it.
If the difference in electronegativity is between 0.5 and 1.7, a bond between two different electronegative atoms becomes polar. Most electronegative atoms get partial negative charge because they attract electrons from least electronegative atom towards it. The least electronegative atoms get partial positive charge because it loses electrons towards most electronegative atoms.
The process of the attraction of electrons from electron-donating atoms (less electronegative atoms) towards electron-withdrawing atoms (most electronegative atoms) is called induction. It can be represented by the following arrow:
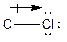
Here, chlorine atom has more electronegative than carbon atom. Chlorine attracts electrons towards it. This difference in electron density is called inductive effect. It can be shown by Greek symbol delta (
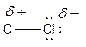
To find: Categorize all polar covalent bonds in the given compound (f)
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 1 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY, WITH SOL. MAN/ STUDY
- If a 5 film plastic film degraded in 30 days at 35C and the same film degraded in 10 days at 55 C and 2 days at 65C what would the predicted life time be at 22C for the same film?arrow_forwardno Ai walkthroughsarrow_forwardI have a aqueous solution (175 ml) of iridium trichloride containing 8,750 ppm Iridium by ICP OES analysis. What is the percent concentration of Iridium trichloride in aquous solution and provide the concentration in moles per liter, percentage by weight.arrow_forward
- no Ai walkthroughsarrow_forward136 PRACTICAL SPECTROSCOPY Compound 78 is a high-boiling liquid (boiling point 189° C) that contains halogen, but will not react with alkoxides to yield an halogen. ether. The Mass, IR, and 'H NMR spectra, along with 13C NMR data, are given below. Elemental Analysis: C, 35.32; H, 2.47; contains BC Spectral Data: doublet, 137.4 ppm; doublet, 130.1 ppm; doublet, 127.4 ppm; singlet, 97.3 ppm Absorbance Mass Spectrum Intensity 77 77 204 M + 128 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 m/e 200 220 280 240 260 300 Infrared Spectrum Wave Number, cm -1 4000 3000 2500 2000 1500 1300 1200 1100 1000 900 800 700 3 6 7 8 9 10 12 13 15 Wavelength, microns 'H NMR wwwww 5 Structure: www ppm, & ©2000 Brooks/Cole Publishing Com-arrow_forwardno Ai walkthroughsarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





